This article is a part of our in-depth technology landscape analysis on solar cells (specifically about nano-photovoltaic solar cells). For your ease, we have divided the entire analysis into 4 major parts and you can jump on the part that is most relevant to you using this menu below:
- Disruptive Breakthroughs In Solar Cells
- Solar Now Cheaper Than Oil, What Future Holds For Nano Photovoltaic Cells
In case if you’re interested in getting your hands on the entire analysis in one single PDF (you can save it for offline reading or for sharing ahead with relevant people), you can download it from here.
This post is focused majorly on future aspects of nanotechnology in the photovoltaic cell domain and what the major companies from this domain are up to.
Due to depleting world petrochemical and coal reserves, the demand for renewable energy is rising continuously. The market size, investment, and rise of the PV cells in the near future are expected to boom. The data from the following researches support this fact:
- The Global annual solar power production is estimated to reach 500GW by 2020, from 40.134 GW in 2014, making this market one of the fastest-growing.
- The global photovoltaic market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18.30% between 2014 and 2020 and the overall market is estimated to be worth $89.52 billion in 2013 to $345.59 billion by 2020. In terms of application, the growing usage of photovoltaics in power plants, military applications, and other utility applications such as space & defense, industrial projects, and so on.
- Nanotechnology in photovoltaic cells is becoming popular in aerospace applications, building integrations, automobile applications, mobile applications, rooftop applications. These applications for solar material fabrication are creating opportunities for new companies to enter into it.
- The proliferation of electric vehicles is another factor promoting solar cells. In July this year, Elon Musk revealed the plan to embed solar cells on roof-tops of Tesla’s cars. The rise of electric vehicles has to lead to a sudden increase in energy demands which in turn has been significantly contributing to the growth of solar cells market in countries such as the USA, China, and Japan.
Market Coverage of Top companies of Nano PV Cells
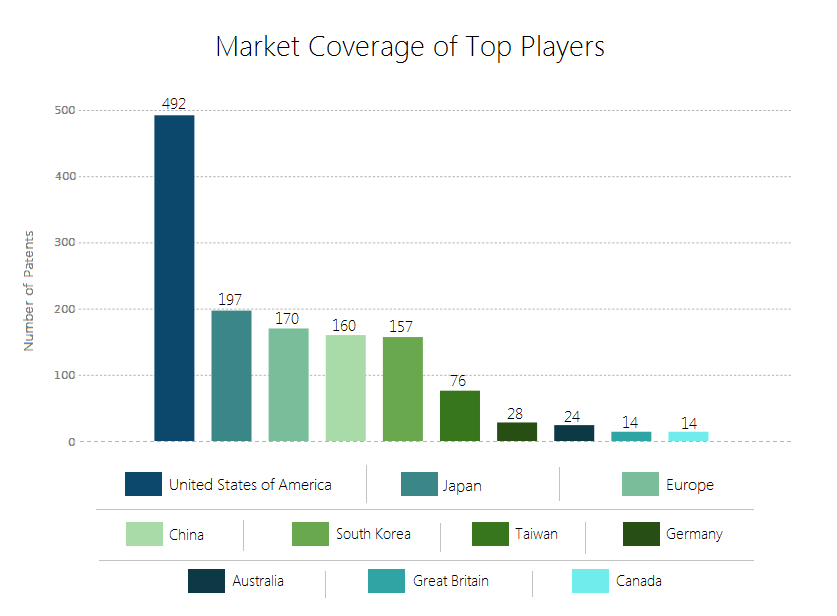
Also, it has been observed that many new companies, with completely different core competencies, are active in the Nano PV cell.
In the last five years, a large part of the total filing is done by companies like Mitsubishi Group, Fujifilm Corporation, Sunpower Corporation, Dow Global Technologies, IBM and 3M Innovative Properties. IBM, for example, has developed a method for electricity-less water disinfection using photovoltaic cells.
The patent filing data indicates the US as the top market but the market analysis narrates a different story of China, as the largest producer of solar electricity.
This is interesting as in Germany, comparatively less research has been conducted on nano-solar cells but it’s still the top solar electricity producing country. This could be taken as another metric to build IP in this country.
Japan, as per the patent filing data, is the second most lucrative market. Japanese researchers recently came up with a breakthrough to produce high-quality mono-silicon at extremely low costs. The new single-seed cast method can grow a single crystal from a small seed crystal making the whole system cheaper than ever. Japan is followed by Europe and China at third and fourth spot respectively.
The Indian and South African markets are expected to have great potential as these countries have a geographical advantage in terms of solar energy production. India is already trying to catch up with major countries in solar power generation capacities and has significantly less IP which means that entering this market is fairly easy that holds good opportunities for new companies.
Challenges to Overcome
The domain of Nano Photovoltaic cells, like every other technological domain, has its own set of challenges to overcome. Some of which are as follows:
- One of the key challenges is to bring down the higher manufacturing cost of the nanotechnology photovoltaic cell.
- Another challenge is to increase the efficiency of the nano photovoltaic cell for which researchers have suggested the use of quantum dots in nano PV Cells.
- At present, the market coverage and research trends are concentrated on a few geographical areas. It is little or almost no research is going on in the African region, which on average receives more sunlight, due to lack of infrastructure. This isn’t a technological challenge, however, it needed to be overcome.
Authored By: Sushant Kumar, Senior Research Analyst, Patent Landscape and Sonu Saini, Research Analyst, Prior Art.