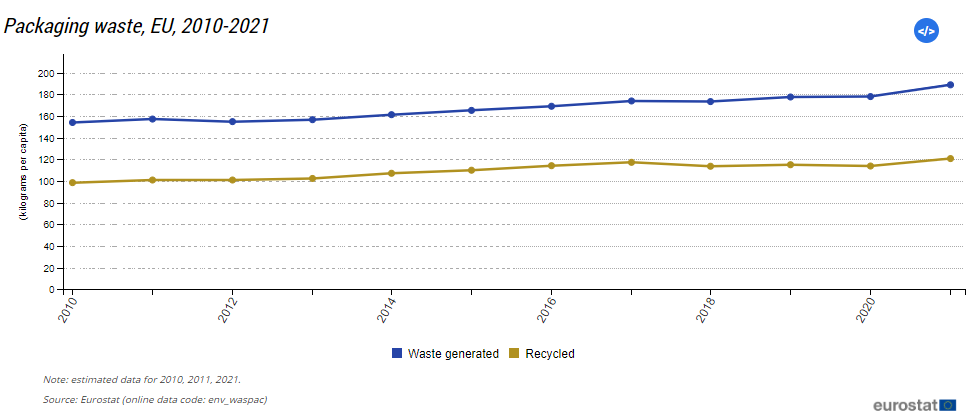
According to Eurostat, in 2021, Europe generated an estimated 188.7 kg of packaging waste per individual. Packaging is one of the primary users of virgin materials. About 40% of plastics and 50% of paper used in the EU are destined for packaging.
The EU has adopted a directive to solve this waste problem and increase its recycling waste over the years. Yet, the core problem remains. By 2030, the EU will see a further 19% increase in packaging waste and even a 46% increase in plastic packaging waste.
The chart below shows how the amount of waste generated and recycled has increased over the last decade.
There are solutions to the challenges, but companies and consumers lack motivation to use them. The EU’s Packaging and Packaging Waste (PPW) Regulation aims to solve this.
The regulation is set to transform how companies approach packaging across various industries. Understanding this regulation is not just about compliance; it’s about seizing the opportunity to innovate, reduce costs, and position your company as a leader in sustainability.
This article comprehensively reviews the PPW Regulation to analyze its importance, impact on different sectors, and compliance strategies. It will help companies navigate the PPW regulation and turn potential challenges into opportunities for the business.
But first things first.
What is the PPW Regulation?
The Packaging and Packaging Waste (PPW) Regulation is a comprehensive framework designed to address the environmental challenges of packaging waste in the European Union. It builds upon and revises the existing Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (94/62/EC), introducing more stringent requirements and ambitious targets for packaging sustainability.
This regulation will reduce packaging waste by reducing waste generation, promoting reusable packaging solutions, and improving recyclability. The plan also aims to improve waste collection and recycling systems and reduce the use of harmful materials in packaging.
Why is the PPW Regulation Important?
The importance of the PPW Regulation cannot be overstated. It represents a paradigm shift in how the EU approaches packaging and waste management. And how it aligns with broader sustainability goals such as the European Green Deal and the Circular Economy Action Plan.
For businesses, understanding and complying with this regulation is crucial for several reasons.
It ensures legal compliance, helping companies avoid fines and reputational damage. It’s also essential for continued access to the EU market. Meeting these regulations with consumers becoming increasingly environmentally conscious can give companies a competitive edge.
Optimizing packaging per the regulation can significantly reduce material and waste management costs. Lastly, the regulation will drive innovation, encouraging the development of new, sustainable packaging solutions.
PPW Regulation Targets
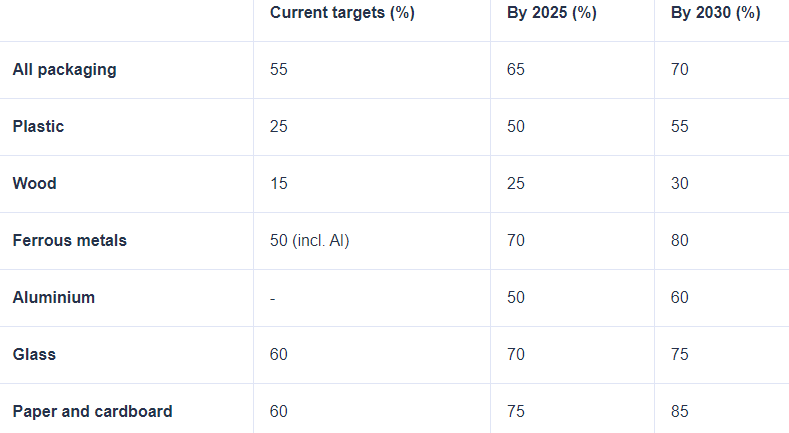
As per the EU, the packaging directive entered into force in 1994. In its last hearing on 30 November 2022, the Commission proposed to revise the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive.
The new review supports the goals of the European Green Deal and the new circular economy action plan. The plan aims to ensure that by 2030, all packaging in the EU market can be reused or recycled in a financially feasible manner. This also aligns with the 2018 Plastics Strategy’s goal to effectively recycle or reuse all plastic packaging on the market by 2030.
Under the Directive, EU countries must have established producer responsibility schemes for all packaging by the end of 2024. Additionally, the Directive specifies the following recycling targets:
What are the Key Elements of PPW Regulation?
Various factors inform packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation. This includes the need for extended producer responsibility (EPR), promoting sustainable packaging practices, and integrating innovative waste management solutions.
Extended Producer Responsibility
Extended producer responsibility is a critical regulatory approach that mandates manufacturers take responsibility for their products’ entire lifecycle, including post-consumer waste management.
This concept has been effectively implemented in various jurisdictions. The European Union, for instance, has enacted directives to ensure that producers are accountable for their packaging.
The EU Directive 94/62/EC emphasizes the need for producers to minimize packaging waste and encourages the development of easier-to-recycle packaging. Such regulations aim to reduce the environmental impact of packaging waste and incentivize manufacturers to design more sustainable and less wasteful packaging.
Promotion of Sustainable Packaging
As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, businesses are increasingly motivated to adopt eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Government regulations encouraging sustainable practices through incentives and legal frameworks support this shift.
The Korean government has set ambitious targets to reduce plastic use in packaging, reflecting a broader trend towards sustainability in packaging design. Sustainable packaging will serve as a competitive differentiator in the marketplace, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and enhancing brand reputation.
Innovative Waste Management
Research indicates that effective waste management systems require manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers collaborating. For instance, integrating compostable packaging into waste management systems presents challenges and opportunities. Efforts must be coordinated to improve recycling and recovery.
Additionally, the exploration of alternative materials, such as cellulose-based packaging, is gaining traction to mitigate the environmental impact of traditional plastic packaging. It aligns with the principles of a circular economy, emphasizing the importance of reusing and recycling materials to minimize waste.
How Will the PPW Regulation Affect Different Industries?
The impact of the PPW Regulation will affect various sectors in different ways. In the food and beverage industry, there will be an increased focus on reusable packaging systems. Stricter requirements for food-contact materials will be implemented, and companies will be pushed towards biodegradable or easily recyclable packaging.
The consumer goods sector should reduce excess packaging and incorporate more recycled content into plastic packaging. Companies must also take responsibility for managing packaging waste.
E-commerce businesses must optimize packaging to reduce shipping waste and potentially shift towards reusable shipping containers. They will take on increased responsibility for packaging take-back schemes.
The pharmaceutical industry must balance safety requirements with sustainability goals. It should explore alternative materials for blister packs and medicine containers and implement track-and-trace systems for packaging recycling.
The electronics sector must develop modular solutions for easier recycling and incorporate recycled materials in product packaging.
Take action to comply with the PPW Regulation and lead your industry.
Now, let’s see how you can navigate the PPW regulation and turn potential challenges into opportunities for your business.
Compliance Strategies and Innovative Solutions
Companies across industries can consider several strategies and innovative solutions to meet the PPW Regulation requirements.
Eco-design
Implementing eco-design principles and cycle assessment tools in packaging development is crucial. This allows companies to identify cost-saving opportunities by reducing material usage and waste. Lightweight materials and efficient structural designs can lower transportation costs and improve supply chain efficiency. Embracing these practices will help businesses stay ahead of regulatory changes, enhance brand value, and meet rising consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
R&D for Compostable Materials
Companies should focus on creating packaging that can break down naturally or be composted. Using recycled materials and designing packaging from a single type of material simplifies recycling processes, cutting operational inefficiencies. Exploring reusable packaging systems can open new revenue streams and build customer loyalty by offering convenient return programs. Streamlining the logistics for returning used packaging supports sustainability goals and strengthens supply chain resilience, giving businesses a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
Smart Packaging
Innovative packaging technologies such as QR codes or RFID tags can enhance recycling and track reuse, adding efficiency to waste management processes. Blockchain solutions take this further by improving supply chain transparency, allowing companies to build trust with consumers while meeting regulatory demands.
Packaging embedded with sensors for freshness monitoring reduces waste and improves product quality and customer satisfaction. These advancements drive operational efficiency, cut costs, and position businesses as forward-thinking industry leaders.
Consumer Education
Clear labeling on packaging recyclability will build consumer trust and simplify recycling. Launching awareness campaigns around proper disposal and recycling practices can drive engagement and reduce contamination in recycling streams, lowering operational costs. Further, offering incentives for packaging return schemes increases participation and helps businesses close the loop on materials, aligning with regulatory goals. These measures turn regulatory challenges into opportunities for cost savings and competitive differentiation.
Supply Chain Optimization
Collaborating with suppliers to minimize packaging waste across the value chain will help cost management. Implementing packaging management systems provides businesses with actionable insights to track and optimize material use, cutting unnecessary expenses. Exploring local sourcing options reduces transportation-related packaging needs, lowers logistics costs, and enhances supply chain resilience. These strategies allow businesses to streamline operations, improve profitability, and stay ahead in a market increasingly driven by efficiency and sustainability.
Conclusion
The PPW Regulation presents challenges and opportunities for businesses across the EU. By proactively addressing the requirements and embracing innovative solutions, companies can ensure compliance and gain a competitive advantage in an increasingly sustainability-focused market.
Understanding and implementing the PPW Regulation will guide organizations through this regulatory landscape while positioning themselves as forward-thinking industry leaders.
Continuous monitoring of regulatory developments, investment in research and development, and collaboration with industry partners will be critical to long-term success in this evolving regulatory environment. By taking decisive action now, companies can ensure that they meet the PPW Regulation requirements and set new sustainability standards in their respective industries.
Next Steps
Inspect your packaging practices to see where you need changes to comply with the new regulations.
Or get GreyB’s sustainability experts to assess your packaging practices and align them with the PPW regulations to make them future-proof.

Authored By: Vipin Singh, Marketing, and Mayank Maloo, Solutons.