The production of high-purity Flue Gas Desulphurization Gypsum (FGDG) will soon end. FGDG is a by-product of coal combustion, and G7 countries are on track to close down coal-fired power plants by 2035.
Gypsum is heavily used to produce plasterboards (or drywall) in the construction and building sector. With synthetic gypsum out of the picture, mined gypsum becomes a reliable source. However, exhaustive mining in gypsum-rich deposits has threatened the natural habitat of various endangered animal and plant species.
Therefore, the construction industry is increasingly adopting gypsum recycling. But the journey to sustainable construction isn’t without its hurdles. Here are some major challenges faced in gypsum recycling.
Challenges Associated with Gypsum Recycling
- Scarcity of Waste Management Facilities: One of the primary challenges in gypsum board recycling is the lack of sufficient waste management facilities capable of processing this material. The U.S. invests heavily in waste management infrastructures through initiatives like the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. However, there is still a gap in facilities capable of processing gypsum board waste effectively.
- Contamination: Gypsum waste from demolition or renovation of buildings is often contaminated with screws, nails, paper, etc., which must be removed for successful recycling. Debris from buildings built before 1990 may also contain hazardous materials like asbestos and lead-based paint. Recyclers have to be cautious while processing such waste. They also have to test the recycled product before it is shipped to ensure there is no asbestos.
- Economic Viability & Logistical Challenges: Successful gypsum recycling depends on the large quantities of C&D debris delivered to the facilities. Consistent and large-scale collection and transportation of this waste must be ensured. Contractors usually dispose of C&D waste in a nearby landfill rather than transport it to remote recycling facilities for economic benefits.
Various companies, institutions, and individuals are developing solutions to overcome these challenges.
Companies Offering Innovative Solutions to Gypsum Recycling Challenges
1. Recycle Track Systems (RTS): Uber for trash
New York-based RTS has developed a system to address the logistical challenges of gypsum board recycling. The company provides an on-demand pick-up service for C&D waste and distributes it to recycling centers. RTS distinguishes its waste management service by offering customers real-time tracking from pickup to drop-off. The asset-light business does not own any trucks. Instead, it uses rideshare technology to connect businesses with independent haulers. RTS Canada was recognized as One of Canada’s Greenest Employers for 2024.

2. USG Corporation: Recycling Gypsum Boards Containing Hydrophobic Additives
The United States Gypsum Corporation has developed a technology to recycle gypsum boards containing hydrophobic materials. The process involves separating the gypsum core from the boards, crushing and grinding it to a specific particle size range (200 μm to 800 μm), and then mixing the crushed gypsum with regular gypsum slurry to make new gypsum boards. The specific particle size range prevents defoaming issues caused by the hydrophobic additives. USG Corporation filed a patent for this innovative method in 2021.
GreyB’s AI research tool, SLATE Pro, shared 10 more novel approaches to gypsum recycling by industry giants such as USG Corporation and Tokuyama Corp. Sign up for the tool or get a Demo today to explore these solutions in more depth.

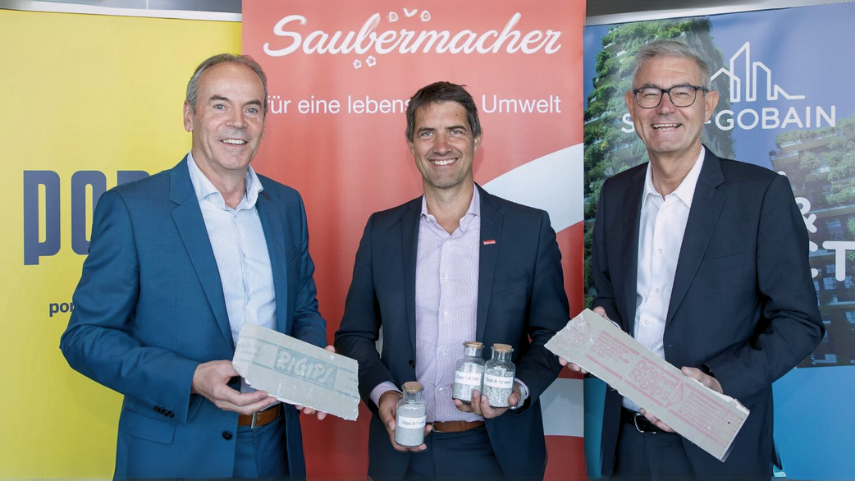
3. PORR, Saint-Gobain, and Saubermacher’s Cross-Sector Partnership
Gypsum can be recycled eternally. This makes it one of the few construction materials that can be reused in a closed-loop recycling system. In 2023, Construction company PORR, dry construction specialist Saint-Gobain, and waste management company Saubermacher set up an example of a circular economy in Austria. PORR and Saubermacher are strong players in the deconstruction and disposal market. They ensure large quantities of gypsum waste are delivered at the recycling facilities for economic viability. Meanwhile, Saubermacher offers logistics solutions for transporting this waste from building sites to recycling plants. After PORR recycles it, Saint-Gobain produces new gypsum plaster boards (RIGIPS boards) from the recycled material. A perfect closed-loop recycling! The system reduces the need for manufacturers to acquire virgin gypsum, thereby supporting a more sustainable manufacturing process.

4. BAMB and EPA: Encouraging DfD to Maximize the Recovery of Materials
Organizations like Buildings as Material Banks (BAMB) and the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) are encouraging the Design for Disassembly (DfD) concept to increase the recycling rate of C&D waste in the future. The concept urges construction companies to design buildings in a way that is easy to modify or dismantle. This helps maximize the recovery of materials and components for reuse and recycling. Their goal is to establish a circular economy with a ‘Zero Waste Vision.’ BAMB and EPA have established guidelines for this design process. Some key highlights of these guidelines are:
1. Material Selection: To reduce the use of hazardous materials during construction, choose recyclable or biodegradable materials.
2. Connection Techniques: Employ methods that allow easy separation of materials. Design for Disassembly (DfD) for Gypsum Board Recycling.
3. Documentation: Materials Passports are developed to serve as datasets listing all the materials included in a product or construction during its life cycle to facilitate recovery and reuse.

5. Bryan A. Diffley: Processing Scrap Drywall On-site
In 2023, Bryan A. Diffley filed a patent in the US for an on-site gypsum board recycling system that uses a portable crusher to reduce scrap drywall volume at construction sites. The portable crusher is designed to fit through doors and elevators for easy access at sites. Crushing reduces drywall volume by at least 20% and helps in easy transportation. It also allows efficient removal and recycling of irregularly shaped drywall pieces without voids between them.

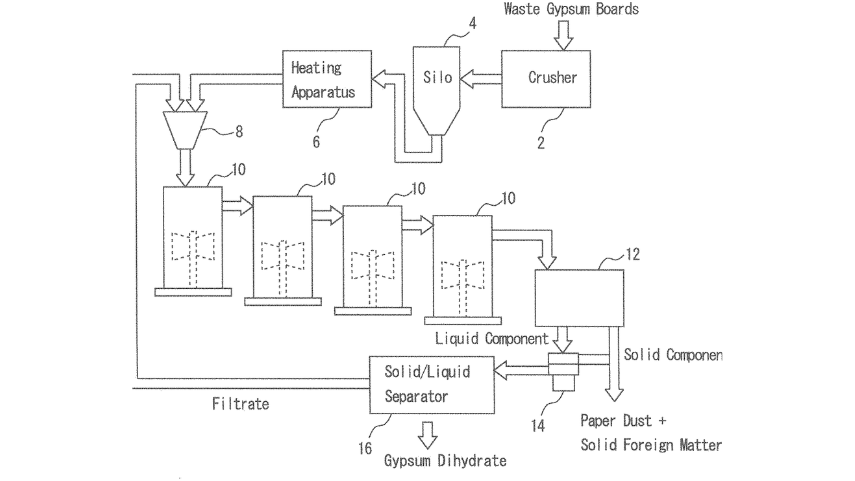
6. Tokuyama Corp: Using Screw Press To Filter Gypsum Slurry
Tokuyama Chiyoda Gypsum Co. uses an innovative technology to filter slurry from waste gypsum boards using a screw press. This method involves continuously pressing the gypsum slurry with a screw press and then sieving the liquid component to separate paper dust and foreign matter. The screw pushes the slurry towards the outlet, ejecting the liquid through a mesh surrounding the screw. With optimized openings (1.5 mm to 3 mm), this mesh retains the unwanted material. Tokuyama filed a patent for this technology in 2021. The system innovatively addresses the contamination issues and maintains the water content of the separated paper dust within an acceptable range.
Conclusion
As environmental concerns and regulations tighten, innovative solutions and collaborative efforts are emerging to transform gypsum waste into valuable resources. The global market for gypsum recycling is anticipated to grow at a rapid rate of 7.2% annually between 2022 and 2030. Companies can benefit from leveraging the latest technology, such as automated sorting systems, to maximize efficiency and reduce costs. These systems can also reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, thus reducing their environmental impact. Additionally, these systems can create new revenue streams for companies by recovering and monetizing waste resources. Recycled gypsum is not only used for producing plasterboards but also as fertilizer to improve agricultural soil, an additive for animal bedding, and in a wide range of plastics, caulks, adhesives, sealants, and specialty cement.
In the coming months, we will see more companies partnering with local environmental organizations to ensure that their gypsum waste is being used responsibly. Partnerships similar to PORR, Saint-Gobain, and Saubermacher’s will also give companies access to a network of environmental experts who can help them identify new opportunities to use gypsum waste. Companies must proactively explore these partnerships to ensure their compliance with the regulations imposed on gypsum recycling.
Stay abreast of the various gypsum board recycling processes to lead a sustainable and eco-friendly tomorrow. Find innovative solutions to your gypsum recycling challenges using GreyB’s research expertise.

Authored by: Tamanpreet Kaur, Market Research
Next Read: Leveraging the latest technology to create Smart Buildings.