As energy crises and prices sharply increase, we are witnessing some amazing innovation trends in the energy storage sector. One such trend we discuss in this post is “Smart Grid technology,” which allows electrical networks to operate more efficiently.
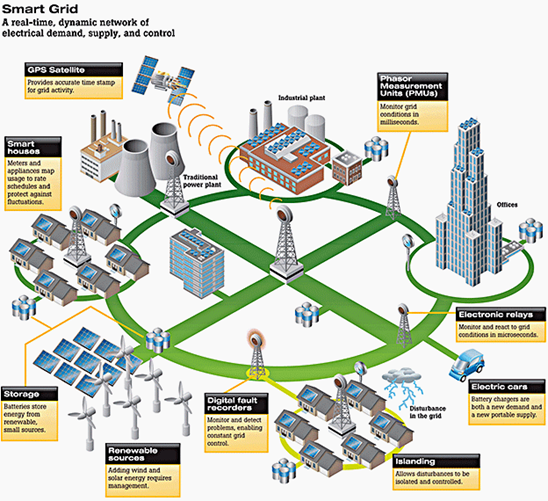
The energy grid is where the crises mentioned above meet. Creating a smart grid is vital in delivering energy resources in the face of supply disruptions while optimizing usage for a healthier planet.
The smart grid electricity network lets devices connect. Thus, allowing them to control demand, safeguard the distribution network, save energy, and drive down costs.
The current energy grid structure provides little flexibility or support for new renewable technologies. Traditional energy grids allow for a one-way power flow from centralized sources like coal, nuclear, and gas to places of consumption such as homes, businesses, and data centers. The need for more power is met by building another power plant.
Hence the need for smart grids.
A smart grid is a highly distributed network of clean, renewable energy deployed at the edge of the existing grid.
It requires an advanced level of computing to manage and optimize the highly distributed intermittent loads introduced. It also requires a “total system” approach to effectively balance multiple fluctuating energy sources, consumption levels, and new renewable technologies. (Source)
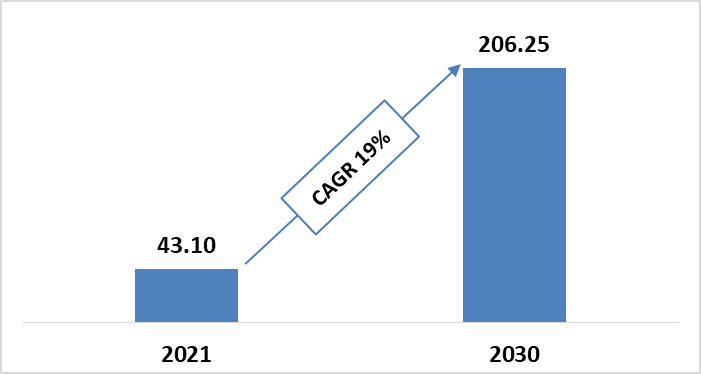
Smart Grid Market Size
In 2021, the global smart grid market size was valued at $43.10 billion. Analysts believe it’ll increase and reach $206.25 billion by 2030. The market will grow at an approximate CAGR of 19% during the forecasted period.
In 2021, the North American region held the largest share of 35% of the global smart grid market.
The growing need for smart infrastructure and the ever-increasing smart city projects were some of the critical factors driving the growth of the smart grid market in North America. (Source)
Canada’s Ministry of Natural Resources introduced the Renewable and Electrical Pathways Program in 2020, a four-year scheme that aided in the roll-out of smart grids. With $4.8 billion received in funding, the project aims to improve the dependability and capacity of its smart grids.
North America was an early user of smart grid technology, and the potential benefits of smart grids encouraged investments in the region’s smart grid infrastructure implementation.
In June 2021, Poland’s power grid operator PSE announced plans to invest $1.23 billion by 2030 across its network in the country’s north to distribute electricity from planned Baltic offshore wind turbines to clients. (Source)(Source)
VC Investments in Smart Grid
In 2021, smart grid startups raised $1.2 billion in 35 rounds of venture capital funding, a 55% increase from the $748 million raised in 2020. With $789 million in 18 deals, smart charging firms received the most venture capital funding in 2021. The smart grid sector documented 19 M&A deals in 2021, compared to 21 in 2020. (Source)
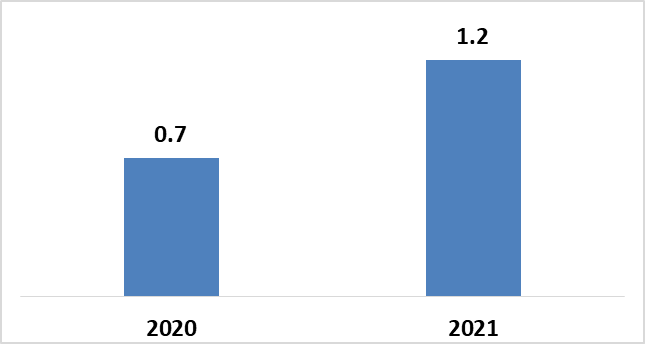
Smart Grid Advantages
Load Balancing on Automatic Mode – A primary advantage of a smart electrical grid is automatic load balancing, which minimizes the likelihood of equipment failure. Companies must make manual modifications since electricity load varies depending on external variables. A smart grid employs technology that analyzes consumption trends to manage loads. This decreases strain on electrical equipment, particularly at peak periods.
Increased Efficiency of Electrical Transmission – Smart grids can regulate electrical transmissions because they use intelligent technologies to reduce electrical wastage during distribution. This boosts the efficiency of electrical transmission, which benefits all stakeholders.
Enhanced Utilization of Renewable Energy – Smart grids offer better choices for integrating renewable energy into the grid. Renewable energy sources, such as residential solar and battery storage, will play a more significant role in future smart grids, supplying regular base-load electricity and responding to demand surges. (Source)(Source)
Smart Grid Challenges
High Initial Costs for Deployment of Smart Grid Technology – The early stage of smart grid adoption requires a significant investment. Therefore, the involvement of local and national governments in modernizing energy infrastructure is critical. In addition, smart grid technology necessitates significant initial investments to establish transmission networks that allow two-way communication between the utility and the customers.
Storing and Managing Complicated Smart Grid Infrastructure Data – The adoption of smart grid technologies has created vast amounts of complex data. The data is largely unstructured and needs analysis to acquire critical insights. Smart grid solution suppliers need help storing and managing network node-generated data. (Source)(Source)
Smart Grid Companies
1. Itron, Inc.
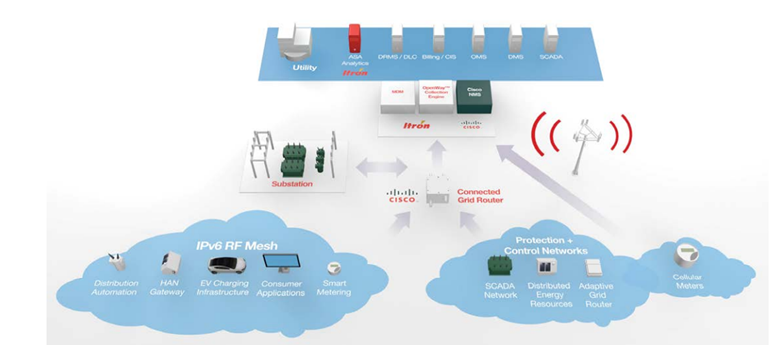
Itron, Inc., based in the United States, assists utilities and cities in managing energy and water more effectively. Its smart grid solutions provide measurable benefits. These smart grid solutions are adaptable to different operating environments, business priorities, and investment objectives. Itron solutions combine information and operations technologies to offer customers unprecedented visibility into measurement and control activities, network management, system operations, data management, and analysis. (Source)(Source)
Acquisition
In 2017, Itron, Inc. announced the acquisition of Silver Spring Networks, a provider of smart grid products, for $830 million. The acquisition’s goal was accelerating Itron’s Smart Grid and Smart City innovation growth. (Source)
2. Siemens
Siemens provides energy intelligence for a more flexible, sustainable power grid. Smart grids utilize digital technologies and IoT solutions to respond and adapt to changes in the grid intelligently. The key to leveraging data in the grid is incorporating energy intelligence into the Siemens Xcelerator for Grids portfolio. This enables grid operators to make grid operations more reliable, cost-effective, flexible, safe, and thus sustainable.
Using Smart Grid Compass methodology, Siemens has designed a road map for NB Power to incorporate its Demand Response Management System (DRMS) and Decentralized Energy Management Suite (DEMS). Thus, enabling the utility to manage electricity distribution in a more flexible, intelligent, and efficient manner. (Source)(Source)
Important Collaborations
In 2022, Siemens Smart Infrastructure partnered with Esri, the global leader in geographic information systems (GIS) and location intelligence. The collaboration aims to broaden Siemens’ ecosystem of partners for its grid software business. The cooperation improves grid operators’ power network planning, operations, and maintenance capabilities by combining Esri’s robust mapping and spatial analytics software with Siemens’ electrical topology expertise. (Source)(Source)
3. Cisco
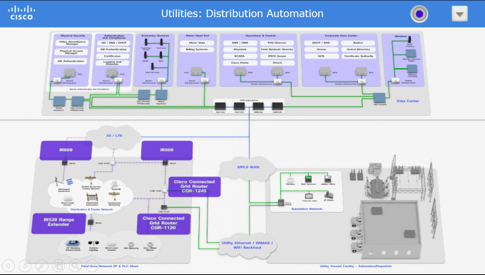
Cisco has been working on Smart grids for a long time. Its Distribution Automation solutions use data communication infrastructure to remotely monitor and control various components of the electrical distribution grid, such as substations and feeders. This allows grid operators to collect and analyze real-time power distribution and consumption data and provide predictive information and recommendations to utilities, suppliers, and customers. (Source)
Important Collaborations
In 2022, Cisco collaborated with Schneider Electric to provide smart grid solutions in Egypt. The duo is constructing a highly efficient and cyber-secure network that would control and assist in integrating traditional and renewable energy sources by utilizing the latest Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
Cisco will supply the IP and security infrastructure, including Cisco routers and switches, as well as various cyber security equipment and tools such as the Cisco Secure Firewall and Cisco Secure Network Analytics. On-site, the grid will be outfitted with Cisco IR1101 5G-ready industrial routers to assist in secure and efficient communication with the control centers. (Source)
Smart Grid Startups
1. AmpereHour Energy
AmpereHour Energy was formed by IIT Bombay alumni and power sector specialists to make an environmental and social difference via technical advancement in energy storage. Off-grid mini-grid solutions from AmpereHour comprise a 3-phase or 1-phase core power storage structure capable of both diesel generator and PV integration.

AmpereHour’s Ah-Stack is a portable, scalable Li-ion energy storage stack. Ah-Stack systems have been deployed in rural off-grid micro-grids, distribution networks, co-located with behind-the-meter solar, and as independent systems. Their power management software, ELINA, enables customers to track and manage storage and mini-grid assets continuously. (Source)(Source)(Source)(Source)
2. SparkMeter
SparkMeter provides complete low-cost metering systems ranging from rural microgrids to existing urban central grid utilities. Through various features, including flexible billing, customer communications, and remote monitoring and control, its simple plug-and-play solution empowers microgrids and distribution utilities to enhance operations and attain financial stability.
SparkMeter’s cloud-based grid management platforms, such as Koios and ThunderCloud, transfer data from the smart grid’s edge to the cloud and back in low-bandwidth areas with sporadic Internet connectivity.
Microgrid utilities can minimize operating expenses with their software by automating customer service and invoicing operations via remote communication. (Source)(Source)(Source)(Source)(Source)
3. SYNDEM
Syndem is a forerunner in developing technologies that strengthen all power electronics-interfaced suppliers. Its goal is to bring together power system stakeholders and create synchronized and equal smart grids worldwide by using power electronic converters as synchronous virtual machines on the supply side, in the network, and on the load side.

The Syndem smart grid research and educational package is a multipurpose power electronic converter. It can enhance grid integration research and education for diverse renewable energy sources. It also has a household solar converter with a 3 kVA capacity and several inverters. (Source)(Source)(Source)
Important Collaborations
In 2020, the U.S. Department of Energy chose Syndem to collaborate and serve as a vendor for a project, ‘The Solar Energy Technologies Office Fiscal Year 2020’. This initiative created a two-stage hybrid PV plant control framework that allowed the coordination of many hybrid PV plants with unpredictable production and improved grid stability via grid-forming inverter controls. (Source)
4. ENLİL (Deveci Tech)
ENLIL develops a smart vertical axis wind turbine that converts highways into renewable energy sources by utilizing city dynamics, thereby giving an additional source of power generation within a Smart City. ENLIL’s wind turbine, installed on highways, provides energy by using both the wind caused by the flow of automobiles and natural winds.
Enlil has an integrated SMART system that allows for the addition of modules such as CO2 measurement tools, data collecting via its IoT platform, traffic management systems, earthquake detection, connectivity for autonomous vehicles, and a built-in Wi-Fi station. (Source)(Source)

5. EdgeGrid
Edgegrid is an Indian smart grid startup that delivers clean energy using its digitally connected energy network. Its clean-tech platform connects sellers with individuals, businesses, and distribution companies that need energy services. With their apps, organizations can take control of their consumption, supply possibilities, costs, new income opportunities, and impact on the climate. (Source)
Conclusion
The International Energy Agency estimates that investment in electricity grids must average around $600 billion annually through 2030 for the global energy sector to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. (Source)
And one of the best ways to invest such a considerable amount is through collaborations. One such collaboration is Edge for Smart Secondary Substation Alliance (E4S), a partnership of eight major electric utilities providers that Intel and other companies are working with to develop a smart grid.
Intel is also collaborating with California providers to transform electrical substation relays into virtualized applications and with Malaysia’s largest energy provider to digitalize its electric grid.
Big countries like China are accelerating investment in smart grids. For the first time, the State Grid Corporation of China announced spending more than CNY 500 billion and focusing on power grids. (Source)
2022 has been a year of reckoning for energy access and climate change crises impacting billions of people’s lives. Energy prices are increasing at an alarming rate. Parallelly, global temperatures are breaking records, with the average temperature for January to September 2022 being the sixth-highest in the last century.
So, it is not surprising that governments are acting on it.
However, capital spending on electricity networks in emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs) stood at around $60 billion in 2021, similar to 2020. These are very low levels compared to the $100 billion spent in 2015 and 2016.
Smart grids will get more exposure and recognition as the current companies will get good results with this energy storage trend. And we’ll be here to witness it.
Here’s our exclusive report on 10 Energy Storage Innovation Trends that you can get by filling out the form below: