The production of hydrogen via Steam Methane Reforming (SMR) emits approximately 830 million tonnes of CO2 annually worldwide, accounting for 2.2% of global CO2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion. Yet, SMR is the primary method for producing hydrogen.
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel usage are huge challenges for the hydrogen industry to become a significant low-emission fuel option for the future energy industry.
To overcome these challenges, scientists and entrepreneurs explore alternative solutions for hydrogen production with microbes like Microbial Electrolysis Cells (MECs).
MECs use electrochemically active microbes/bacteria to convert waste organic matter and wastewater into hydrogen. This biological process bypasses fossil fuels in hydrogen fuel production and tackles waste management challenges, creating a win-win for energy and environmental sustainability.
This article introduces four startups working on MEC technology in the hydrogen fuel industry to meet future energy needs with green solutions. These startups have the potential to grow rapidly, are in a good market position, or can introduce game-changing technology to the market in the next 2-3 years.
This makes them a great option to partner, collaborate, or acquire.
1. Wastewater Fuels: Using Energy in Polluted Water to Produce Hydrogen
| Founding Year | 2021 |
| Headquarters | Coventry, England |
| Total Funding Amount | £100K |
| Last Funding Round | Grant |
| Website | https://www.wastewaterfuels.com/ |
Due to financial and energy barriers, untreated wastewater exceeds 80% of global waste. Wasterwater Fuels proposes a solution that treats wastewater and generates clean energy (hydrogen and electricity) and water by introducing a modular and scalable technology suitable for both on-grid and off-grid setups. It promotes a circular economy by transforming wastewater into a valuable resource for fuel production.
Unlike traditional methods that rely on high-energy processes like electrolysis, Wastewater Fuels’ technology harnesses the energy present in wastewater.
This UK-based startup is pioneering hydrogen production with microbes using microbial electrolysis cells (MECs) method for treating wastewater. Its innovative technology employs microorganisms to break down organic matter in wastewater, releasing hydrogen in the process. The MECs apply an electrical current to electrodes colonized by microbes, which convert the organic matter into hydrogen ions. These ions are then transformed into hydrogen gas, which can be captured and utilized as a clean energy source.
This innovative approach is distinguished by its sustainable system design, which promises a 20-year lifespan with minimal maintenance and operates without moving parts.

The startup is led by CEO Martyn (Stephen) Lathbury, who holds an MBA from the University of Derby. Baasit Siddiqui, known for the Gogglebox and his educational initiatives like Siddiqui Education and T.I.M.E, is also an alumnus of this University.
Wastewater Fuels received a grant of £100K from TechX Clean Energy Accelerator in 2023.
2. Electro-Active Technologies Converting Waste Food Into Hydrogen
| Founding Year | 2017 |
| Headquarters | California, US |
| Total Funding Amount | £100K |
| Last Funding Round | Seed |
| Website | https://www.electroactive.tech/ |
Traditional waste management methods often result in environmental pollution and inefficient resource utilization.
To address this challenge, Electro-Active utilizes an advanced microbial and electrochemical process. Its system leverages advanced microbes and electrochemistry to effectively convert organic waste into clean hydrogen fuel.
The patented process fosters a robust microbial community that can break down any organic waste source, generating electrons used in hydrogen production. Utilizing waste as a feedstock, the technology boasts over 100% greater electrical efficiency than traditional water electrolysis. This translates to a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly approach to creating hydrogen.
Its CEO, Dr. Alex Lewis, holds a Ph.D. in Energy Science and Engineering.
The startup has raised funding for three rounds, with the last Seed round in September 2021.
Transform challenges into opportunities and stay ahead of the curve with cutting-edge market insights and technology trend analysis.

3. Ossus Biorenewables Generating Hydrogen with Its OB Hydracel
| Founding Year | 2017 |
| Headquarters | Karnataka, India |
| Total Funding Amount | ₹197 Million |
| Last Funding Round | Seed |
| Website | https://www.ossusbio.com/ |
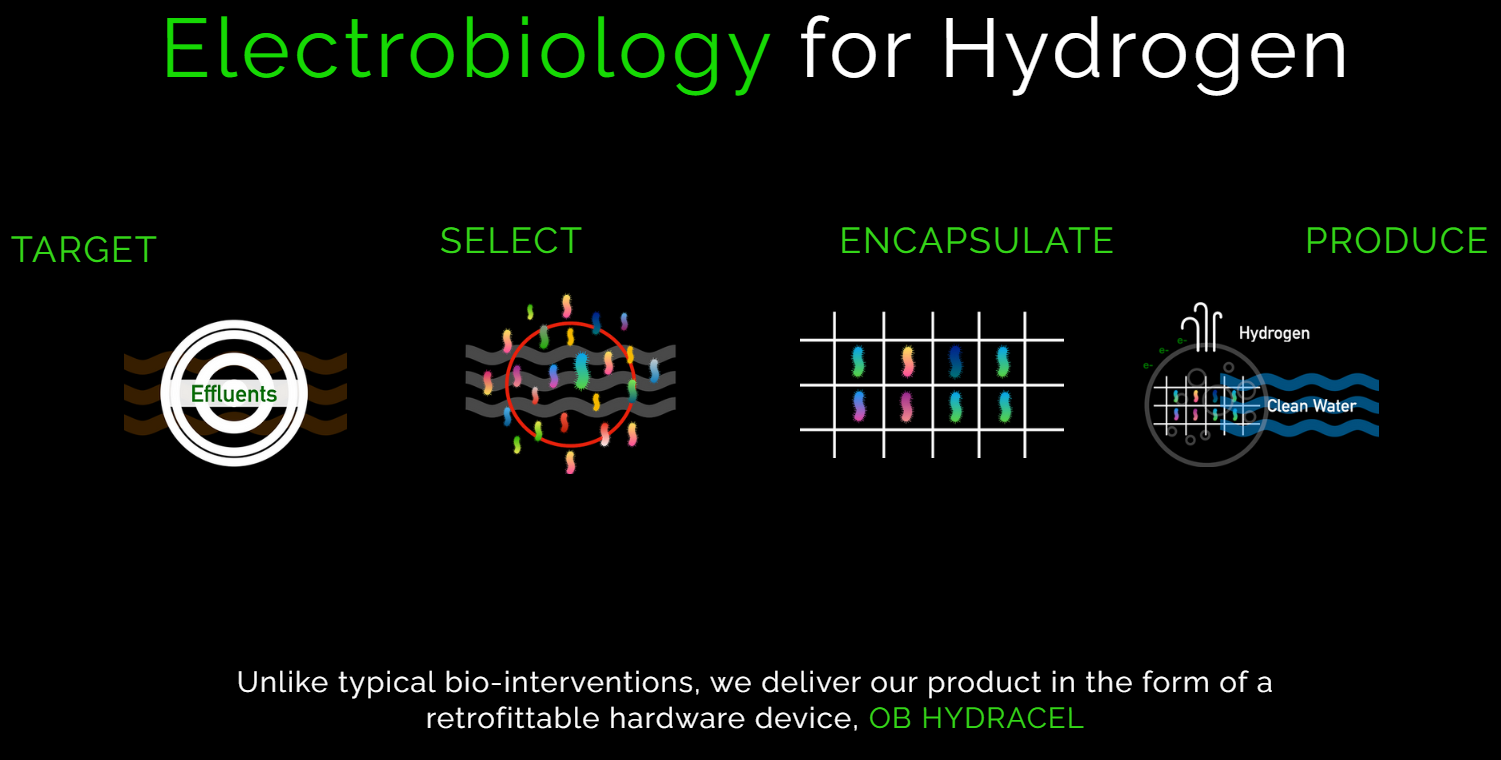
Ossus Biorenewables is developing a process for generating biohydrogen from renewable feedstocks such as industrial effluents, municipal sewage, and polluted water bodies.
Its proprietary technology, OB Hydracel, utilizes intelligent electroactive microbial communities to selectively target and break down the dilute organic content of effluents for biohydrogen production. OB Hydracel has a self-sustaining localized power, minimum downtime, and seamless retrofittable design. It attaches directly to effluent pipelines, facilitating an efficient, space-saving bypass solution.
The founding team behind this startup producing hydrogen with microbes includes CEO Suruchi Rao, CTO Kamar Suhail Basha, and CLO Shanta Rao. Suruchi holds a Ph.D. in bioprocess technology from the Institute Of Chemical Technology.
Ossus Biorenewables raised seed funding in April 2023. The startup was also supported by incubator IKP.
4. Cemvita Producing Hydrogen from Dried Oil Wells
| Founding Year | 2017 |
| Headquarters | Texas, United States |
| Total Funding Amount | $11.5M |
| Last Funding Round | Venture Round |
| Website | https://www.cemvita.com/ |
Cemvita is pioneering “gold hydrogen” production by utilizing bacteria to break down residual oil hydrocarbons in depleted wells, generating hydrogen and CO2. This innovative process, demonstrated in Texas, capitalizes on abandoned oil reservoirs to produce cost-effective hydrogen, aiming for $1 per kilogram.
This approach offers a new life to orphaned wells and aligns with the global shift towards sustainable energy sources by leveraging existing subsurface infrastructure for hydrogen extraction. A significant advantage of Cemvita’s process is the accessibility and existing infrastructure of oil wells, which facilitate gas transport.
The major challenge with this approach is managing CO2 byproducts to prevent atmospheric leakage and climate impact. The firm proposes solutions, including CO2 sequestration underground, biological fixation, or finding commercial applications for greenhouse gas, although storing it below ground presents challenges.
The startup is led by CEO Moji Karimi, who has experience at Weatherford, Biota Technology, and CleanTX, and CSO Tara Karimi, who holds dual Ph. Ds in tissue engineering and stem cell programming from the University of South Carolina and Tulane University.
Its last funding of $6.5 million was raised in February 2024 from a Venture—Series Unknown round.
Partner with growth-stage startups with innovative technologies to tackle your industry’s toughest challenges and stay on top of the competition.
Reach out to find similar ventures that perfectly fit your needs.

Author: Naveen Kumar, Marketing
Read Next: Innovation Trend Analysis of Hydrogen Energy Storage