The article was first published on September 6, 2017. It was later updated every year with the advancements in Autonomous Vehicles. The article was last updated on September 15, 2023.
A remarkable amount of progress has been made in the Autonomous Vehicle market each year, underscoring the industry’s unwavering commitment to innovation.
In 2022, the estimated value of the worldwide autonomous vehicle market was approximately USD 121.78 billion. Forecasts suggest that this market is set to reach roughly USD 2,353.93 billion by 2032, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 35% from 2023 to 2032. Furthermore, the autonomous vehicle market in the United States, with a valuation of USD 36.4 billion in 2022, demonstrates its significant presence.
Despite facing various challenges and obstacles, the community related to mobility unanimously acknowledges and recognizes the revolutionary and groundbreaking potential that autonomous driving possesses, not only for the transportation industry but also for consumer behavior and society as a whole.
Several major companies are researching and developing semi- and fully autonomous vehicles. This is due to a rising demand from both individuals and corporations for this technology, which is expected to revolutionize the industry.
A comprehensive market analysis of the autonomous vehicle industry was conducted to acknowledge its groundbreaking potential and we bring forth the Top 30 Self Driving Technology and Car Companies.
Through this article, we have tried to gauge the current market and research status of autonomous vehicles in as many details as possible. From companies involved in researching and manufacturing this technology to market challenges and strategies to solve them, we have covered almost everything you might want to know about autonomous vehicles.
As you might have already anticipated, this article is going to be really detailed, and to ease you in navigation, here we have created an index that you can use to jump to the section of your interest:
Also, to make it even more convenient, the whole article is present in a printable PDF. You can download it using the form below:
Introduction
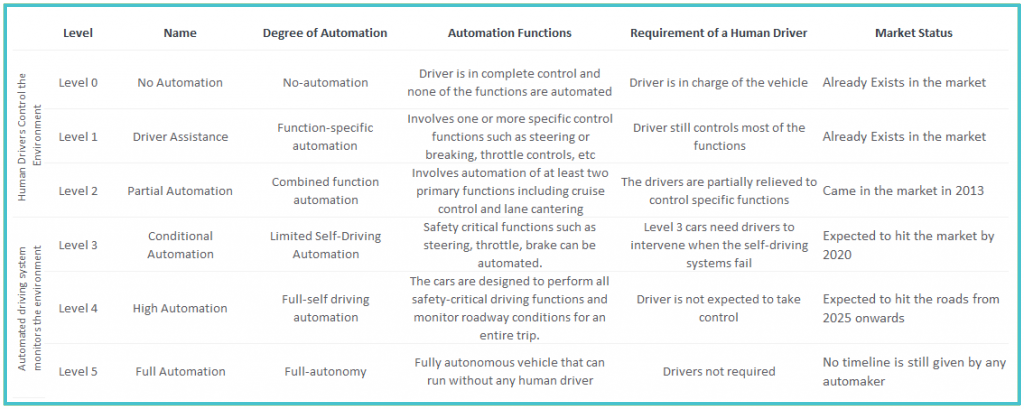
Level of Autonomy
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, autonomous cars are segmented under six levels of autonomy, from Level 0 to Level 5. The following table explains the autonomy levels in the vehicles.
Autonomous Vehicles Market Size And Growth
Various global consulting and research firms have devised different autonomous vehicle market size estimates.
In one of their reports, Lux Research revealed that the self-driving vehicle market has the potential to become an $87 billion opportunity by 2030. Level 2 vehicles are estimated to capture 92% of the total market share even in 2030, while level 3 cars will capture the rest. According to their report, no Level 4 or Level 5 vehicles will be operational by 2030.
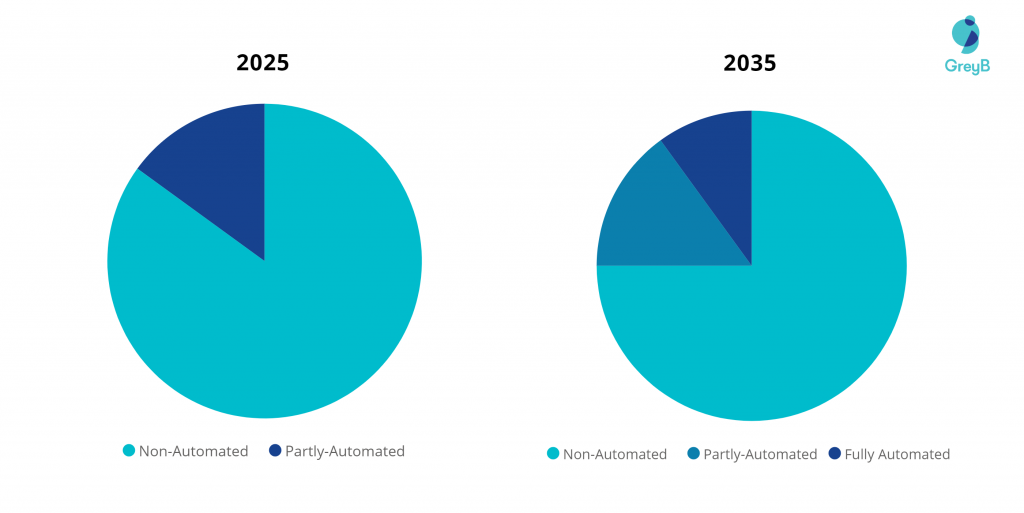
On the other hand, according to Allied Market Research, the global autonomous vehicle market was valued at $76.13 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $2,161.79 billion by 2030. 25% of the total cars sold in 2035 are projected to be autonomous vehicles, comprising 15% partially and 10% fully autonomous.
The share of Autonomous Vehicle Sales in the Total Market (2025 vs 2035)According to most industry experts, North America will become the leading market for such cars. Another analysis published by IHS highlights that the US will be an early player in the autonomous car segment.
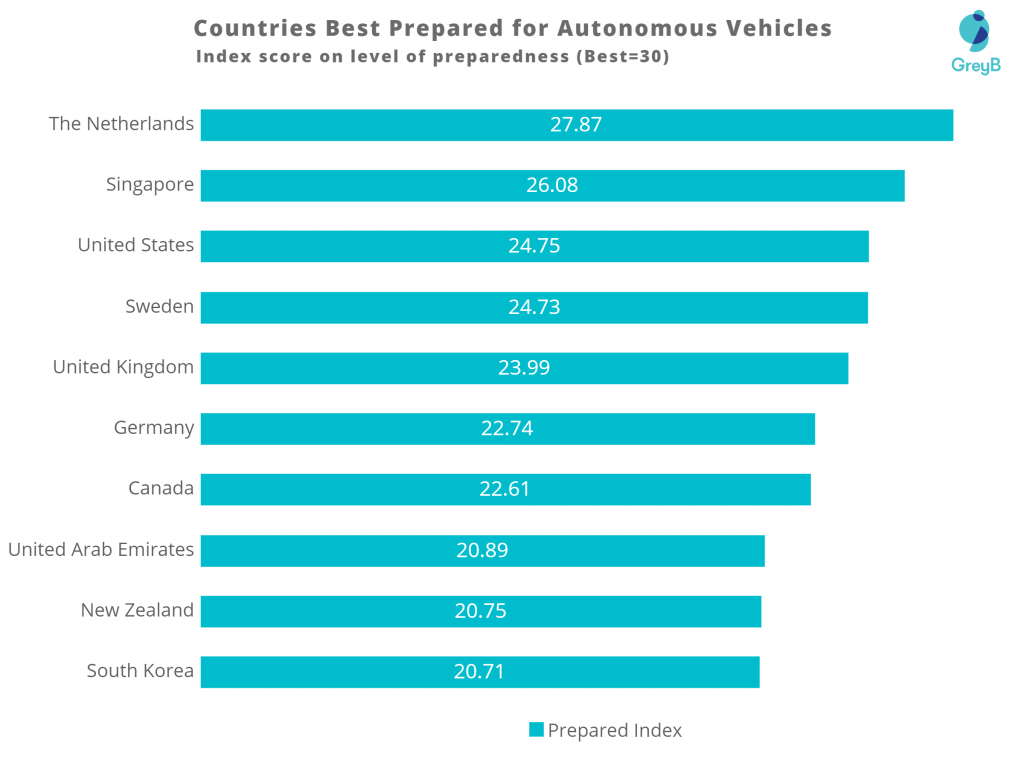
However, according to Statista, some countries are better prepared than the US.
Higher Safety And Possible Decline In Road Accident
According to industry experts, autonomous cars are expected to be safer than traditional cars. Advanced modern-day sensors and machine-learning technologies are being used in these cars. Additionally, these cars are backed up with impressively advanced artificial intelligence systems developed by some leading companies such as Nvidia, Intel, and many more. As a result, the chances of failure are less.
Using driverless cars will let the vehicles travel much closer to each other and also allow the vehicles to notice parking spots and auto parks. Parking management systems may also be automated with support from license plate reader cameras, ensuring driverless cars are accurately monitored and accounted for. Hence, this results in smoother traffic flow and leads to better fuel competence of the vehicles. According to the researchers, driverless cars could reduce fatal accidents by 90% which equals 300,000 lives saved each decade in the US.
Reduced Cost And Human Efforts
Autonomous vehicles will most definitely decrease the requirement for human drivers and can be helpful to industries facing a lack of manpower. The precious time saved using autonomous cars can be used for other, more significant tasks.
Challenges For Autonomous Vehicles
Regulatory Uncertainty
Most countries that have started testing autonomous vehicles have not yet provided concrete regulatory guidelines for such autonomous vehicles. There are still no guidelines or regulatory frameworks in which autonomous vehicles can run.
Even though the governments of some countries, including the US, Japan, and Singapore, showed interest in commercializing autonomous technologies, it is still in a stage of development.
Many research organizations have cited Laws, licensing, and regulations as one of the biggest challenges in marketing AVs. Trials of such cars are going on in multiple states in the US, including California, Michigan, Florida, and Nevada.
Many European countries such as Germany, the UK, Spain, Belgium, Italy, and France are also undergoing trials of autonomous cars. According to the European Commission, automated vehicles face challenges in establishing rules for technologies that are not yet applied.
Another challenge is deciding how the safety of automated vehicles should be tested and by whom. Such Regulatory uncertainty could cost a lot to several companies that have heavily invested in autonomous technologies.
Technical Challenges
Predictions that say AVs will hit roads in the next five to ten years’ timeline are highly positive. Modern-day AVs, on the other hand, are hardly road-ready.
ScienceNews Magazine listed five key technological challenges that might become a roadblock for autonomous cars.
One of the key problems of these five includes cybersecurity. In 2015, a cyber breach activity forced a Jeep to stop on a St. Louis highway while driving at 70mph. Hackers wirelessly accessed the car’s braking and steering through the onboard entertainment system.
In addition, further research in technology and affordability is essential to make vehicles compliant and hazard-free. In many cases, AVs are still struggling to relate with human-driven vehicles on the road, and they face huge obligations, insurance, and even moral concerns that have yet to be determined. For instance, Tesla’s autonomous vehicle test 2016 resulted in serious crashes that resulted in a human loss.
When technologies are already running efficiently, changing the current vehicles into a robotic fleet may take a couple of decades. Presently, more than 250 million vehicles are on the road in the U.S. alone, with an average beneficial life of more than 11 years. It could be difficult to accomplish this huge fleet to arrange autonomous technologies.
Autonomous Vehicle Ecosystem
There are over 250 autonomous vehicle companies, including automakers, technology providers, services providers, and tech start-ups, that are taking serious steps to make self-driven or driverless cars a reality. This market report categorizes cars into four broad segments: car companies and auto parts providers, technology companies, services providers, and tech start-ups.
Car Companies Working on Autonomous Vehicles
Ford
Ford is one of the most aggressive players and fastest autonomous vehicle companies aiming to launch a highly autonomous vehicle. It has plans to launch a fully autonomous vehicle by 2021. For the same, it has taken several strategic steps as well.
Unlike competitors, which are slowly ramping up autonomy systematically from Level 2 to 3 to 4, Ford aims to jump several steps and go right to Level 4. According to the experts, the price is the leading factor for this decision.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On Jan 9, 2018, Ford announced its invention called “Transportation Mobility Cloud,” which it created working with Qualcomm. Ford said that it is tired of being just a car company, and now it wants to be seen as an operating system for the future of mobility.
- On July 24, 2018, Ford said that it was creating a separate $4 billion unit for its self-driving vehicle operations and also seeking outside investors.
- On October 31, 2018, Ford Motor Company announced its collaboration with Baidu. Soon, both will kickstart trials to test autonomous vehicles in Beijing, China, following efforts by Ford engineers to equip the vehicles with Baidu’s Apollo Virtual Driver System. The two-year initiative was expected to commence by year-end and involve autonomous vehicles designed to meet Level 4 driving automation standards established by SAE International.
- On November 15, 2018, Ford publicly stated that it plans to have self-driving cars on the road in commercial capacity by 2021 and has been building a testing facility in Miami for the last nine months.
- On March 20, 2019, Ford Motor Company said it would build its first autonomous vehicles at a $50 million production center in Michigan as part of an earlier pledge to invest $900 million in manufacturing operations in the state.
- On April 26, 2019, Ford said that the company intends to deploy upwards of 100 driverless vehicles by the end of 2019 and start testing in a new city as it increases the development of its autonomous technologies.
- On May 22, 2019, Ford, in a press release, announced its exploratory partnership with Agility Robotics, an Albany-based spinoff of Oregon State University’s Dynamic Robotics Laboratory, which specializes in bipedal machines.
- On July 14, 2019, Ford and Volkswagen announced that they are collaborating on autonomous vehicle technology and investing more than $7 billion (£5.57 billion) in the autonomous vehicle technology platform Argo AI. Argo AI focuses on delivering a Society of Automobile Engineers (SAE) Level 4-capable self-driving system. Level 4 self-driving cars drive independently in certain specified conditions; a driverless taxi is one example of a Level 4 vehicle.
- Ford also partnered with Walmart to explore delivery with autonomous vehicle technology. Walmart is already offering grocery delivery in nearly 100 metro areas and is continuing to innovate to find new ways to serve customers – better, faster, and easier.
- On July 22, 2019, Ford announced that the company is pushing to introduce a high volume of fully autonomous vehicles by 2021. After establishing a $45 million advanced manufacturing center in Michigan last year, Ford is betting on futuristic technologies to help speed manufacturing innovation.
- On July 30, 2019, Ford purchased Quantum Signal — the 20-year-old company behind computer-generated environments (ANVEL) used by militaries to test unmanned remote and autonomous systems — for an undisclosed amount. The company said that it will use Saline, Michigan-based Quantum’s “extensive experience” in real-time simulation to build out its transportation-as-a-service (TaaS) platform and uses that support functional safety and other vehicle technologies.
- Ford has partnered or invested with four different technology companies doubling its presence in Silicon Valley. The effort to build fully autonomous vehicles by 2021 is the main pillar of Ford Smart Mobility.
- On Dec 17, 2019, Ford disclosed its multi-million dollar plans to build autonomous vehicles in Michigan. The news came shortly after Ford unveiled its first all-electric crossover, the 2021 Mustang Mach-E, which has already proved controversial among muscle-car fans.
- On March 05, 2020, Ford disclosed that it uses simulation tools using Quantum Signal AI mathematical modeling that helps the company understand, test, and validate its autonomous vehicles.
- On March 19, 2020, Ford released its autonomous vehicle dataset containing data collected from its fleet of autonomous cars in the Greater Detroit Area. The researchers can freely use the data set to improve the robustness of driverless cars. The data is time-stamped and contains raw data from the sensors, calibration values, pose trajectory, ground truth pose.
Post-COVID Activities
- In 2022, with Agro.AI, Ford shut down its AV project. (Source)
General Motors
General Motors is another contender to introduce highly autonomous vehicles prior to its competitors. It has the most aggressive test plans for autonomous vehicles among the players.
In March 2023, General Motors unveiled its latest semi-autonomous vehicle, the Ultra Cruise, starting with its integration into Cadillac models. This technology aims to ensure no crashes, emissions, or traffic jams. Ultra Cruise builds upon Super Cruise, which enables certain Chevy vehicles to self-drive on compatible highways using LiDAR, radar, GPS, and cameras. Through smart diagnostics and learning, Ultra Cruise identifies software upgrades applied via over-the-air updates. The system includes a Human Machine Interface to alert drivers to take control when needed. However, Ultra Cruise isn’t fully autonomous; drivers must remain attentive and ready to intervene. Vehicles with Super Cruise cannot utilize the new Ultra Cruise tech.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On March 15, 2018, General Motors announced that it would start producing its self-driving electric Chevy Bolts in a Michigan facility by spending $100 million. The car, which GM calls the “Cruise AV,” will be the automaker’s first production-ready vehicle built from the ground up to operate with no steering wheel, pedals, or manual controls.
- On April 3, 2019, Three major automakers, General Motors Co., Ford Motor Co., and Toyota Motor Corp, joined forces with automotive engineering group SAE International to form a consortium to help draw up safety standards for autonomous cars that could eventually help create regulations in the United States.
- On July 10, 2018, as per RBC Capital Market, Cruise could be worth a whopping $43 billion. The startup has been growing fast ever since its acquisition for $581 million. GM said it hopes to increase Cruise’s headcount to 1,648 in California by 2021 thanks to a tax-credit package worth $8 million approved by state officials in 2017.
- In 2018, General Motors filed a trademark for something called “Ultra Cruise.” The new technology would have even more capability than Super Cruise. The technology can continue to improve with the number of places you can use it.
- On Oct 3, 2018, Honda announced that it’d taken a stake in General Motors subsidiary Cruise Holdings as part of a plan for the Japanese and American automakers to work together in developing and building an autonomous vehicle. The investment of $2.8 billion over the next 12 years includes Honda paying GM $750 million immediately as it takes a 5.7 percent stake in Cruise Holdings.
- On February 06, 2019, General Motors stated that it spent much less than it expected last year on its Cruise autonomous vehicle operations. As part of its 2018 earnings report, GM said it spent $728 million on the business, almost $270 million less than what it estimated.
- On March 12, 2019, GM announced that it is hiring 1,000 people over the next year to work on Cruise autonomous vehicle operations. The hiring spree would double the staff currently under the Cruise and mark a major investment in autonomous efforts.
- On March 20, 2019, the USPTO published a new patent filed by GM, which mentions converting any or every vehicle into a self-driving one.
- On July 8, 2019, the Trump administration approved Softbank’s $2.25 billion investment in General Motors’ (GM) self-driving unit, Cruise Automation. After the investment, SoftBank would own nearly 19.6% of GM Cruise. General Motors also announced that it would contribute ~$1.1 billion to its GM Cruise subsidiary after the SoftBank transaction closed.
- On July 24, 2019, GM CEO Dan Ammann said that Cruise would launch an autonomous taxi service on the challenging, crowded streets of San Francisco.
- On Jan 21, 2020, Cruise, a startup owned by GM, announced that its electric self-driving vehicle, Origin, was headed for production. The vehicle is designed to be more spacious and passenger-friendly. The vehicle lacks traditional controls like pedals and a steering wheel, thus able to make more room to share rides.
- On March 4, 2020, GM made an announcement of investing more than $20 billion through 2025 on its next-gen electric and autonomous vehicles, including capital and engineering resources. As a fast-growing market, the company wants to gain a foothold in new auto technologies.
- On April 3, 2020, USPTO published a patent application of General Motors that discloses an invention related to “Decentralized Distributed Map Using Blockchain.” The issue that this patent looks to be trying to solve in the driving space is related to the dynamic feedback of mapping around a car. As mapping is one of the important systems an autonomous vehicle requires, blockchain would make it more secure.
- In March 2021, Cruise acquired the self-driving startup Voyage in a notable consolidation within the autonomous vehicle industry. This news follows reports of their acquisition discussions emerging just a week prior. The deal’s specifics remain undisclosed. Cruise focuses on urban autonomous vehicle operations, particularly in downtown San Francisco, while Voyage manages a fleet of low-speed autonomous vehicles catering to residents of retirement communities. Both companies have conducted tests without safety drivers and aim to introduce fully operational commercial robot taxi services.
- In April 2021, Cruise, GM’s subsidiary, announced that it is broadening its global reach by venturing into Dubai. The San Francisco-based company has inked an exclusive agreement with the Dubai Roads and Transport Authority to offer self-driving taxis and ride-hailing services until 2029. While the public availability date is undisclosed, Cruise intends to commence operations in Dubai in 2023. According to the outlined strategy, the company aims to have around 4,000 self-driving vehicles in Dubai by 2030.
- In June 2021, Cruise announced that it obtained a fresh $5 billion credit line to support the upcoming launch of its autonomous ride-hailing service. This new credit arrangement, disclosed on Tuesday, originates from GM’s automotive financing division and is designated for acquiring Cruise’s self-driving Origin shuttles. Production of these shuttles is anticipated to commence at a Detroit factory in early 2023. Cruise’s available funds now exceed $10 billion with this addition, as Cruise CEO Dan Ammann stated.
- In September 2021, General Motors announced a $300 million investment in the Chinese autonomous driving startup Momenta to collaborate on advancing self-driving technologies for upcoming vehicle models in China. This partnership marks GM’s inaugural collaboration of this kind in the world’s largest automotive market. Momenta stands out as one of the select companies granted permission to compile high-definition maps in China, a crucial asset for autonomous driving systems. The company actively engages with automakers to create mass-produced vehicles that incorporate self-driving capabilities, allowing real-time data collection.
- In Sep 2021, General Motors announced that it made a fresh investment in Oculii, a software startup dedicated to enhancing radar sensor spatial resolution by 100 times. This additional funding, amounting to millions, follows closely after Oculii’s successful closure of a $55 million Series B round earlier this year. Oculii and GM have been engaged in collaborative efforts for some time, as CEO Steven Hong revealed in a recent TechCrunch interview. While GM’s exact utilization of Oculii’s software remains unspecified, it could potentially bolster the capabilities of GM’s hands-free advanced driver assistance system, Super Cruise. Hong also mentioned that Oculii is partnering with several other original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), with one being part of Oculii’s investor lineup.
- In Oct 2021, Cruise, a part of General Motors, and Waymo secured the distinction of being the initial companies to acquire autonomous vehicle permits in California that allow them to provide passenger rides. Cruise’s permit permits them to offer driverless nighttime rides in specific San Francisco areas granted by the California Department of Motor Vehicles. Meanwhile, Waymo has obtained a permit from the same authority to operate autonomous vehicles with safety drivers present.
- In Oct 2021, Cruise has set its sights on achieving a fleet of no less than 1 million self-driving vehicles by 2030. At a General Motors investor presentation on Wednesday, Cruise’s CEO, Dan Ammann, unveiled a visual representation of the division’s rapid fleet expansion. The graph indicated Cruise’s intent to escalate its operations, aiming for a fleet size of 1 million or more vehicles by the close of the 2030 decade.
- In June 2022, Cruise announced that it secured the first permit in San Francisco to offer paid self-driving car rides, overcoming prior objections from city officials. The streets of San Francisco have witnessed the presence of self-driving test vehicles, both with human safety drivers and increasingly without them. Transforming this presence into a nascent business within a major U.S. city represents a notable step in the lengthy and delayed progression toward autonomous taxi services. This permit marked Cruise’s final regulatory challenge in California. The company revealed plans to commence paid services in the upcoming weeks, utilizing a fleet of up to 30 driverless Chevrolet Bolt electric vehicles.
- In Sep 2022, In pursuit of achieving $1 billion in revenue by 2025, Cruise said it is extending its operations beyond San Francisco. Initially launching its self-driving taxi service in San Francisco, where Chevrolet Bolt EVs offer rides without human safety drivers for a fee, Cruise utilizes a fleet of 30 Bolts to transport passengers within specific city areas. Currently manufactured at the Orion Assembly plant in Orion Township, these Bolts have been the backbone of Cruise’s service. Now, Cruise, headquartered in San Francisco and predominantly owned by GM (80% stake), is set to introduce a driverless taxi fleet to Austin, Texas, and Phoenix, Arizona, within the coming three months, as stated by Cruise CEO Kyle Vogt.
- In Sep 2022, GM’s Cruise said it aims to avoid dependence on external chip manufacturers for its autonomous vehicles by producing its own. According to Carl Jenkins, the company’s Vice President for Hardware Engineering, the primary driving factor behind this transition is the significant expenses of procuring chips from other companies, as highlighted in his conversation with Reuters.
Post-COVID Activities
- In Mar 2021, Cruise acquired the self-driving startup Voyage in a notable consolidation within the autonomous vehicle industry. This news follows reports of their acquisition discussions emerging just a week prior. The deal’s specifics remain undisclosed.
Cruise focuses on urban autonomous vehicle operations, particularly in downtown San Francisco, while Voyage manages a fleet of low-speed autonomous vehicles catering to residents of retirement communities. Both companies have conducted tests without safety drivers and aim to introduce fully operational commercial robot taxi services. (Source)
- In Apr 2021, Cruise, GM’s subsidiary, announced that it is broadening its global reach by venturing into Dubai. The San Francisco-based company has inked an exclusive agreement with the Dubai Roads and Transport Authority to offer self-driving taxis and ride-hailing services until 2029. While the public availability date is undisclosed, Cruise intends to commence operations in Dubai in 2023. According to the outlined strategy, the company aims to have around 4,000 self-driving vehicles in Dubai by 2030. (Source)
- In June 2021, Cruise announced that it obtained a fresh $5 billion credit line to support the upcoming launch of its autonomous ride-hailing service. This new credit arrangement, disclosed on Tuesday, originates from GM’s automotive financing division and is designated for acquiring Cruise’s self-driving Origin shuttles. Production of these shuttles is anticipated to commence at a Detroit factory in early 2023. Cruise’s available funds now exceed $10 billion with this addition, as Cruise CEO Dan Ammann stated. (Source)
- In Sep 2021, General Motors announced that it made a fresh investment in Oculii, a software startup dedicated to enhancing radar sensor spatial resolution by 100 times. This additional funding, amounting to millions, follows closely after Oculii’s successful closure of a $55 million Series B round earlier this year.
Oculii and GM have been engaged in collaborative efforts for some time, as CEO Steven Hong revealed in a recent TechCrunch interview. While GM’s exact utilization of Oculii’s software remains unspecified, it could potentially bolster the capabilities of GM’s hands-free advanced driver assistance system, Super Cruise. Hong also mentioned that Oculii is partnering with several other original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), with one being part of Oculii’s investor lineup. (Source)
- In Sep 2021, General Motors announced a $300 million investment in the Chinese autonomous driving startup Momenta to collaborate on advancing self-driving technologies for upcoming vehicle models in China. This partnership marks GM’s inaugural collaboration in the world’s largest automotive market.
Momenta stands out as one of the select companies granted permission to compile high-definition maps in China, a crucial asset for autonomous driving systems. The company actively engages with automakers to create mass-produced vehicles incorporating self-driving capabilities, allowing real-time data collection. (Source)
- In Oct 2021, Cruise, a part of General Motors, and Waymo secured the distinction of being the initial companies to acquire autonomous vehicle permits in California that allow them to provide passenger rides. Cruise’s permit permits them to offer driverless nighttime rides in specific San Francisco areas granted by the California Department of Motor Vehicles. Meanwhile, Waymo has obtained a permit from the same authority to operate autonomous vehicles with safety drivers present. (Source)
- In Oct 2021, Cruise has set its sights on achieving a fleet of no less than 1 million self-driving vehicles by 2030. At a General Motors investor presentation, Cruise’s CEO, Dan Ammann, unveiled a visual representation of the division’s rapid fleet expansion. The graph indicated Cruise’s intent to escalate its operations, aiming for a fleet size of 1 million or more vehicles by the close of the 2030 decade. (Source)
2022
- In June 2022, Cruise announced that it secured the first permit in San Francisco to offer paid self-driving car rides, overcoming prior objections from city officials. The streets of San Francisco have witnessed the presence of self-driving test vehicles, both with human safety drivers and increasingly without them. Transforming this presence into a nascent business within a major U.S. city represents a notable step in the lengthy and delayed progression toward autonomous taxi services. This permit marked Cruise’s final regulatory challenge in California. The company revealed plans to commence paid services in the upcoming weeks, utilizing a fleet of up to 30 driverless Chevrolet Bolt electric vehicles. (Source)
- In Sep 2022, In pursuit of achieving $1 billion in revenue by 2025, Cruise said it is extending its operations beyond San Francisco. Initially launching its self-driving taxi service in San Francisco, where Chevrolet Bolt EVs offer rides without human safety drivers for a fee, Cruise utilizes a fleet of 30 Bolts to transport passengers within specific city areas. Currently manufactured at the Orion Assembly plant in Orion Township, these Bolts have been the backbone of Cruise’s service. Now, Cruise, headquartered in San Francisco and predominantly owned by GM (80% stake), is set to introduce a driverless taxi fleet to Austin, Texas, and Phoenix, Arizona, within three months, as Cruise CEO Kyle Vogt stated. (Source)
- In Sep 2022, GM’s Cruise said it aims to avoid dependence on external chip manufacturers for its autonomous vehicles by producing its own. According to Carl Jenkins, the company’s Vice President for Hardware Engineering, the primary driving factor behind this transition is the significant expenses of procuring chips from other companies, as highlighted in his conversation with Reuters. (Source)
2023
- In March 2023, General Motors unveiled its latest semi-autonomous vehicle, the Ultra Cruise, starting with its integration into Cadillac models. This technology aims to ensure no crashes, emissions, or traffic jams. Ultra Cruise builds upon Super Cruise, which enables certain Chevy vehicles to self-drive on compatible highways using LiDAR, radar, GPS, and cameras. Through innovative diagnostics and learning, Ultra Cruise identifies software upgrades applied via over-the-air updates. The system includes a Human Machine Interface to alert drivers to take control when needed. However, Ultra Cruise isn’t fully autonomous; drivers must remain attentive and ready to intervene. Vehicles with Super Cruise cannot utilize the new Ultra Cruise tech. (Source)
Audi
In January 2017, Audi announced its plans to launch its highly automated vehicle in 2020 and a level 3 vehicle by the end of 2017. The company announced using NVIDIA’s AI technology in its autonomous vehicle.
In 2017, Volkswagen-owned Audi started a new subsidiary focused on autonomous driving. This new unit, Autonomous Intelligent Driving, works for the entire Volkswagen Group.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On June 26, 2018, Audi announced that it has partnered with autonomous vehicle simulation platform provider Cognata Ltd to speed up the development of autonomous vehicles. Cognata simulation platform virtually recreates real-world cities and thus can provide Audi with a range of testing scenarios, including traffic models that simulate realistic conditions, before physical roadway tests of autonomous vehicles.
- On July 27, 2018, Audi unveiled a second-generation version of its Q3 compact SUV, a larger and more comfortable form with semi-autonomous driving features. The new SUV will be heading to the Paris Motor Show and is expected in dealerships by the end of 2018.
- On October 11, 2018, Huawei and Audi announced a partnership on intelligent connected vehicles, with the networking giant’s Mobile Data Center (MDC) being integrated into the Audi Q7 as a showcase prototype. Huawei and Audi signed a memorandum of understanding for manufacturing intelligent connected vehicles together in July. Besides, Audi was also working with Ericsson on using 5G technologies during automotive production and smart factories.
- On November 27, 2018, German automakers Audi, Airbus, and Italdesign presented a scaled-down version of their future vision. The vision includes a drone that can pluck the cab off an autonomous electric vehicle and then fly off to its intended destination.
- On December 4, 2018, Audi said it would invest €14 billion ($15.95 billion) over the next 5 years in transportation technologies such as electric mobility, autonomous driving, and digital services. Audi’s total projected expenditure for the five-year planning period will be €40 billion ($45.6 billion). These investments will include spending on property, factories, equipment, and research and development.
- On December 18, 2018, Autonomous Intelligent Driving (AID), Audi’s driverless technology spinoff, announced a collaboration with Alto startup Luminar and a supplier for Volkswagen Group brands, such as VW and Porsche, to accelerate the goal of bringing fully self-driving cars in markets by 2021.
- On August 23, 2019, Audi announced it was prepared to join an alliance with Daimler and BMW to develop advanced driving assistance systems. The alliance was expected at the Frankfurt auto show in September. The collaboration would help companies develop highly automated driving functions to Level 3 autonomous driving and automated parking.
Post-COVID Activities
- No Major activities after 2020.
Nissan – Renault
Nissan is one of the first movers in the segment and started the initiatives as early as 2013. It unveiled its first public prototype in 2013 at the Nissan 360 event in California and announced it would launch a highly automated vehicle by 2020. Since then, it has been testing an autonomous Nissan LEAF on the roads of Tokyo and Detroit.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On February 22, 2018, Nissan Motor and DeNA announced that field tests of Easy Ride, the self-driving taxi service they developed together, will begin next month in Japan. This means that Nissan and DeNA now rank among Uber, Lyft, GM, Didi Chuxing, and other companies pioneering self-driving taxi pilots to launch commercially within the next few years.
- On March 28, 2018, Nissan said it included ProPilot Assist in the 2018 Leaf electric car and top-selling Rogue SUV. With the addition of the Altima, Nissan already established itself as a leader, offering highly automated driving in its mass-market vehicles.
- On June 20, 2019, Renault-Nissan announced that they entered into a partnership with Waymo to develop self-driving systems for vehicles that will carry passengers and haul packages. The companies said they would work together exclusively to develop technology for vehicles that could be deployed in France and Japan.
- On July 23, 2019, Nissan announced that its new revised ProPilot 2.0 now includes facial recognition software and 3D mapping navigation in addition to a massive upgrade of its cameras and sensors. For the first time, a driver will be able to experience no-hands driving from the on-ramp to the off-ramp of highways, according to Nissan.
- On Aug 22, 2019, Nissan’s ProPilot Assist was one of the first super-advanced driver-aid suites to be widely available in an affordable car. Nissan’s not doing Version 2.0 by itself, which makes us even more excited — because it’s working with Intel’s Mobileye to power its hands-off freeway driving feature.
- On Aug 29, 2019, Nissan rolled out its ProPilot 2.0 driver-assistance technology feature in the new Nissan Skyline to enable hands-off driving for single-lane cruising. ProPilot is said to be a Level 3 autonomous drive system that engages with the vehicle’s navigation system to maneuver the car as per a predefined route.
- On Oct 14, 2019, Renault started a public trial of its on-demand car service on the Paris-Saclay urban campus. Around 100 people used the service, consisting of two electric autonomous and shared Renault Zoe Cab prototypes – on the campus from Oct 14 to Nov 8. Users can request a car on-demand or book it in advance.
- On Feb 5, 2020, Nissan announced that it completed a 230-mile driverless journey in Britain. The trip started from Nissan’s European technical center in Cranfield, southern England, and ended at its Sunderland factory in the northeast. Using advanced positioning technology, it included roads with no or minimal markings, junctions, and roundabouts.
- In June 2021, Chinese autonomous driving startup WeRide secured $310 million in its latest funding round, with prominent contributions from the venture capital division of the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance and the state-supported China Structural Reform Fund. Having initially invested in WeRide in 2018, the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance remains a strategic partner, engaging in joint efforts with WeRide to advance autonomous driving technology research, development, and business expansion within China, according to the company’s press release.
Post-COVID Activities
- In June 2021, Chinese autonomous driving startup WeRide secured $310 million in its latest funding round, with prominent contributions from the venture capital division of the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance and the state-supported China Structural Reform Fund. Having initially invested in WeRide in 2018, the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance remains a strategic partner, engaging in joint efforts with WeRide to advance autonomous driving technology research, development, and business expansion within China, according to the company’s press release. (Source)
Tesla
In April 2017, Tesla’s CEO, Elon Musk, confirmed that Tesla would be able to launch a Level 5 vehicle within the next two years, depending on software validation and regulatory updates.
It is the most aggressive timeline provided by any other automaker. Elon Musk also said that by the end of 2017, Tesla will bring a car that can drive itself from Los Angeles to New York City, with no human needed.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On Jun 5, 2018, Elon Musk announced plans for a free trial of Autopilot to be released within the next couple of months. The enhanced Autopilot will cost an additional $5,000 at purchase in the current generation of Teslas or an additional $1,000 if it’s purchased after the car itself.
- On Aug 1, 2018, Tesla announced it would create its own AI chips for self-driving cars. By having its own AI chips, the company can build for its own needs faster.
- On Aug 11, 2018, Elon Musk announced the plan to make the autonomous software in Tesla units available on open-source platforms. Musk has often noted growing concerns over hackers getting access to Tesla’s software, and preventing a large-scale hack is one of Tesla’s biggest security priorities.
- On Jul 16, 2019, Tesla announced an increase in the price of its Autopilot driver assistance system’s “full self-driving” version by around $1,000 starting August 16th. The higher-tier package currently costs $6,000 if customers choose the option when buying a car, but the company will charge $8,000 if they decide to upgrade after taking delivery.
- On July 31, 2019, Tesla launched its Full Self-Driving computer, claiming it is ‘objectively the best chip in the world’. They claimed a factor of 21 improvements in frames per second processing versus the previous generation Tesla Autopilot hardware, which was powered by Nvidia hardware. The company’s new computer can process 2,300 frames per second and perform 144 trillion operations per second.
- On Apr 14, 2020, Tesla announced that it is moving ahead with its plans to launch commercially in Israel. According to an anonymous source, Tesla recently appointed Ilan Benano as its technical service manager in the country.
- On Jan 28, 2022, According to Chief Executive Elon Musk, Tesla’s most pivotal offerings for the upcoming year and the one after won’t solely be vehicles. Instead, the focus will be on autonomous driving software and a humanoid robot. While these ambitious plans from renowned billionaires in the electric car sector hold promise, they are confronted with significant hurdles encompassing both technological and regulatory aspects. Tesla and other automotive technology firms have consistently fallen short of their self-imposed deadlines to introduce self-driving cars, illustrating the challenges in this endeavor.
- On Feb 13, 2022, Tesla launched new features such as the FSD Beta, the latest EV company driver-assistance system update. Tesla now offers Autopilot, a system that can match a vehicle’s speed to surrounding traffic and assist with steering. The company also offers features such as auto lane change and parking assistance in packages called ‘Enhanced Autopilot’ or ‘Full Self-Driving Capability,’ depending on countries.
- On March 20, 2022, In a recent study conducted by AutoPacific, Tesla emerged as the “most-trusted” brand in the race toward fully autonomous vehicles. The survey gauged consumer attitudes towards the technology, encompassing 56 automotive brands. Tesla secured the top spot, garnering 32% of the votes, surpassing Toyota with 19% and BMW with 18%, as indicated in the study’s findings reported by Teslarati.
- On Aug 22, 2022, Tesla announced an increase in the cost of its contentious “full self-driving” driver-assist feature, raising it to $15,000. Until September 5, buyers can secure it for $12,000, a price that has been in place since January. This recent price hike marks a fivefold increase from its initial introduction as a $3,000 add-on. Despite the slower-than-projected development and facing criticism and regulatory scrutiny, Tesla continues to adjust the pricing of this software.
- On Dec 28, 2022, Starting in 2023, a new California law will prevent Tesla and other car manufacturers from promoting their vehicles as “fully self-driving.” The law, known as Senate Bill (SB) No. 1398 and backed by Democratic state senator Lena Gonzales, specifically disallows Tesla from utilizing the term “Full Self-Driving” (FSD) for their Advanced Driver Assist System (ADAS) package.
Post-COVID Activities
2022
- On Jan 28, 2022, According to Chief Executive Elon Musk, Tesla’s most pivotal offerings for the upcoming year and the one after won’t solely be vehicles. Instead, the focus will be on autonomous driving software and a humanoid robot. While these ambitious plans from renowned billionaires in the electric car sector hold promise, they are confronted with significant hurdles encompassing both technological and regulatory aspects. Tesla and other automotive technology firms have consistently fallen short of their self-imposed deadlines to introduce self-driving cars, illustrating the challenges in this endeavor. (Source)
- On Feb 13, 2022, Tesla launched new features such as the FSD Beta, the latest EV company driver-assistance system update. Tesla now offers Autopilot, a system that can match a vehicle’s speed to surrounding traffic and assist with steering. The company also offers features such as auto lane change and parking assistance in packages called ‘Enhanced Autopilot’ or ‘Full Self-Driving Capability,’ depending on countries. (Source)
- On March 20, 2022, In a recent study conducted by AutoPacific, Tesla emerged as the “most-trusted” brand in the race toward fully autonomous vehicles. The survey gauged consumer attitudes towards the technology, encompassing 56 automotive brands. Tesla secured the top spot, garnering 32% of the votes, surpassing Toyota with 19% and BMW with 18%, as indicated in the study’s findings reported by Teslarati. (Source)
- On Aug 22, 2022, Tesla announced an increase in the cost of its contentious “full self-driving” driver-assist feature, raising it to $15,000. Until September 5, buyers can secure it for $12,000, a price that has been in place since January. This recent price hike marks a fivefold increase from its initial introduction as a $3,000 add-on.
Despite the slower-than-projected development and facing criticism and regulatory scrutiny, Tesla continues to adjust the pricing of this software. (Source)
On Dec 28, 2022, Starting in 2023, a new California law will prevent Tesla and other car manufacturers from promoting their vehicles as “fully self-driving.” The law, known as Senate Bill (SB) No. 1398 and backed by Democratic state senator Lena Gonzales, specifically disallows Tesla from utilizing the term “Full Self-Driving” (FSD) for their Advanced Driver Assist System (ADAS) package. (Source)
BMW
In March 2017, BMW announced its plan to launch Level 5 autonomous cars by 2021. The primary aim of BMW is to gain a competitive advantage in the space by launching a level 5 autonomous vehicle while most of the other competitors are running for level 4 cars.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On March 21, 2018, BMW announced the heavy investment in research and development of new electric cars, which could set the investment at an all-time high this year.
- On April 4, 2018, In Unterschleißheim (near Munich, Germany), BMW opened a facility that will help systematically develop highly and fully automated driving at the BMW Group.
- On April 26, 2018, BMW inked a deal with Innoviz, an Israeli startup building LiDAR remote sensing technology for self-driving cars, to use the company’s sensors and computer vision software in autonomous BMW vehicles.
- On May 16, 2018, BMW announced that they were given the German automaker the green light to test its autonomous tech on public roads in China, according to an agreement with Chinese authorities.
- On Jul 10, 2018, Chinese internet search giant Baidu and Germany’s BMW Group announced the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the BMW Group to join Baidu’s Apollo, the company’s open autonomous driving platform, as a board member. The agreement marks the beginning of a new partnership on autonomous driving between the BMW Group and Baidu.
- On Oct 24, 2018, BMW Group announced a partnership with India’s KPIT and Austria’s TTTech for software development, which aimed to move ahead with the scalable autonomous driving platform and to work together on the development of Level 3 and Level 4/5 functions (Highway Pilot and Urban Pilot).
- On December 8, 2018, BMW announced the new head of its driver assistance and autonomous driving development department i.e. Alejandro Vukotich who will be taking a start from January 2019. Vukotich will replace Elmar Frickenstein, who has been in charge of the department since it was created in May 2016.
- On Jan 10, 2019, At CES, BMW provided demonstrations of its self-riding motorcycle. The motorcycle can start, slow down, turn, and stop by itself. The invention is an accomplishment of a suite of proprietary software housed in some hard pack cases mounted on the back of the bike — an otherwise stock-looking R 1200 GS, save for the inclusion of a tall radio antenna on the rear.
- On April 2, 2019, Self-driving cars start-up Aurora teamed up with BMW and Daimler to develop self-driving cars, the technology company’s Chief Executive Chris Urmson said.
- On Apr 03, 2019, Israel’s Globes publishes that BMW is on a path to start testing its autonomous vehicles in Israel by the end of the year. The German automaker will reportedly have a fleet of self-driving vehicles on the road in the country which also coincides with when BMW plans to open an R&D center in Israel, too.
- On April 08, 2019, DXC Technology signed an agreement to support BMW’s autonomous vehicle development via the High-Performance D3 platform. DXC provides services that help deliver and simplify data analysis and algorithmic training to reduce the time and cost to develop autonomous vehicles.
- On May 15th, 2019, a recent report from Automotive News said that the FCA brand and Maserati will be using technology developed by BMW on their cars. The exact timeline is yet to be confirmed, but this is the first report about autonomous tech being shared by BMW with any other car maker.
- On June 10, 2019, ANSYS and BMW Group announced the industry’s first holistic simulation toolchain for developing autonomous vehicle (AV) technologies. The simulation toolchain will enable highly automated and autonomous driving (AD) with the first vehicle launch expected in just two years.
- On July 7, 2019, BMW and Mercedes-Benz joined forces primarily to reduce the cost and lead time of autonomous driving technology. The two companies committed 1,200 autonomous technicians, built a trio of self-driving test centers in Germany, and are sharing a data storage center dedicated to the tech. The group is attempting to build driver-assist programming in a rapid fashion.
- On Jul 11, 2019, BMW China announced its partnership with China Unicom to test autonomous cars using 5G networks. This is the first partnership between a global automaker and a state-owned mobile carrier. The collaboration highlights China’s accelerated pace in developing connected vehicles using 5G networks.
- On Jul 15, 2019, BMW China announced that it is looking to expand its autonomous driving in China as they entered into a partnership with Beijing-based navigation company NavInfo to develop high-precision maps for autonomous cars.
- On July 22, 2019, BMW Brilliance Automotive (BBA) become the first automobile manufacturer to enable full 5G wireless coverage at all its plants. The new wireless standard allows large quantities of data to be transferred within a very short space of time thus making the process faster.
- On July 31, 2019, BMW’s investment arm – BMW i Ventures division – announced an addition to its portfolio; Recogni – a company that seeks to solve the problem of processing power for autonomous cars. The US-based company is founded by RK Anand, along with Ashwini Choudhary, Eye-Fi founder Eugene Feinberg, former Lilium sensor systems engineer Gilles Backhus, and Valerie Chan.
- On Jul 19, 2019, BMW announced that it is extending its partnership with NavInfo, a high-precision map producer. The company is also teaming up with Chinese internet giant Tencent to use big data to research and develop autonomous driving technologies.
- On Jan 23, 2020, BMW unveiled one of the strangest cars ever designed known as “BMW i Interaction EASE”. The car looks to be shaped like a rectangular block with absolutely no aerodynamics integrated into it. Although, its front and back end do have some aerodynamic contours. It showcased at CES as BMW said that it “offers a glimpse into a future where autonomous driving has become commonplace”.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In July 2021, BMW I Ventures, the venture capital division of BMW Group, introduced a fresh fund totaling $300 million to extend their investments in technologies that enhance the sustainability of transportation, manufacturing, and supply chains. The previous fund, Fund I, was primarily directed toward areas like autonomous and digital vehicle technology, enhancing customer experience, and advancing production methods. Notably, companies like Kodiak Robotics, which focused on autonomous trucks and recently received an investment from BMW i Ventures, were part of this initial fund. (Source)
- In July 2021, By implementing two track sections ahead of schedule, the BMW Group crafted testing scenarios for novel autonomous driving assistance systems. These involve exclusive trial sessions with prototypes on a dedicated six-kilometer motorway-style track. The track is anticipated to be fully operational by the summer of 2023. (Source)
2022
- In March 2022, As per the statement, Arriver, BMW, and Qualcomm united to collaboratively create a software stack tailored for level 2 Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and level 3 Autonomous Driving (AD). This initiative will bring together BMW’s level 2 AD stack, Arriver’s Vision Perception and NCAP Drive Policy, and Qualcomm’s Snapdragon Ride platform. The cooperative development draws upon the extensive research and development of the three firms spanning decades, involving over 1,400 engineers stationed across China, the Czech Republic, Germany, Romania, Sweden, and the United States. (Source)
2023
- On Jan 7, 2023, BMW revealed that the upcoming 7 Series G70 will feature a Level 3 self-driving system, scheduled for introduction later this year. Speaking at CES 2023 in Las Vegas during the unveiling the i Vision Dee concept, Chief Technology Officer Frank Weber confirmed that this functionality would be integrated into the company’s flagship model in 2023. He emphasized that this is an accurate Level 3 system, with the vehicle assuming control instead of the driver. Initially, the system’s operational speed will be electronically limited, but it is expected to increase over time progressively. (Source)
- Renowned for its high-speed stretches, the German Autobahn is a fitting arena for BMW’s advanced driver assistance system, known as Autobahn Assistant, which has secured the distinction of being the first approved in Germany. This approval, granted by the German Federal Motor Transport Authority, enables BMW to operate its Level 2 partially automated system at speeds of up to 130 km/h (81 mph) on this renowned roadway. BMW officially announced this milestone, highlighting the system’s capacity to function effectively at these elevated speeds within Germany. (Source)
- In Feb 2023, NavInfo disclosed the execution of a licensing agreement with BMW Group, under which NavInfo will supply ADAS maps, HD maps, LBS, and other offerings for BMW’s upcoming autonomous driving capabilities in the Chinese market. (Source)
- In May 2023, BMW provided additional insights into its upcoming electric i5 and the new 5-Series models, sharing information about a notable automation feature it claims as a “world first” – the ability to initiate lane changes through eye activation. Manufacturing of both the sedan and its electric counterpart will commence in Bavaria, Germany, during the summer, with the official launch of these vehicles planned for October. (Source)
- In Jul 2023, BMW’s progress in autonomous driving took a significant stride as they inaugurated a new Research and Development center in the Czech Republic. This center, known as the Future Mobility Development Centre (FMDC) in Sokolov, is pivotal in expediting BMW’s integration of self-driving vehicles. Located roughly three hours from Munich’s headquarters, this €300 million (£260m) endeavor underscores BMW’s substantial commitment. Spanning 600 hectares, the site offers ample space to simulate diverse driving scenarios, encompassing highways, cross-country routes, and urban settings. (Source)
- In Aug 2023, BMW and Innoviz collaborated on advanced technology integrating LiDAR for highly automated capabilities for several years, set to debut on the BMW 7 Series later this year. The partnership is now broadening, emphasizing the development of second-generation LiDAR technology through a B-sample phase. This phase involves incorporating the sample into demonstration vehicles as a step in the vehicle testing. (Source)
Honda
Honda is comparatively less vocal about autonomous cars. On the other hand, it has indeed taken strong steps towards testing and launching driverless cars. Honda has been roiling out semi-autonomous functionalities, comprising forward-collision warning, lane- departure warning, and lane-keeping assistance.
You might have seen these features in Honda Acuras and the Civic year 2016 models.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- In 2015, Honda received consent from California to test independent vehicles on public streets (with limitations on the number of vehicles and the testing methods). Honda is using the GoMentum Station proving ground, with 5,100 acres of a testing area for its self-driving fleet.
- In 2016, Honda launched a new Civic LX, priced at $20,440, Sedan with features such as automatic braking and cruise control. Honda Sensing technologies installed in Civic include Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) and Lane Keep Assist (LKAS) that help the car follow the vehicles ahead and keep itself in the correct lane.
- On January 03, 2018, Honda Motor announced its partnership with Alibaba Group Holding on developing services for connected cars. Now, a good number of automakers have already started working with Chinese internet conglomerates in hopes of making further inroads into the world’s largest auto market.
- On June 15, 2018, Honda Motor announced that it joined a consortium led by Chinese tech giant Baidu aimed at advancing autonomous driving technology, hoping to carve out a share as China races to become the world’s largest market for self-driving vehicles.
- On Oct 3, 2018, Honda Motor Co. Ltd. announced its investment of $2 billion and take a 5.7% stake in General Motors Co’s Cruise self-driving vehicle unit. The investment also extends the cooperation between the two automakers in a technology that has enormous costs and risks but no market-ready products.
- On Oct 8, 2018, Honda said to introduce, in a limited capacity, its “Smart Intersection” technology, that could help cut down on accidents that take place on cross paths. The company was also working on launching a test run of the technology in the city of Marysville, Ohio, as part of its 33 Smart Mobility Corridor project.
- On December 18, 2018, Honda stated that it has been testing prototypes in search and rescue, firefighting, construction, agriculture, landscaping, and snow removal applications, and is looking for partners to come on board to further the technology.
- On Oct 30, 2019, Honda and Hitachi announced to merge their four car parts businesses to create a components supplier with more than $17 billion in sales. Honda and Hitachi said Wednesday they will combine Hitachi Automotive Systems and Honda affiliates Keihin Corp., Showa Corp., and Nissin Kogyo Co. Following a tender offer and an interim step, Hitachi will own two-thirds of the new entity, with Honda owning the rest, the companies said.
- On Jan 4, 2020, Honda said it is preparing to be the first Japanese automaker to launch a Level 3 autonomous vehicle. Honda is expected to offer Level3 capabilities only in slow traffic on congested expressways.
- On Apr 2, 2020, Honda announced a deal with Cruise, a GM subsidiary, to jointly develop a purpose-built electric driverless vehicle. GM also announced that it would spend $2.2 billion to refurbish its Detroit-Hamtramck plant to produce driverless and electric vehicles. The Honda vehicles are likely to be built in that plant.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In March 2021, Honda revealed that its luxury sedan, the “Legend,” has achieved a significant milestone by becoming the world’s inaugural passenger vehicle furnished with “level-3 autonomous driving technology.” With this pioneering advancement, Honda seeks to strengthen its standing in the automotive realm. A noteworthy aspect of the Legend is its capacity to activate its self-driving system while navigating through congested traffic on expressways. (Source)
- In April 2021, Honda China collaborated with AutoX to advance autonomous driving research within China. Under this partnership, Honda will supply AutoX with test vehicles, including Accord and Inspire models. The primary objective of this endeavor, as outlined by the Japanese automaker, is to enhance its comprehension of China’s complex traffic conditions. Additionally, Honda aims to foster wider public acceptance and ensure the safety of autonomous driving technology within the region. (Source)
- In Sep 2021, Honda announced it would initiate public tests in Utsunomiya City and Haga Town, Tochigi Prefecture, in 2022. This marks the initial phase of Honda’s venture towards establishing an autonomous vehicle mobility service (MaaS) business in Japan. To pave the way, a high-definition map of the region will be created using specially modified Chevrolet Bolt vehicles. Following map completion, Honda will deploy its autonomous vehicles for on-road testing, simulating real-world situations such as congested traffic and challenging road and weather conditions. (Source)
- In Nov 2021, Honda revealed its path for advancing its advanced safety technology suite, aiming to reduce traffic fatalities involving its vehicles by half worldwide by 2030 and eliminate them by 2040. The initial phase focuses on artificial intelligence (AI) systems that monitor the road and the driver. To comprehend the origins of driving mistakes, Honda employs fMRI technology to study the driver’s brain and assess risk-taking behaviors. (Source)
2022
- In Apr 2022, Honda Mobility Solutions announced the signing of a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with two transportation service providers in Japan: Teito Motor Transportation Co., Ltd. (Teito) and Kokusai Motorcars Co., Ltd. (km Group). This MoU aims to initiate specific discussions regarding the future of Japan’s Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) business. The objective is to launch an autonomous vehicle mobility service in central Tokyo by the mid-2020s. As part of this endeavor, HMS will collaborate with the two companies on various aspects, including legal considerations, service design, and defining roles and responsibilities among the partners. (Source)
- In Nov 2022, By the close of this decade, Honda is set to introduce its hands-free highway driver-assist technology to the United States, thus joining the ranks of automakers providing customers with partially automated driving technology. Honda’s Level 2 advanced driver-assist system (ADAS), known as Honda Sensing, is currently accessible to vehicle owners who can equip their cars with this feature. Building upon this, two enhanced systems, namely Honda Sensing 360 and Honda Sensing Elite, will incorporate novel functionalities attributed to enhanced sensors and advanced AI software crafted by Honda. (Source)
- On Dec 9, 2022, Honda introduced their new advancement in autonomous driving known as “Sensing 360.” Set for a global launch in 2024, this technology suite from Honda will encompass features for assisted driving. These include expanded capabilities like autonomous emergency braking with cross-traffic and pedestrian detection, front cross-traffic alert, active lane-change assist (integrated with blind-spot monitoring), and lane-change collision mitigation (complementing blind-spot assistance). (Source)
2023
- At the CONEXPO-CON/AGG 2023 event in Las Vegas from March 14-18, 2023, Honda will demonstrate the enhanced features of its latest prototype, the Honda Autonomous Work Vehicle (AWV). This presentation aims to enhance operational efficiency within the construction industry and worksites. Interested construction organizations will be provided insights on potential field testing of this robust off-road platform at their respective worksites. (Source)
Toyota
Earlier Toyota was reluctant to launch an autonomous car; however, since Mid-2016 it took a completely different approach to the autonomous vehicle. It now spends nearly $10 billion a year on researching autonomous vehicle technology.
Toyota plans to launch a highly autonomous vehicle by 2021.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On Mar 2, 2018, Toyota announced a new company called Toyota Research Institute-Advanced Development, or TRI-AD for pursuing its self-driving car goals. The company will be formed in conjunction with automotive suppliers Aisin Seiki and Denso. They also planned to invest $2.8 billion into TRI-AD in the upcoming years and hire around 1,000 employees in order to develop software systems to powerfully self-driving vehicles.
- On April 12, 2018, the truck divisions of Toyota and Volkswagen agreed to work together in electric vehicles and self-driving technology. As per the agreement, Hino Motors and Volkswagen Truck & Bus GmbH will co-operate in procurement and logistics in addition to hybrid engines, connectivity, and other technologies.
- On June 13, 2018, Toyota Motor Corp announced that it agreed to buy a $1 billion stake in Southeast Asia’s Grab. This would make the biggest investment by a carmaker into a ride-hailing firm. The deal comes as the auto industry faces a spike in the need for technological prowess with the advent of features such as autonomous driving, while app makers offer passengers the option to forgo car purchases by connecting them with drivers.
- On October 4, 2018, Toyota and SoftBank formed a joint venture to use autonomous vehicles for providing services. The business, which will be called Monet Technologies Corp, will start with 2bn yen (£13.5m) offering the Japanese market ride-hailing services for public agencies and private companies, before looking to go global.
- On Dec 13, 2018, Toyota AI Ventures contributed to Parallel Domain’s $2.65 million seed round led by Costanoa Ventures, with participation from Ubiquity Ventures and others.
- On March 19, 2019, Toyota Research Institute-Advanced Development (TRI-AD) announced a new collaboration with NVIDIA to develop, train, and validate self-driving vehicles. The partnership builds on an ongoing relationship with Toyota to utilize the NVIDIA DRIVE AGX Xavier AV computer and is based on close development between teams from NVIDIA, TRI-AD in Japan, and Toyota Research Institute (TRI) in the United States.
- On May 2, 2019, Toyota announced a $100 million venture funding to invest in autonomous driving and robotic technology start-ups as automakers increasingly push into the self-driving market.
- On May 30, 2019, Toyota Research Institute-Advanced Development Inc. (TRI-AD) and joined forces with Carmera Inc. to conduct a proof of concept about developing camera-based automation of high-definition (HD) maps for urban and surface roads.
- On July 24, 2019, Toyota made a new investment of $600 million in DiDi Chuxing to set up a joint venture to provide Toyota vehicle-related services to drivers on Didi’s ride-sharing platform.
- On Jul 16, 2019, Toyota Motor Europe (TME) announced the beginning of autonomous driving (AD) on public roads in Europe. After successful simulations and trials on closed circuits, TME is testing its in-house developed autonomous driving technology in the city center of Brussels, Belgium. The tests will include a modified Lexus LS sedan navigating a fixed loop in the city over the next 13 months.
- On July 10, 2019, Toyota Motor Corp and auto-parts maker Denso Corp agreed to set up a joint venture to develop next-generation automotive semiconductors. As the industry moves toward connected and autonomous vehicles, the venture will help in focusing on components such as power modules for electric vehicles and periphery monitoring sensors for automated vehicles.
- On Aug 27, 2019, Toyota announced its partnership with Chinese startup Pony.ai to conduct its first self-driving tests on public streets in China. Lexus SUVs equipped with Pony.ai’s autonomous driving system will travel to Beijing and Shanghai.
- On Aug 28, 2019, Toyota announced its partnership with Suzuki on self-driving technology. Toyota will own a 4.9% stake in Suzuki with a $96 billion valuation. In turn, Suzuki will invest $48 billion in Toyota. As per the agreement, the two companies are cooperating in the Indian market and expand their collaboration.
- On Dec 4, 2019, Toyota invested $50 million yet in another autonomous startup known as May Mobility, a Michigan-based startup that operates autonomous shuttle services in three US cities.
- On Mar 11, 2020, Toyota Research Institute-Advanced Development, Inc. (“TRI-AD”) announced new results from its ongoing partnership with CARMERA Inc. A follow-up to the companies’ successful camera-based mapping work in Tokyo, this latest phase used commercially available dashboard-mounted cameras to detect key road features with the relative accuracy performance necessary for automated driving.
- On December 20, 2019, Toyota said that it plans to introduce its advanced autonomous driving technology on commercial vehicles before passenger cars. It also said that the company still needs time to improve its Level 4 “mind off” driving system for personal cars.
- On Mar 18, 2020, Toyota partnered with Momenta, a Chinese autonomous driving startup, to develop a high-definition mapping platform in China for self-driving vehicles.
- On Mar 24, 2020, Toyota Research Institute announced that it is working with TomTom and Denso to build high-definition maps to improve the development and implementation of autonomous vehicle technology. The companies are combining Denso sensor technology with TRI’s automated mapping platform and TomTom’s cloud-based mapping platform. Vehicle sensors are used to collect road observations, which are converted and corrected by TRI’s system for input into TomTom’s platform.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Feb 2021, Aurora established an agreement with Toyota and auto-parts provider Denso to collaborate on developing and testing vehicles incorporating the self-driving startup’s technology. This partnership will kick off with a series of Toyota Sienna minivans. Joint engineering efforts between Aurora and Toyota will be devoted to creating and constructing these self-driving Sienna minivans to commence testing with a fleet by the conclusion of 2021. (Source)
- In Apr 2021, Toyota Motor Corp announced to purchase of Lyft’s self-driving technology division for $550 million. This move is part of Toyota’s increased focus on automation through its newly established Woven Planet division. Acquiring Level 5 automation capabilities will bolster Toyota’s automation goals and grant the company access to Lyft’s pool of over 300 employees specializing in advanced autonomy technology. (Source)
- In Apr 2021, Apex.AI, a developer of software systems, revealed a collaboration with Woven Planet, a subsidiary of Toyota. This partnership aims to assist in creating and implementing a production-ready autonomous technology stack. Utilizing Apex.OS, Woven Planet will integrate it into Arene, Toyota’s vehicle development platform. This incorporation will facilitate the application of contemporary software development tools and industry-best practices within the automotive sector. (Source)
- In Apr 2021, In Japan, Toyota Motor Corp. introduced upgraded versions of the Lexus LS and Toyota Mirai, incorporating advanced driver-assistance technology. Toyota representatives in the US informed Autoweek that the 2022 LS 500h AWD equipped with Advanced Drive, as the system is named, is anticipated to be available at dealerships in the autumn. The Advanced Drive system offers Level 2 autonomous capabilities, contributing to lane keeping, maintaining safe following distances, and aiding with lane changes. In Level 2, the driver remains responsible for monitoring the road, gripping the steering wheel most of the time, and being prepared to regain control promptly. (Source)
- In Jul 2021, Toyota announced its acquisition of Carmera, a U.S.-based company specializing in maps and data for autonomous vehicles. This move underscores Toyota’s ongoing commitment to advancing its autonomous technology portfolio, coinciding with the competition between traditional automakers and tech giants like Apple and Amazon in the autonomous realm. The acquisition, facilitated through the newly formed subsidiary Woven Planet, was carried out for an undisclosed amount.
- Through this acquisition, Toyota gains access to real-time, high-definition maps and crowdsourced data crucial for self-driving vehicles to navigate and determine their location effectively. The collaboration between the two companies began in 2018 and has led to various projects, including technology to update high-definition maps with accurate details of repainted lane markings. (Source)
- In Sep 2021, Toyota acquired automotive operating system software company Renovo to help accelerate the development of fully autonomous connected vehicles. (Source)
2022
- In Apr 2022, Taking a cue from Tesla Inc., Toyota Motor Corp’s division Woven Planet strives to propel self-driving technology forward using cost-effective cameras. According to Reuters, Woven Planet shared that it has successfully harnessed cameras to gather data and efficiently train its self-driving system—a noteworthy “breakthrough.” This achievement is anticipated to contribute to cost reduction and the expansion of the technology on a larger scale. (Source)
2023
- In May 2023, Komatsu and Toyota are excited to introduce a collaborative initiative to create an Autonomous Light Vehicle (ALV) to operate within Komatsu’s Autonomous Haulage System (AHS). This partnership seeks to enhance safety and productivity in mining operations by combining autonomous haul trucks and automated ALVs governed by AHS. To advance these technologies, both companies are presently conducting trials with the concept ALV at their respective testing grounds. Their shared goal is to achieve a proof of concept at a customer site by approximately January 2024. (Source)
Mercedes Benz (Daimler)
Like its competitors, Mercedes has also begun to take significant steps toward self-driving cars during the last couple of years. Mercedes started deploying semi-automated advanced driver assistance systems to many of its newer models.
Mercedes faced challenges when it tried to market its new E-class sedan as a self-driving car in its new 2017 advertisement. The company had to pull the ad due to pressure from consumer groups claiming the ad overstated the vehicle’s capabilities.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On June 7, 2018, Daimler’s trucks division set up a research and development center for autonomous driving in the United States. The recent move of the German manufacturer’s commitment to getting self-driving trucks on the road.
- On July 6, 2018, Daimler received the green light to start testing highly automated vehicles on public roads in China. It is the first international automaker to receive approval and the company is all starting to test in Beijing.
- On September 10, 2018, Daimler AG developed an autonomous electric vehicle that can toggle between a people carrier and a delivery van as the German manufacturer seeks an edge over rivals such as Alphabet Inc.’s Waymo and Deutsche Post AG in shaping the future of mobility.
- On October 3, 2018, Renault-Nissan Chief Executive Carlos Ghosn told a news conference in Paris that the company may expand its cooperation with Daimler for battery, autonomous cars technology, and mobility services. It could be an advantage for the companies to pursue different avenues of battery research and to pool their findings as the industry seeks better battery chemistry for electric cars.
- On October 24, 2018, Germany’s Daimler announced to set up a ride-hailing joint venture in China with Geely Group. The partnership was a sign that the Chinese firm is making progress in its drive for closer relations with the maker of Mercedes-Benz cars. The possibility of autonomous cars hitting the road has intensified competition between technology companies, ride-hailing firms, and traditional carmakers to roll out fleets of smartphone-hailed taxis, or strike cooperation deals.
- On March 29, 2019, Daimler Trucks agreed to buy a majority stake in Torc Robotics, a self-driving truck software maker, as part of a broader push to develop autonomous vehicles. Torc Robotics can help Daimler accelerate software development by giving the German manufacturer access to 120 skilled staff, Daimler Trucks CEO Martin Daum said.
- On May 31, 2019, Daimler Trucks formed a global autonomous driving group, i.e. Autonomous Technology Group (ATG), to help reach its goal of having autonomous trucks on US roads by 2020.
- On July 08, 2019, Two German giants – BMW Group and Daimler AG – joined forces in developing autonomous driving technologies. The representative of the two companies planned a collaboration earlier this year and now an official agreement for long-term strategic cooperation has been signed.
- On Jul 23, 2019, Daimler, the parent company of Mercedes-Benz, and Bosch, a global auto supplier, announced that they received approval from local authorities in Stuttgart, Germany, to test an autonomous parking valet system. The testing will take place in the Mercedes-Benz Museum parking garage, which has been fitted with sensors to guide and monitor the vehicles as they park themselves autonomously.
- On Mar 10, 2020, Mercedes announced that it shifted its approach to self-driving vehicles. The company said it would be focused on electric vehicles and autonomous trucks rather than self-driving cars.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In July 2021, The 2022 Mercedes-Benz EQS electric sedan was a tech marvel. Soon, in Germany, testing starts for Drive Pilot self-driving. It’s Level 3, adept at road shifts like avoiding slow traffic. But drivers must stay vigilant. The aim is to bring this hands-free driving to the U.S. in under two years. (Source)
- In July 2021, Mercedes-Benz’s subsidiary, Daimler Greater China Ltd., partnered with Tencent Cloud Computing Beijing Ltd. to advance high-level autonomous driving. They’ll leverage cloud computing, AI, and big data to accelerate the testing and application of Mercedes-Benz’s self-driving tech. This collaboration boosts R&D efforts, aiding the joint development of self-driving cars by Mercedes-Benz and Nvidia in China. A shared autonomous driving lab will be set up, expediting research and development for the Chinese market. (Source)
- On Dec 11, 2021, Mercedes-Benz achieved a significant milestone as the first automotive company globally to fulfill the prerequisites for approving a Level 3 autonomous driving system. This recognition comes from UN-R157, a United Nations regulatory body establishing the Level 3 autonomous vehicle driving standard. The luxury automaker revealed that their driving technology, DRIVE PILOT, will be accessible in S-Class and EQS models during the first half of 2022. (Source)
2022
- In May 2022, Mercedes-Benz commenced selling its Drive Pilot system in Germany. This SAE Level 3 autonomous technology is available for the S-Class and electric EQS models. The German Federal Motor Transport Authority (KBA) approved Level 3 autonomy in December 2021. This endorsement permits Drive Pilot to manage driving in specific zones and speeds of up to 60 km/h (around 37 mph), with a driver present and ready to resume control when needed. (Source)
- In May 2022, Mercedes-Benz announced the inauguration of a research and development (R&D) center in Shanghai. This facility, its second in China, will concentrate on mobility technology. As per the company’s statement, the center’s scope encompasses connectivity, automated driving, and big data within the tech domain. (Source)
- In Jul 2022, Mercedes-Benz announced the plans to file the necessary documentation to obtain Level 3 hands-off autonomous driving certification for select upscale vehicles in the U.S. If the process goes smoothly, drivers of the S-Class or EQS electric sedan equipped with Drive Pilot Level 3 might be legally allowed to read emails or watch movies in specific states by mid-2023. Having secured international Level 3 autonomy certification in Germany in late 2021, Mercedes-Benz was the global pioneer in achieving this distinction. The technology is now accessible on their flagship sedans. (Source)
2023
- In Jun 2023, The California Department of Motor Vehicles approved Mercedes-Benz’s automated driving system on designated highways under certain conditions without the active control of a driver. According to Reuters calculations, California is one of Tesla’s largest markets, accounting for 16% of the carmaker’s global deliveries last year. But the German carmaker beat Tesla to become the first carmaker to receive authorization to sell or lease cars with an automated driving system to the public in California. The approval was granted to the Level 3 Mercedes-Benz “Drive Pilot” system that allows a driver to take their eyes off the wheel legally but must be available to resume control in need. (Source)
- In Jul 2023, Mercedes-Benz announced that it is modifying its Automatic Lane Change (ALC) feature for European deployment, aligning with SAE-Level 2 standards. The ALC function is already integrated into models like C-Class, E-Class, and S-Class, as well as all EQ series vehicles available in the US and Canada. (Source)
Volkswagen
In September 2015, Volkswagen was summoned by the United States Environmental Protection Agency for cheating on emissions tests to certify diesel vehicles around the world.
Volkswagen admitted to the scandal and agreed to recall all the vehicles in question. The cost of fines and recalling vehicles was estimated at well over $20 Billion. Post this serious setback, the company has shifted its focus towards autonomous cars. Volkswagen already showcased a prototype of its first driverless car in 2017.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- At CES 2018, NVIDIA announced autonomous vehicle partnerships with Volkswagen. it comes after NVIDIA’s announcement that it will be making Xavier, the AI chip made for self-driving vehicles it announced in 2016, available to customers. Volkswagen will use the technology to bring to life their previously announced I.D. buzz electric bus, combining the look of a vintage VW van and the future of driverless cars.
- On January 5, 2018, Volkswagen joined forces with Aurora, the Silicon Valley company headed by Google’s former self-driving chief Chris Urmson, to research and develop autonomous cars. The deal will also help the automaker offering the technology from Aurora to help adapt to a self-driving future.
- On April 13, 2018, as part of a pilot project, Volkswagen, Audi, and Porsche vehicles tested for autonomous parking within a multi-story car park near Hamburg Airport’s terminal.
- On May 2, 2018, Chinese ride-hailing giant Didi Chuxing approached an agreement with Volkswagen (VW) to deploy a “purpose-built” fleet of VW vehicles in its home country. The deal would help Didi quickly scale up its autonomous driving technologies and maximize their revenue-generating potential. The ride-hailing behemoth — it counts over 400 million users — has been working on autonomous driving technologies for at least the last two years.
- On May 24, 2018, Apple reportedly signed a deal with Volkswagen to make self-driving vehicles. At present, the agreement is believed to center on Volkswagen’s T6 transporters, which Apple plans to adapt into self-driving shuttles for employees on its campus – the so-called Palo Alto Infinite Loop (PAIL) – but it has the potential to expand into a wider collaboration.
- On June 11, 2018, IOTA and Volkswagen demonstrated a Proof of Concept (POC) using IOTA’s Tangle for interconnected vehicles. IOTA’s Tangle is a sophisticated form of blockchain, a DAG, without blocks or miners, designed specifically for machine-to-machine communication. A Tangle has both suitable infrastructure for microtransactions and improved scalability which are vital for autonomous vehicles.
- On August 29, 2018, Volkswagen Group acquired a minority stake in eastern German software startup FDTech, in a bid to strengthen its expertise in autonomous driving technologies.
- On Nov 5, 2018, The Volkswagen Group, Intel’s Mobileye, and Champion Motors announced a joint venture called New Mobility in Israel to deploy Israel’s first self-driving ride-hailing service in 2019.
- On November 16, 2018, Volkswagen Group announced it will spend 44 billion euros ($50.2 billion) on electric vehicles, digitalization, autonomous driving, and new mobility services by 2023. The automaker also plans to increase the productivity of its factories by 30 percent by 2025, by building more vehicles with different brands on the same production line.
- On May 28, 2019, Volkswagen revealed that it has set scientists in Wolfsburg, Germany, on the task of studying motion sickness in autonomous cars and developing anti-puke solutions.
- On May 31, 2019, The German automaker signed an agreement with JAC and the Hefei city government Barcelona, Spain. As a part of the agreement, Volkswagen planned to roll out autonomous vehicles and offer mobility services such as ride-hailing and short-term rental in Hefei with local partner Jianghuai Automobile.
- On Jun 11, 2019, Volkswagen Group ended the partnership with Aurora Innovation, the autonomy startup founded by former Google self-driving head Chris Urmson.
- On Jul 12, 2019, As part of the deal, VW announced an investment of $2.6 billion in Argo AI, the autonomous vehicle startup based in Pittsburgh which also got the investment of an eye-popping $1 billion from Ford. Besides, Ford and Volkswagen also announced their plan to expand their seven-month-old alliance to include autonomous and electric vehicles.
- On July 15, 2019, Volkswagen autonomous driving executive, Alexander Hitzinger revealed that the company will launch small fleets of autonomous vehicles “in the near future.” The executive also suggested these fleets will be limited in scope as legal, economic, and technological challenges that need to be solved. So, the company can launch a “large-scale deployment” of autonomous production models.
- On Aug 5, 2019, Electrify America, a subsidiary of Volkswagen Group of America, said that it will work with fleet charging firm Stable Auto to roll out robotic fast charging systems for self-driving electric vehicles (EVs).
- On Oct 28, 2019, Volkswagen Group announced the creation of a subsidiary called Volkswagen Autonomy (VWAT) with a plan to “make autonomous driving market-ready.”
- On Dec 15, 2019, Volkswagen Group and Qatar agreed to develop a public transit system of autonomous shuttles and buses by 2022 for the capital city of Doha. The agreement signed Saturday by VW Group and the Qatar Investment Authority is an expansive project that will involve four brands under VW Group, including Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles, Scania, its shared ride service MOIA and Audi subsidiary Autonomous Intelligent Driving, or AID.
- On Dec 11, 2019, Volkswagen made a significant investment in Aeva, startup research on vision sensors for driverless cars. The Silicon Valley-based group, founded in 2017 and with 80 employees, claims to have invented a new kind of lidar — light detection and ranging sensor — that manages to be small and low cost, yet is high performing and consumes little power.
Post-COVID Activities
- In Oct 2022, it Shut down its AV Project. (Source)
Kia-Hyundai
Kia, an affiliate of Hyundai Motors, aims to launch a fully autonomous vehicle by 2030. On the other hand, Hyundai is exploring the market differently from the other players. It is trying to build technology that will be reasonable for a good portion of car buyers.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On May 21, 2018, Hyundai Mobis outlined its plans to become a leader in innovative vehicle technologies. The company has set a goal of releasing fully operational autonomous driving sensors, pivotal to the successful operation of autonomous vehicles by 2020.
- On Feb 18, 2018, Hyundai demoed Level-4 autonomous driving with a fleet of fuel cell electric cars across a distance of 190km. The manufacturer’s electric units were driven from Seoul to Pyeongchang in South Korea.
- On February 28, 2019, Hyundai planned to invest 45.3 trillion won ($40 billion) in the development of new models and technologies for electrified and autonomous vehicles as well as transportation services for the next five years.
- On October 10, 2018, Mobis Technical Centre, India (HMTCI), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Hyundai Mobis of South Korea, announced its collaboration with Tata Elxsi for the development of Synthetic Scene Generator Tool. HMTCI and Tata Elxsi are working on developing a tool that can replicate every real-world scenario an automobile could encounter. This tool would help accelerate the ongoing research and development support HMTCI is providing to its OEMs in Autonomous Driving.
- On November 5, 2018, Hyundai announced a strategic investment in Allegro.ai, a start-up focused on developing deep learning technologies for our future cars. The South Korean-based firm said its interest in Allegro.ai is based in the firm’s deep learning technologies used for computer vision in self-driving vehicles.
- On November 5, 2018, Tech giant Samsung Electronics, automaker Hyundai Motor, and telecommunications company KT announced that they will jointly showcase autonomous driving technology running on the 5G network later this month. The three conglomerates will demonstrate autonomous vehicles running on the next-generation network in an event to celebrate the opening of K-City, a self-driving vehicle testing and research facility in Hwaseong City, Gyeonggi Province, in late November.
- On December 4, 2018, Hyundai MnSoft, a Hyundai Motor Group subsidiary specializing in location-based services (LBS), got partnered with, Netradyne, an AI technology to focus on driver and fleet safety, for cloud-based connected navigation software and future high definition (HD) maps for autonomous vehicles.
- On April 1, 2019, Hyundai Mobis Co appointed Gregory Baratoff and Carsten Weiss as heads of its Autonomous Vehicles System Development Center and IVI (in-vehicle infotainment) System Development Center, respectively. This is the first time the Korean automaker gave the opportunity to non-Korean experts as R&D heads, breaking its long tradition of placing only Koreans at the control tower to stay competitive in the race for future mobility technologies.
- On April 6, 2019, Hyundai Motor Co and Chinese technology firm Tencent Holdings announced their plan to conduct joint research and development on safety and security systems for self-driving cars, which Hyundai seeks to roll out commercially by 2030.
- On June 13, 2019, Hyundai Motor Group announced that it’s expanding its partnership with the Silicon Valley self-driving start-up, Aurora, by investing more money to develop autonomous cars. Hyundai and Kia are joining Aurora’s series B financing round. Aurora declined to disclose the amount of Hyundai’s investment but said the round has now raised more than $600m, including $530m originally announced in February.
- On July 2, 2019, Hyundai Autron, a Hyundai Motor Group company, and Wind River signed a partnership to develop an autonomous driving and connectivity software platform to power next-generation automobiles. The partnership will leverage each company’s specialties and experiences to develop a best-in-class software platform for functional safety and Adaptive AUTOSAR for next-generation autonomous driving and connectivity for the global market.
- On July 11, 2019, Hyundai Motor Co. said that it moved up the start of its volume production of autonomous vehicles to 2024, around the time when Mercedes, BMW, and other global automakers are expected to begin mass production of self-driving cars. Hyundai Motor plans to introduce sophisticated autonomous driving technology that can be used on all courses, not autonomous driving which can be used only on simple courses based on current deep learning technology.
- On July 11, 2019, Russian tech giant Yandex inked a deal with Hyundai to build self-driving car tech for the latter’s Mobis division, marking the company’s first official partnership with an automaker. This morning, Yandex revealed the fruit of its labor with an autonomous Hyundai 2020 Sonata that is launching this fall with Yandex’s software and sensor suite.
- On July 16, 2019, according to local reports in South Korea, Hyundai Motor said it plans to begin trials of an autonomous taxi fleet in Russia later this year. The Korean automaker is working with the Russian internet search engine company Yandex, which has been testing autonomous vehicles on public roads in Russia since 2017.
- On July 22, 2019, Using high-performance small digital cameras, Hyundai Mobis, a parts-making unit of South Korea’s Hyundai auto group, developed a camera monitoring system that would be used widely for mirrorless next-generation and self-driving vehicles.
- On July 30, 2019, Hyundai Autron and Wind River® signed a partnership to develop an autonomous driving and connectivity software platform to power next-generation automobiles. A signing ceremony was conducted at Wind River headquarters in Alameda, California.
- On Oct 22, 2019, KT and Hyundai announced that they tested their real-time traffic navigation technology on 5G networks for autonomous cars. Two Hyundai arms, i.e. Hyundai Mobis and Hyundai Mnsoft – worked with KT Telecom to conduct the test. The real-time traffic navigation technology that was being trialed sends traffic data collected by cars to a server. The server then updates the map used by cars in real-time with the data collected, and then sends that information to other cars for safety. To test the speed and accuracy of the map updates, KT and Hyundai deployed three cars, dubbed M-Billy, for the trial.
- On Oct 25, 2019, Hyundai announced that it will launch a free ride-hailing service with a fleet of autonomous electric cars in Irvine, California, starting on November 4th.
- On Nov 7, 2019, Hyundai said that it selected Blackberry QNX to power its next-gen advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving software platform.
- On Nov 13, 2019, Hyundai announced that it successfully conducted its first autonomous truck platooning demonstration on the country’s Yeoju Smart Highway replicating real-world traffic conditions.
- On Nov 22, 2019, Hyundai signed a memorandum of understanding with Seoul City in order to develop downtown self-driving technology in Gangnam. As per the MOU, the city is planning to provide Hyundai with traffic signals and road infrastructures essential for autonomous driving. Hyundai will test six such cars on 23 roads in Gangnam starting from next month. The cars are hydrogen-electric vehicles and 15 are scheduled to be tested in 2021.
- On Dec 4, 2019, Hyundai announced that it will spend 20 trillion won ($17 billion) over the next six years on new technology to help make the switch to electric and autonomous vehicles. Announcing its strategic plan to 2025, Hyundai planned to spend almost half the new money on electrification whereas Autonomous driving will soak up 1.6 trillion won of the total.
- In 2019, Hyundai and Kia Motors recorded a new high in annual R&D investment. The two automakers’ R&D spent a total of 4,807 billion won, 3,038.9 billion won from Hyundai Motor and 1,768.1 billion won from Kia Motors. The amount increased a record 9.0 percent from 4,407.3 billion won in 2018.
- On Mar 30, 2020, Hyundai announced that it formed a 50/50 autonomous driving joint venture with Aptiv to develop advanced driving technologies and solutions. The collaboration will leverage Hyundai’s design, engineering, and manufacturing expertise and Aptiv’s autonomous driving technologies. Under the new company, the two aim to commercialize an autonomous driving platform suitable for robotaxi providers, fleet operators, and automotive manufacturers.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Jun 2021, Hyundai announced that it gained a majority share in the renowned robotics company Boston Dynamics. Despite earlier reports, the acquisition was awaiting regulatory approval, which has now been granted.
The acquisition would help develop future technologies, including autonomous driving, artificial intelligence (AI), Urban Air Mobility (UAM), smart factories, and robots. (Source)
- In Jul 2021, Hyundai Motor launched an autonomous, on-demand shuttle service in South Korea. The initial route spans 6.1 km in Sejong Smart City, accessible through the ‘Shucle’ app. Passengers can request rides at 20 stops. Expansion plans include introducing the service to additional regions, including the Hyundai Motor and Kia Namyang Research and Development Center, during the latter part of this year. (Source)
2022
- In April 2022, Hyundai broadened its collaboration with IonQ to leverage Quantum computers for object detection in self-driving endeavors. This novel initiative taps into Quantum computing’s capabilities to execute machine learning algorithms for image classification and 3D object comprehension to advance future vehicle technologies.
Computer vision, rooted in object detection and image classification, underpins self-driving and ADAS innovations. IonQ and Hyundai seek to elevate computational prowess and training efficiency in their machine-learning algorithms through Quantum computers, which outperform traditional methods in speed and accuracy.
A significant breakthrough lies in encoding images into a quantum state, a feat already demonstrated by IonQ, which has classified 43 road sign types utilizing Quantum computers. Hyundai will apply this machine learning data to their testing environment, simulating diverse real-world scenarios. (Source)
- In May 2022, Hyundai announced its intention to allocate over $10 billion to accelerate the advancement of electrification and autonomous vehicle technology in the United States by 2025.
A significant portion of this sum, including Hyundai’s commitment of $5.5 billion, will be directed to establishing an electric vehicle manufacturing facility and battery plant in Georgia. The participation of independent suppliers adds an additional $1 billion to the project’s total cost, resulting in a $6.5 billion investment.
The remaining $4.5 billion of Hyundai’s U.S. investment will be channeled into what the company deems “key future businesses.” These include robotics, AI technologies, advanced air mobility, and autonomous driving capabilities. Hyundai noted that these funds will be utilized through joint ventures and subsidiary collaborations. (Source)
- In Aug 2022, Hyundai invested approximately $308.19 million to bolster its ownership in a local startup named 42dot Inc., which specializes in autonomous driving tech. At that time, Hyundai and its subsidiary Kia Motors together held a 20.4% stake in the startup. The investment aligned with Hyundai and Kia’s focus on self-driving technology. Hyundai’s ambitious plan includes launching over 31 electric vehicles by 2030, aiming for a 12% global electric vehicle market share. Most of these cars will feature a broad range of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and self-driving capabilities. (Source)
- In Sep 2022, Hyundai announced that it has chosen TomTom its maps and real-time traffic data have been chosen by Hyundai Motor Group (HMG) to support its entire vehicle lineup in Europe. Over the coming years, millions of HMG vehicles will be equipped with this standard technology. As was already the case for Genesis drivers, all Hyundai and Kia customers in Europe will now enjoy TomTom’s high-quality maps supporting their vehicles’ in-dash navigation and level-two automated driving features. (Source)
- In Oct 2022, Hyundai Motor Group unveiled a global strategy to transition all vehicles to Software Defined Vehicles (SDVs) by 2025. This revolutionary plan, introduced during the Unlock the Software Age forum, promises an era of mobility where customers can enhance their vehicles’ performance and features remotely.
The Group’s vision extends to transforming the entire customer experience over a vehicle’s lifespan, embracing evolving software technology to usher in a new mobility era.
Hyundai Motor Group’s dynamic mobility and software tech will ensure continuous updates for all models, even those already owned. This approach enables upgrades to safety, convenience, connectivity, security, and driving performance through Over-The-Air (OTA) software updates. Leveraging the next-gen EV platform, integrated controller, and an in-house developed Connected Car Operating System (ccOS), all Group vehicles will be OTA-ready by 2025. (Source)
- In Oct 2022, Hyundai announced that by 2028, Hyundai aims to integrate hydrogen fuel cell technology into its commercial vehicles. Teaming up with WeRide, a highly funded Chinese robotaxi operator, Hyundai plans to establish self-driving hydrogen-powered vehicle pilot zones in Guangzhou. This city has emerged as a prominent self-driving hub in China over the past few years. (Source)
- In Nov 2022, Hyundai and Kia announced their plans to expand a self-driving ride-hailing pilot service in Seoul’s Gangnam district. This expansion is aimed at enhancing their comprehensive self-driving technology. Working together with Kakao Mobility Corp., the pilot RoboRide autonomous service will see the inclusion of more vehicles and the introduction of new services linked to the Kakao T platform. RoboRide offers passengers Level 4 autonomous vehicle-driven mobility, enhancing convenience. To achieve this goal, Hyundai and Kia will also gather additional urban self-driving data while validating the platform to ensure more dependable self-driving services. (Source)
2023
- In Jan 2023, Hyundai announced that it and Kia intend to introduce vehicles equipped with Level 3 autonomous driving technology this year, as indicated in a New Year’s message from Hyundai Motor. The upcoming Genesis G90 sedan and Kia’s EV9 will feature a highway-driving pilot, enabling Level 3 self-driving capability. If the timeline proceeds without issues, these models will mark Korea’s debut of this advanced automobile feature. (Source)
- In Apr 2023, Kia unveiled the EV9, a three-row electric SUV set to debut later this year. It features Level 3 “hands-off” automation using its Highway Drive Pilot (HDP) technology on specific road sections. The company announced plans to enhance this feature in 2024 through over-the-air (OTA) updates. These updates will enable higher autonomous driving speeds and expand the range of recognized roads, offering greater “eye-off,” hands-free capabilities. (Source)
Jaguar – Land Rover
In October 2015, JLR launched a new £11 million research program in collaboration with the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) for the development of autonomous and connected vehicle technology. This research will take place at ten UK universities and the Transport Research Laboratory. Jaguar Land Rover also joined a $7.9M UK program for further autonomous driving R&D, aiming to gather data on driving habits and test vehicle communications technology. This project is led by a German-based Robert Bosch Group.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On June 12, 2017, The UK-automaker Jaguar Land Rover invested $25 million in Lyft to support the ride-hail company’s autonomous and connected vehicle activities. The money was invested through InMotion, Jaguar Land Rover’s mobility services subsidiary, and was included in Lyft’s latest round of fundraising, which ended in April 2018.
- On June 22, 2017, Jaguar Land Rover fired its most powerful shot yet into the realm of autonomous vehicles: a self-driving Range Rover Sport. The vehicle is capable of Level 4 autonomous driving which means it can theoretically handle itself in just about every conceivable driving scenario within a selected environment.
- On November 17, 2017, Jaguar Land Rover said that it has been testing driverless cars on public roads. The trials have been underway for several weeks on a half-mile route in Coventry city center. The vehicles rely on sensors to detect traffic, pedestrians, and signals but have a human on board to react to emergencies.
- On January 15, 2018, Jaguar Land Rover announced that it will open a new R&D center in the UK. The £24bn revenue firm says it is developing fully and semi-automated driving technologies and looking to hire more experts in AI, safety-critical systems, and vehicle architecture.
- On March 23, 2018, Automotive group Jaguar Land Rover and Chinese technology giant Baidu began new self-driving car tests. Despite the US accident, Beijing has given the go-ahead for Baidu to test driverless cars on 33 roads – the first time a company has been given permission to conduct open-road tests in the Chinese capital.
- On Jun 4, 2018, Jaguar Land Rover pumped £3.7 million into a project that will see autonomous driving technology developed for off-road use. The British firm wants its autonomous vehicles to be the most capable on the market and able to tackle the widest range of terrains including off-road. Vehicles such as the Discovery and Discovery Sport will eventually be fitted with Level 4 and Level 5 autonomous technology.
- On September 4, 2018, Jaguar Land Rover created self-driving cars with eyes that are used to communicate with pedestrians when it’s safe to cross in front of them. Currently being tested in Coventry, England, the prototype autonomous vehicles sport two eyes in front, giving them a friendly face.
- On October 10, 2018, Jaguar Land Rover’s autonomous Range Rover Sport became the first autonomous vehicle to drive itself a round-about which it calls one of the most challenging journeys in the UK. The demonstration was part of the £20 million government-funded UK Autodrive project, in which around a dozen cars and pods took part.
- On November 01, 2018, Jaguar Land Rover announced that it is developing a system for autonomous cars that will detect motion sickness in individual passengers and automatically adjust settings until they feel better. The company collected over 15,000 miles of data on car sickness and tested the effects of carrying out tasks like checking emails while in transit.
- On Jan 23, 2019, Jaguar Land Rover developed a system that projects an autonomous vehicle’s direction of travel on the road ahead. The system casts a series of bars on the road to indicate when it’s turning, setting off or stopping. The gap between the bars can expand or shrink to indicate changes in speed.
- On July 5, 2019, Jaguar Land Rover and Waymo announced a long‑term strategic partnership. The two companies are working together to develop the world’s first premium self‑driving electric vehicle for Waymo’s driverless on-demand transportation service.
- On Sep 6, 2019, Jaguar Land Rover partnered with BlackBerry to develop autonomous vehicles. BlackBerry will assist Jaguar in various areas via AI and machine learning to develop next-generation cars.
- On Sep 30, 2019, Jaguar Land Rover joined hands with Swiss automotive Tier-1 supplier OSR Enterprises for enhanced Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), automated driving, and secure connected technologies.
- On Oct 24, 2019, Jaguar tested a self-driving prototype called the I-PACE in Dubai. The all-electric, zero-emissions I-PACE includes enhanced vehicle detection and avoidance capabilities through a combination of radar and cameras, alongside a traffic light detection system. The vehicle’s speed and steering, from stationary up to highway speed, were also controlled autonomously during test drives.
- On Feb 18, 2020, Jaguar Land Rover unveiled an electric and autonomous shuttle pod designed for shared use in urban settings. The concept is known as Project Vector and the carmaker has high hopes to have some version of the concept on the road for testing by 2021.
Post-COVID Activities
2022
- In Mar 2022, Jaguar Land Rover announced that it joined forces with American software leader Nvidia to bring enhanced connectivity and advanced autonomous driving capabilities to all vehicles released from 2025. This multi-year collaboration will involve joint software development, departing from Nvidia’s off-the-shelf technology approach. The Drive software architecture from Nvidia will be seamlessly integrated into every new Jaguar and Land Rover model, furnishing them with cutting-edge automated driving systems and AI-enhanced services for an enriched customer experience. (Source)
2023
- In Feb 2023, Jaguar Land Rover announced the establishment of three autonomous vehicle hubs in Europe with Nvidia. This initiative arises from their ongoing partnership, forged last year, showcasing the deepening connections between automakers and the tech industry. These self-driving car centers will be in Munich, Bologna, and Madrid. (Source)
- In Apr 2023, Jaguar Land Rover announced its commitment of £15bn across the next five years to invest in autonomous driving, AI and vehicle electrification. Aside from autonomous driving, Jaguar Land Rover’s spending includes transitioning its Halewood plant in Merseyside to producing all-electric vehicles. The plant will house production for an electric Range Rover launching in 2025. (Source)
Continental AG
Continental AG, the German carmaker has taken a gradual route to launch autonomous cars. Unlike other players, it is taking a more cautious approach to the race. The company believes that it will be better placed if they slowly implement driver-assisted technologies such as automatic braking and pedestrian detection.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On January 4, 2018, Continental and Bosch, the world’s largest automotive suppliers, have each bought a 5 percent stake in digital mapping firm HERE, as the industry pool resources with major carmakers to develop self-driving cars.
- On Feb 5, 2018, Auto supplier Continental and chip supplier NVIDIA announced a partnership to create Artificial Intelligence self-driving vehicle systems based on NVIDIA’s computing platform, with a planned market introduction in 2021 for Level 3 autonomous features. The partnership enables the development of AI computer systems scaling up from modest Level 2 features to full Level 5 self-driving capabilities, where the vehicle has no steering wheel or pedals.
- On April 27, 2018, Continental said that it is expanding its global development activities for the safe launch of automated driving. The engineers are now testing their prototype vehicles on autobahns in Lower Saxony under real traffic conditions. The prototypes are always monitored and operated by a development expert in the driver’s seat. Continental is developing sensors, vehicle computers, operating systems, and software for automated driving, particularly in Japan, China, the US, and Germany.
- On October 30, 2018, Continental said that it had hired Dirk Abendroth, a former BMW executive now employed at Chinese carmaker Byton, to become chief technology officer at the German auto supplier’s Automotive division. Abendroth will be responsible for technology trend scouting, research and development, and combining Continental’s autonomous driving and connected mobility efforts.
- On Nov 18, 2018, German automotive component maker Continental has announced that the company will be commencing work on driverless mobility solutions with French autonomous vehicle technology company, EasyMile. Both companies have signed an MoU and will have a joint R&D team in place at Continental’s Singapore-based facility.
- On Dec 13, 2018, Continental introduced an intelligent door brake system and smart autonomous door support system that is intended to support convenient opening and closing operations and avoiding uncontrolled slamming. The obstacle detection function has been designed to prevent dents and paint scratches in traffic scenarios.
- On January 10, 2019, German automotive company Continental said that it wants to use a system of autonomous vans packed with dog-like four-legged robots to deliver packages. The company revealed its vision for the future of goods and parcel delivery this week at the tech show CES in Las Vegas, where it held a press conference with a prototype of one of the robots on stage.
- On July 18, 2019, Continental AG announced that it has developed a smart voice assistant for usage in vehicles. The company claims, this smart voice assistant can understand multiple questions in one sentence and detect logical connections. Continental claims that the system also comes with a hybrid solution like a cloud connection and it also gets smart algorithms and system architecture precisely tailored for cars.
- On August 1, 2019, Continental said that it is using technologies such as ABS, radar, and redundant brake systems in series production for Robo-taxis for the first time. This year, Continental’s technology for driverless vehicles will be in production for the first time in French company EasyMile’s EZ10 autonomous shuttle. Continental has held a stake in this driverless vehicle manufacturer since 2017.
- On August 09, 2019, Baidu and Elekrobit signed a strategic partnership with Apollo Computing Unit, an advanced in-vehicle computing platform for autonomous driving owned by the Chinese company. Elektrobit is a supplier of embedded and connected software products and services for the automotive industry, wholly owned by Continental. The company claims that its software powers more than one billion devices in over 100 million vehicles.
- On Aug 14, 2019, Continental AG announced that it developed what it calls a “Road AND Driver” camera, that monitors both the driver and traffic in front of the vehicle. The dual-camera system continuously detects whether the driver is paying attention to the road, while also monitoring the surroundings. Continental says the camera provides a holistic model of the environment and is a prerequisite for the safe deployment of self-driving vehicles.
- On Sep 5, 2019, Continental AG acquired a minority stake in Cartica AI, which develops algorithms for accelerating machine learning systems for object recognition. The technology could be used to enable automated and autonomous driving systems to more rapidly adapt to and handle new traffic situations.
- On Sep 16, 2019, Continental A.G. unveiled a concept technology system dubbed Conti CARE (connected, autonomous, reliable, and electrified) for managing tires in electric and autonomous vehicles. With the web-based ContiConnect Live application, Conti claims Conti CARE optimizes costs through monitoring tire wear and adjusting the tire pressure on the go.
- On Feb 18, 2020, Continental North America announced it will build a 215,000-square-foot manufacturing and research facility focused on technology for autonomous driving in New Braunfels, Texas. Construction on the $110 million plant is scheduled to begin later this year with production starting in 2021. The plant will employ around 575 workers and produce products for Continental’s advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Jul 2021, Continental announced that Ten months after its partnership with LiDAR expert AEye, it is incorporating AEye’s long-range LiDAR technology into its comprehensive sensor stack solution, forming the initial fully integrated automotive-grade system for automated and autonomous driving applications ranging from Level 2+ to Level 4. Built on AEye’s LiDAR tech, this solution significantly contributes to the sensor configuration required for advanced automation systems. It supplements Continental’s sensor system, which includes radar, camera, and ultrasonic technologies, establishing a dependable and redundant Automated Driving platform capable of managing intricate traffic situations and challenging weather conditions. (Source)
- In Sep 2021, Continental’s Technical Centre India (TCI) showcased remarkable innovation through the creation of cost-effective ADAS solutions: a radar sensor and Rear-View System (RVS231), strategically targeting emerging markets. These systems are built upon a proven platform designed for upscale passenger vehicles. Introducing budget-friendly radar sensors and rear-view systems will facilitate the integration of Continental’s ADAS technologies into entry- and mid-level passenger cars, effectively elevating the vehicles’ safety features. (Source)
2022
- In Sep 2022, Continental and software-defined lidar manufacturer AEye revealed their collaboration to integrate their advanced lidar sensor model into NVIDIA DRIVE Sim. This move positions them as the newest sensor creators’ broad network members, leveraging NVIDIA’s comprehensive cloud-based simulation platform for advancing technology. (Source)
2023
- In Jan 2023, Continental and Ambarella have deepened their collaboration through a strategic partnership aimed at co-creating scalable full-stack systems catering to Level 2+ to highly automated vehicles. Additionally, they will collaborate on camera-based perception solutions for ADAS. These comprehensive system solutions will adopt a multi-sensor strategy, encompassing Continental’s high-resolution cameras, radars, lidars, relevant control units, and the necessary software components. (Source)
- In Aug 2023, Continental announced an advanced lidar sensor for self-driving vehicles, touting it as the “missing link” for autonomous cars navigating intricate surroundings. Developed in collaboration with AEye, this long-range lidar sensor can perceive objects up to 3,281 feet (1,000 meters) away, including overpasses and signs. It can identify vehicles from a distance of 300 meters and discern objects on the road at approximately 525 feet. Dubbed the HRL 131 Micro-Electro-Mechanical (MEMs) Scanning Lidar, this sensor is tailored for Level 3 and 4 autonomous vehicles that require extended object recognition abilities. (Source)
Aptiv (Delphi)
Aptiv, previously known as Delphi, is a global technology company that develops safer, greener, and more connected solutions enabling the future of mobility. The company is focused on developing and commercializing autonomous vehicles and systems that enable point-to-point mobility via large fleets of autonomous vehicles in challenging urban driving environments.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On October 24, 2017, Delphi Automotive PLC announced that it signed an agreement to acquire nuTonomy, Inc. for an upfront purchase price of $400 million and earn-outs totaling approximately $50 million.
- On May 3, 2018, as part of its partnership with ridesharing giant Lyft, Aptiv launched a fleet of 30 autonomous vehicles in Las Vegas for commuting convenience. The fleet of 30 cars will operate using Aptiv’s fully-integrated autonomous driving platform and will be equipped with Aptiv’s mobility technology.
- In Aug 2018, Aptiv announced that they are teaming up with Rental car company Hertz for implementing fleets of autonomous vehicles, starting with a pilot program of an initial 75 vehicles in Las Vegas, to launch this fall. Aptiv had already been testing a fleet of 30 self-driving BMW in Las Vegas since May. The cars were available through the Lyft ride-hailing platform.
- On March 29, 2019, Aptiv said that it wants to help advance research into computer vision and autonomous driving technologies by sharing some of the information it has already gathered in the real world. Aptiv announced this week it will share what it’s calling the largest public dataset to date of autonomous driving data. The data is open-source and free to use.
- On April 17, 2019, Aptiv opened an autonomous mobility center in Shanghai to focus on the development and deployment of its technology on public roads. The expansion marks the fifth market where Aptiv set up R&D, testing, or operational facilities. Aptiv has autonomous driving operations in Boston, Las Vegas, Pittsburgh, and Singapore. But the company said that China was perhaps its most ambitious endeavor.
- On June 4, 2019, Aptiv announced that they’ve completed more than 50,000 rides in Aptiv’s self-driving BMW 5 series vehicles via the Lyft app. The average ride received a rating of 4.97 out of 5 stars, according to Lyft, which added that 92% of riders said they felt very safe or extremely safe during the ride.
- On Jan 8, 2020, Aptiv unveiled its new Smart Vehicle Architecture (SVA) at CES. SVA is a flexible and scalable vehicle-level architecture designed to reduce vehicle complexity during assembly while improving safety and support software for connected and autonomous vehicles.
- On Feb 11, 2020, Lyft and Aptiv announced that they’ve completed 100,000 driverless rides. A total of 98% of customers provided a five-star rating after taking a ride. Moreover, the companies said that the cars now service over 3,400 destinations in the Las Vegas area.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Jan 2021, Aptiv introduced its latest-generation technology platform for automated driving, designed to be adaptable across various vehicle types and capable of remote wireless updates. According to Aptiv’s Chief Technology Officer, Glen De Vos, the core framework of this platform remains consistent whether building a compact car or a full-size sedan; the primary difference lies in the number of sensors or cameras needed for larger vehicles. A significant challenge for automakers worldwide in self-driving technology development is the associated expenses of sensors, radars, and cameras. While fully autonomous vehicles are still years away, advanced driving features like adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assistance are becoming increasingly prevalent. (Source)
2022
- In Feb 2022, Aptiv PLC contributed significantly to Vienna-based TTTech Auto’s recent funding round, raising a substantial USD 228 million (EUR 200 million). Additionally, Audi has boosted its existing stake by USD 57 million (EUR 50 million). TTTech Auto specializes in crafting software for automakers to effectively handle data from sensors and safety systems essential for driving automation. Their Motionwise software aids engineers in expediting the creation of new automated driving and safety software solutions. (Source)
- In Feb 2022, Aptiv PLC announced the acquisition of Wind River® valued at $3.5 billion. Wind River software enables the secure development, deployment, operations, and servicing of mission-critical intelligent systems. The company’s technology is in over two billion edge devices across over 1,700 customers in high-value industries, including aerospace and defense, telecommunications, industrial, medical, and automotive. (Source)
2023
- In Aug 2023, Aptiv partnered with Horizon Robotics, a leading provider of energy-efficient computing solutions for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) in consumer vehicles, in China. This partnership signifies Aptiv’s inaugural alliance with a domestic Chinese supplier specializing in automotive-grade computing solutions for ADAS and automated driving. Within this arrangement, Horizon Robotics, alongside Aptiv and Wind River, will collaboratively create comprehensive hardware and software solutions customized for Chinese civil automakers. (Source)
Stellantis (Formerly PSA Group)
France-based PSA Group is one of the top European car makers to enter into space. It started testing autonomous vehicle technologies extensively from 2015 onwards and plans to launch a highly autonomous car by 2018.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On May 02, 2017, NuTonomy, a developer of software for self-driving cars, teamed with Groupe PSA to integrate its software, along with sensors and computing platforms, into fully autonomous Peugeot 3008 sport utility vehicles that have been customized by the French carmaker for the purpose.
- On September 06, 2017, PSA Group and self-driving startup AImotive entered into a partnership to develop technology capable of level 4 autonomy, which requires no human intervention in defined conditions. The pilot will be deployed on French highways at speeds up to 80 miles an hour. The companies did not say when the pilot would launch or how many vehicles will be involved.
- On February 09, 2018, Groupe PSA acquired a controlling interest in Jian Xin, a Chinese automotive spare parts distributor. With the acquisition, Groupe PSA will be able to accelerate the rollout of its aftermarket offering in China by rapidly establishing its position in the market representing 130 million vehicles.
- On Mar 07, 2018, Harman International Industries, acquired by Samsung, announced a new cybersecurity collaboration with European automaker Groupe PSA. The companies revealed they are collaborating on a cybersecurity strategy for Groupe PSA’s next-generation connected and autonomous vehicles platform. The companies have worked on multiple projects together over the past two years.
- On February 5, 2019, Groupe PSA obtained a license to begin autonomous vehicle testing on public roads in Chongqing, China. As the first French carmaker to do so in China, Groupe PSA is taking monumental strides in the development of vehicle connectivity and autonomous driving technology and reinforces the group’s commitment to the Chinese market.
- On February 14, 2019, FCA Italy and Groupe PSA signed an agreement to extend until 2023 their successful LCV cooperation, which started 40 years ago. The terms of this new agreement also include continued manufacture by the JV of Fiat Ducato, Peugeot Boxer, and Citroën Jumper large vans as well as additional versions to cover the needs of Opel and Vauxhall brands.
- On July 15, 2019, Groupe PSA and VINCI Autoroutes tested new autonomous vehicle features in Saint-Arnoult-en-Yvelines (France), following on from the trial carried out in July 2017, which led to the crossing of a tollgate in fully autonomous mode for the first time.
- On Jul 17, 2019, in an announcement, Groupe PSA said the goal of the testing was to see how vehicles could communicate with “surrounding infrastructure in a complex urban environment.” PSA is conducting tests in the Spanish city of Vigo to “advance the development of autonomous driving”.
- On Dec 18, 2019, Groupe PSA announced a 50/50 merger with Fiat Chrysler Automobiles that formed the fourth-largest global automaker by volume and third-largest by revenue. Mobility options, especially electric and electrified and autonomous vehicles are also key goals for the new company, with Tavares, Group CEO, stating, “clean mobility is a must but affordable mobility is what our customers expect.”
- On Feb 10, 2020, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles collaborated with Chinese startup AutoX to deploy robot taxis in China later this year. It’s the latest move by Fiat to cast a wide net for autonomous vehicle suppliers as it seeks to catch up to its crosstown rivals.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Dec 2021, Stellantis formed a partnership with BMW as a Part of the STLA AutoDrive initiative, which focuses on the development of continuous OTA-updated Level 2, Level 2+, and Level 3 autonomous driving capabilities. (Source)
- In Dec 2021, Stellantis announced its intention to invest €30 billion ($34 billion) by 2025 in creating new vehicles built around the software. This approach will enable the company to offer its automotive customers entertainment, navigation, and subscription services. This software-centric strategy is integral to their broader electric and autonomous vehicle initiatives. Collaborative ventures with BMW involve the development of hands-free driving tech, while Waymo partnerships center around self-driving vehicle advancements. (Source)
2022
- In Apr 2022, Stellanis announced a partnership with Qualcomm, leveraging the cutting-edge Snapdragon Digital Chassis advancements for dynamic and personalized in-vehicle experiences. This collaboration aligns with Stellantis’ strategy to consolidate software functions into High-Performance Computers, utilizing Qualcomm’s Snapdragon Automotive Platforms across key vehicle domains. Additionally, it enhances the security of Stellantis’ supply chain for vital components. (Source)
- In Jun 2022, Stellantis announced that it opted for Valeo’s third-generation LiDAR technology to outfit various models across its diverse automotive brands starting in 2024. Implementing the Valeo SCALA 3 LiDAR will enable these vehicles to achieve level 3 automation certification, enabling drivers to relinquish control of the steering wheel and their visual focus from the road. (Source)
- In Nov 2022, Stellantis revealed its acquisition of aiMotive, a move that strengthens the company’s artificial intelligence and autonomous driving technology. This acquisition not only widens Stellantis’ global talent base but also accelerates the development of the upcoming STLA AutoDrive platform. (Source)
Bosch
Bosch, one of the world’s largest automotive suppliers, has responded to an increase in demand by dedicating more than 2,000 engineers to driver-assistance systems. The company is also partnering with GPS maker TomTom for the mapping data necessary for this endeavor. The company has projected that self-driving cars will be in action by 2020, at least on highways. In an April 2016 interview, a Bosch marketing director reiterated the company’s commitment to autonomous, connected, and electric vehicles.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On Mar 15, 2017, Nvidia announced a new partnership with Bosch to sell its Drive PX 2 driver-assist platform to automakers. In effect, the deal gives Nvidia a go-to-market strategy for its self-driving hardware and software platform. Bosch joins ZF as the two so-called tier-one suppliers that will sell Nvidia’s technology to automakers.
- On Jun 7, 2017, Bosch and TomTom announced that they’ve teamed up for what the companies call “a breakthrough in the development of high-resolution maps for automated driving.
- On Jun 19, 2017, Bosch announced that it is investing heavily in where the market is headed, with a newly-announced $1.1 billion facility that will produce semiconductors uses in self-driving cars, smart homes, and smart city infrastructure.
- On February 21, 2018, Bosch bought Detroit-based ride-sharing startup SPLT (Splitting Fares Inc.), marking Bosch’s first foray into territory dominated by the likes of Uber and Lyft. SPLT was founded in 2015 and claims to have 140,000 users in the United States, Mexico, and Germany. Unlike most other ride-sharing services, SPLT is aimed specifically at commuters who travel the same route every day.
- On Jul 25, 2018, Bosch introduced a predictive road condition service that can help make sure self-driving vehicles remain safe even on wet and icy roads. The technology takes multiple possible weather forecast scenarios from Finnish company Foreca into consideration, so a vehicle that uses it knows how and where it can drive autonomously.
- On Oct 10, 2018, Automotive technology company Bosch said that it is calling for automated driving to be included as part of the UK driving test to help improve driver acceptance and understanding. A recent report from Thatcham highlighted a poor understanding of the levels of automation, and they recommended caution when using the word ‘autonomous’ to avoid further misunderstanding.
- On Dec 12, 2018, Bosch said that it is following the lead of Continental and ZF by producing its own self-driving electric shuttle. A preview of the concept EV for four passengers has just been released ahead of the official debut at the CES in Vegas.
- On Jan 21, 2019, Bosch has given the green light to test its self-driving cars on rural roads in Victoria, Australia, as it looks to refine its autonomous vehicle technology. The German multinational has received an AUD$2.3mn state government grant to test the technology on high-speed rural roads.
- On Jan 31, 2019, Robert Bosch announced a push into parking, recharging, and maintenance services for electric and self-driving vehicles as it posted a flat annual operating profit on Wednesday. Bosch said it was in talks to expand a research alliance on autonomous vehicles and planned to invest 4 billion euros ($4.6 billion) to develop self-driving cars by 2022. Bosch has 4,000 engineers working on autonomous vehicles technology and is working with Daimler to develop self-driving cars.
- On July 23, 2019, Bosch announced it received regulatory approval in Germany for a system that enables driverless vehicles to navigate the ramps and pillars of parking garages themselves and glide into their pre-assigned spots alone. The parking garages of the future may be designed specifically for self-driving vehicles because more cars could be packed in if they don’t need enough space for their drivers and passengers to open the doors and climb out.
- On Sep 2, 2019, Bosch developed an MPC3 camera with artificial intelligence for autonomous vehicles. As Bosch claimed, the camera uses a combination of multi-path approach and AI for object recognition to make surround sensing more reliable and roads much safer. It can also improve legacy driver assistance systems and extend their application range.
- On Sep 30, 2019, Robert Bosch Venture Capital GmbH (RBVC), the corporate venture capital arm of the Bosch Group, invested in Trunk, a startup based in Beijing. Trunk provides combined hardware and software solutions for autonomous trucking.
- On January 2, 2020, Bosch said that it developed production-ready LiDAR sensors for use in vehicles. It’s hoping to keep costs down by making them at scale. That way, it might be able to offer them at a lower price and bolster more widespread adoption of autonomous driving systems.
- On Mar 16, 2020, Bosch unveiled its Internet of Things (IoT) concept shuttle that incorporated a number of the firm’s most advanced technologies and provided a future look into how electric driverless vehicles could convey passengers in the not too distant future. The concept vehicle comes complete with interactive screens for every passenger and that’s just the beginning.
Post-COVID Activities
2022
- In Jan 2022, Bosch announced that it is collaborating with Cariad to create software for automated driving, intended for integration into Volkswagen vehicles. Leveraging data from Volkswagen’s vehicle fleet, they will work on Level 2 autonomous driving software, enabling hands-free driving across cities, rural areas, and highways. Additionally, they are developing a Level 3 system that assumes full driving control on the motorway. (Source)
- In Feb 2022, Bosch announced the acquisition of Atlatec, a specialist in high-definition maps for autonomous driving and simulation. Upon integration, Atlatec will operate as an independent entity within Bosch’s Cross-Domain Computing Solutions division. With this acquisition, Bosch expects to expand its automated driving expertise and strengthen its market position. (Source)
- In Mar 2022, Bosch announced the integration of Atlatec GmbH into Bosch’s Cross-Domain Computing Solutions division as a self-sustained entity. The formal contracts sealing this collaboration have been signed by Bosch and Atlatec. Originating as a spin-off from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Atlatec operates in Germany, the U.S., and Japan. It is recognized as a leading innovator providing high-resolution digital maps for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving applications. (Source)
- In Apr 2022, Bosch acquired Five.ai, an autonomous driving startup. Initially aiming to establish a robotaxi fleet, Five.ai shifted its focus to software development for B2B applications. This aligns with Bosch’s own active role in software for autonomous systems and next-gen hardware. Bosch has also invested in autonomous vehicle enterprises, including Momenta in China. (Source)
- In May 2022, Bosch announced its strategic investment in WeRide, a company specializing in Level 4 autonomous driving technology. The entities have entered into a strategic cooperation agreement to create autonomous driving (AD) software collaboratively. This partnership will expedite the advancement of Bosch China’s sophisticated driving solution, propelling SAE Level 2-3 AD technology closer to widespread production. (Source)
- In Nov 2022, Bosch announced its collaboration with WeRide to jointly develop an upgraded iteration of their advanced driver assistance system (ADAS), set to be available by late 2023. The system has also secured its inaugural pilot customer, the identity of which Bosch has not yet disclosed. (Source)
2023
- In May 2023, Bosch announced the partnership with Plus for a significant advancement in commercial truck-assisted driving technology received. The collaboration involves integrating their software and hardware solutions to achieve Level 2 autonomy capabilities. This collaborative approach is tailored to facilitate partial automation by assisting drivers in acceleration, braking, and steering. These features will enhance driver retention, realize fuel economy benefits, and reduce accidents. (Source)
Denso
Denso has been working on autonomous vehicles for a long time. The company has been researching the LiDAR system for a long time. In 2012, a miniaturized and low-cost linear LIDAR was commercialized and was adopted in Smart Assist, which is a DAIHATSU’s collision avoidance assistance system.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On Dec 24, 2016, Denso agreed to a comprehensive partnership with tech company NEC to jointly develop components for use in self-driving vehicles.
- On Jun 18, 2019, Denso announced a collaboration with Ottopia (www.ottopia.tech), a technology company enabling remote vehicle operation. Ottopia launched its Advanced Teleoperation (ATO™) platform that provides both direct and indirect remote control of driverless vehicles. Ottopia’s ATO platform offers a unique integration of human operators with AI software to set a new safety standard for teleoperation in the automotive industry.
- On Jul 10, 2019, Denso Corp announced an agreement with Toyota to set up a joint venture to develop next-generation automotive semiconductors for connected and autonomous vehicles. Denso will own 51% of the new company, with Toyota holding the remainder. The companies aimed to establish the venture in April 2020 with a capitalization of 50 million yen ($458,968) and about 500 employees.
- On Aug 12, 2019, Denso opened a research and development office in Seattle. The company wants to team up with the region’s tech companies and universities to develop cloud computing technology, autonomous driving capabilities, and mobility software.
- On Aug 17, 2019, Denso joined the Mobility Open Blockchain Initiative (MOBI), the global consortium of businesses and organizations dedicated to innovating mobility services through blockchain technology.
- On Sep 11, 2019, Denso and Blackberry announced the launch of their co-developed human-machine interface (HMI) digital cockpit system that will be first shipped in vehicles by Subaru, a Japanese Automaker. As per the companies, vehicles have traditionally been equipped with multiple HMI systems that require device-specific operating systems to work.
- On Nov 5, 2019, DENSO announced its latest Series A funding round for Metawave Corporation, a Silicon Valley-based automotive startup developing radar for autonomous driving and wireless solutions for the deployment of 5G cellular networks.
- On 16 December 2019, DENSO and NTT Communications announced that they will begin validating their jointly developed Vehicle Security Operation Center (V-SOC) technology for monitoring and analyzing the vehicle’s security status from January 2020. The two companies are creating technology to realize resilient security solutions for connected cars.
- On Jan 9, 2020, DENSO Corporation announced a joint effort with Qualcomm for developing next-generation cockpit systems. With these opportunities for vehicle-driver communication, human-machine interfaces (HMI) play a key role in providing updates to drivers swiftly, effectively, and safely, and in a way that does not cause distraction.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Jan 2021, Denso partnered with Aeva, a US-based LiDAR and perception systems firm, to collaborate on developing cutting-edge sensing and perception systems. Their joint efforts aim to advance Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) LiDAR, an innovative solution capable of measuring depth, reflectivity, and velocity. This technology will be introduced to the broader vehicle market for widespread adoption. (Source)
- In Feb 2021, Denso announced that it, with Toyota, will team up with self-driving car startup Aurora to develop and build autonomous minivans for ride-hailing networks. Aurora’s new agreement with Toyota and Denso expands on the earlier collaboration between the Japanese companies and Uber ATG. Toyota remains an investor in Uber and transferred its equity stake from ATG to Aurora as part of the December transaction, according to a source familiar with the deal. (Source)
- In Apr 2021, Denso announced that it has crafted components for Advanced Drive, an advanced driver assistance technology showcased in Japan’s recently launched Lexus LS and Toyota Mirai vehicles. The newly designed products for Advanced Drive encompass LiDAR for discerning surrounding vehicle and road shapes; Locator Telescopic Camera for anticipating the road ahead; Spatial Information Service Electronic Control Unit (SIS ECU) for pinpointing vehicle position; Advanced Drive System Electronic Control Unit (ADS ECU) and Advanced Drive Extension Electronic Control Unit (ADX ECU) for rapid processing of data furnished by these components. (Source)
2023
- In Jan 2023, Denso announced that it has further strengthened its ties with AMD as it adopts the Xilinx Automotive (XA) Zynq UltraScale+ adaptive system-on-a-chip. Following the collaboration announcement with Aisin, the semiconductor leader has disclosed that Denso, a prominent Japanese automotive manufacturer, will incorporate this multi-processor SoC into its forthcoming lidar platform. (Source)
- In Jan 2023, Embracing NXP Semiconductors’ latest innovation, Denso Corporation has become the lead customer for their groundbreaking 28nm RFCMOS radar one-chip IC family. This innovative SAF85xx series amalgamates NXP’s radar sensing and processing technologies into a singular device, providing a novel approach to address short-, medium-, and long-range radar applications. This versatility is pivotal in meeting increasingly stringent NCAP safety regulations for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving. This pioneering one-chip radar family complements NXP’s extensive radar lineup, which draws from over 15 years of technological leadership. (Source)
Technology Companies Working on Autonomous Vehicles
Apple
In 2016, Apple confirmed for the first time that they are working on self-driven cars. It also announced its investment in machine learning and automation. This project is internally known as Project Titan and started in 2014. However, the company is less vocal about its autonomous car projects.
Apple holds the record for the 3rd largest fleet of self-driving test vehicles in California, just behind Waymo and GM with 135 and 258 cars, respectively. Its interest in the self-driving industry is still a mystery, with reports saying that Apple intends to use the technology within the company. Others speculate that the tech giant is planning to compete in the self-driving market in the future. Apple has recruited an additional 33 drivers for its autonomous car project. According to a report filed with the Department of Motor Vehicles of California, Apple now has 143 pilots for their autonomous system evaluations on Lexus SUVs equipped with self-driving technology.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On Mar 20, 2018, Based on figures provided by the Department of Motor Vehicles in California, Apple had permits to test a total of 45 self-driving vehicles on public roads in its home state. That number is up from 27 just a few months ago and just three to start almost a year ago. As FT highlights, Apple’s 45 permits top of Tesla’s 39 permits and Uber’s 29 permits.
- On May 23, 2018, Apple signed a deal with Volkswagen to turn some of the carmaker’s new T6 Transporter vans into Apple’s self-driving shuttles for employees — a project that is behind schedule and consuming nearly all of the Apple car team’s attention, said three people familiar with the project.
- In recent years, Apple sought partnerships with the luxury carmakers BMW and Mercedes-Benz to develop an all-electric self-driving vehicle, according to five people familiar with the negotiations.
- On June 14, 2018, a new patent application published describes a number of different methods a self-driving car could use to figure out exactly where its owner wants to go. The patent application refers to these clues as ‘intent signals.’ One method would be the owner using an indirect steering wheel or joystick to direct the car. In this case, the steering wheel wouldn’t be connected to the car mechanically but would guide the electronics in the right direction. But the patent mostly focuses on more indirect methods.
- On Jun 16, 2018, Apple Inc hired a senior self-driving car engineer from Alphabet’s Waymo unit. The hiring indicates a sign that the iPhone maker maintains autonomous vehicle ambitions.
- On Dec 17, 2018, Andrew Kim, the designer who first rose to prominence with a fan-made reimagining of Microsoft’s design language, has left his role as a senior designer at Tesla to join Apple.
- On Feb 20, 2019, Apple had an opportunity to pull back the curtain on the so-called “Project Titan” with the release of its voluntary safety report to federal regulators. In the report, Apple describes its interest in self-driving systems in broad, world-saving terms, but it’s noticeably silent on practically every key detail surrounding the project.
- On Jun 26, 2019, Apple acquired startup Drive.ai in what appears to be part of a renewed effort by the company to branch out into self-driving cars.
- On July 18, 2019, an intriguing patent from Apple indicates that the technology company is still very much interested in getting involved in the automotive market. Patently Apple recently stumbled across a patent filed by Apple two years ago, but only just published by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. The patent relates to the suspension architecture of a car and the incorporation of a steer-by-wire system. The steering and suspension systems outlined by Apple in the patent would work best for an autonomous vehicle.
- On July 24, 2019, The iPhone maker hired Steve MacManus, former vice president of engineering at Tesla, for a senior director role. This is the third change in the 12 months that a Tesla engineering executive has revealed a move to Apple.
- On Aug 8, 2019, Apple expanded its driverless car project as it added 33 more drivers to test its fleet of 69 autonomous vehicles. Apple at that time had 143 pilots registered to evaluate autonomous systems on specially equipped Lexus SUVs.
- On Oct 18, 2019, Macrumors published that Taiwanese manufacturer Quanta Computer was supplying Apple with unspecified “autonomous driving solutions.
- On Jan 28, 2020, USPTO published an Apple patent that presents a future self-driving automobile that is integrated and operated through interactions. The newly published patent gives us a hint on how such a system would work with an autonomous car. There are three ways of passenger interaction for the autonomous car revealed in the patent, which are touch, gestures, and voice. The interaction mechanism is similar to what Apple offers on its devices.
- In 2019, Apple’s autonomous vehicle testing program saw a significant downward trend as its fleet drove 72,201 miles less than it did in 2018. Further, Apple reported 64 disengagements across the 7,544 miles driven, which equates to 8.48 disengagements per 1,000 miles. This compares to a whopping 69,510 disengagements, or 871.65 disengagements per 1,000 miles, recorded in 2018.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Nov 2021, Bloomberg reported that Apple is intensifying its efforts to break into the automobile industry by introducing an autonomous electric vehicle in 2025. The tech giant’s long-speculated automotive venture has gained momentum under new leadership and is actively pursuing the development of a completely self-driving vehicle devoid of a steering wheel or pedals. The car’s interior is envisioned to accommodate hands-free driving, with one potential design concept involving passengers seated in a U-shaped arrangement. (Source)
- In Nov 2021, Bloomberg reported that Apple recruited a former Tesla software engineer to further its self-driving car project. Christopher “CJ” Moore marks the second hire from Tesla to join Apple’s autonomous vehicle initiatives, following in the footsteps of Stuart Bowers, who departed Tesla’s Autopilot team approximately two years ago. Moore, who spent over seven years at Tesla and made notable comments regarding Tesla’s Autopilot features, will be reporting to Bowers in his new role at Apple. (Source)
2022
- In Aug 2022, Apple hired Gregory Baratoff, the former VP of the Autonomous Vehicles Lab at Hyundai MOBIS. Before his tenure at Hyundai MOBIS, he accumulated nearly 12 years of experience at Continental Corporation in Germany, serving as the Head of Camera Sensors Development. This appointment marks another significant addition to Apple’s Project Titan. (Source)
- In Dec 2022, Bloomberg reported that the anticipated Apple car launch has faced another setback. The Apple’s electric vehicle is now expected to be available for purchase in 2026. In addition, Apple has adjusted its self-driving aspirations, including conventional driving controls in the car and focusing primarily on enabling autonomous driving exclusively on highways. The objective remains to offer the Apple car at a price point below $100,000. Furthermore, Apple is actively searching for a partner to supply the electric skateboard platform that will serve as the foundation for building the vehicle. (Source)
2023
- In Mar 2023, information from the California Department of Motor Vehicles revealed that Apple has 201 individuals actively testing autonomous driving functionalities on public roadways. At that time, Apple was maintaining a fleet of 67 vehicles. Although the total size of Apple’s self-driving vehicle fleet has remained relatively consistent since 2021, the number of testers involved is steadily growing. In 2022, Apple augmented its testing team by 51 members, and in the initial months of 2023, an extra five testers were brought on board. (Source)
Microsoft
Microsoft is taking a different approach to autonomous vehicle technology development. It aims to collaborate with carmakers to implement its autonomous technologies. According to the senior management of the company, it has no intention to make its own autonomous vehicle. Some of the popular Microsoft solutions that might be used in such cars include the Azure cloud platform, Office 365, and the Windows operating system. The company already provides software for Ford, Kia, BMW, Nissan, and Fiat.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On March 22, 2017, Microsoft Corp. announced a new patent licensing agreement with Toyota Corp. that includes broad coverage for connected car technologies. The agreement builds on Toyota and Microsoft’s strong partnership, which includes their collaboration on the Azure-based Toyota Big Data Center. Microsoft invests $11.4 billion annually in research and development and for more than 30 years has been developing innovative technologies that are powering today’s connected car experiences.
- On July 6, 2017, China’s search engine giant Baidu named Microsoft as a partner on its new open-source autonomous driving platform, Apollo. Technology analysts say the partnership is a smart call by Redmond.
- The Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi alliance will debut its next-generation connected-car platform later this year in the Nissan Leaf electric vehicle and redesigned Renault Clio’s small car. The technology was developed by the auto group and U.S. technology giant Microsoft using Microsoft’s Azure platform. Microsoft is working on connectivity with other automakers, including Volvo and BMW. But, Nissan and Renault will be the first to use Microsoft’s entire suite of software.
- On Sep 28, 2018, Volkswagen’s supervisory board gave the green light for a strategic partnership between the Wolfsburg-based carmaker and Microsoft that will see the two companies develop connected cars together using cloud technology. The two sides agreed to create a Volkswagen Automotive Cloud on Microsoft’s platform for the Internet of Things, Microsoft Azure.
- On Jan 9, 2019, LG planned to harness Microsoft’s artificial intelligence smarts to improve its Advanced Driver Assistance Systems, DriverStatus Monitoring Camera, and MultiPurpose Front Camera — parts that it said last year it was providing to an undisclosed “premium German auto-maker”.
- On Jan 27, 2019, a collaboration of researchers from MIT and Microsoft developed a system that helps identify lapses in artificial intelligence knowledge in autonomous cars and robots. These lapses, referred to as “blind spots,” occur when there are significant differences between training examples and what a human would do in a certain situation — such as a driverless car not detecting the difference between a large white car and an ambulance with its sirens on and thus not behaving appropriately.
- On Apr 03, 2019, BMW and Microsoft announced a partnership to launch a new open-source industrial manufacturing platform called the Open Manufacturing Platform, or OMP. It’s based on Microsoft’s Azure, which BMW already uses to run its more than 3,000 machines at 30 production and assembly sites around the world. The OMP is meant to make self-driving systems in a simplified and more cost-efficient way and could eventually help with other things, like digital supply chain management and predictive maintenance.
- On June 3, 2019, Microsoft execs announced a “limited preview” of a piece of its autonomous systems toolchain at Build 2019. The company was seeking customers interested in test-driving its machine teaching and simulation technologies. Microsoft acquired machine-teaching vendor Bonsai in 2018 to jump-start its already existing work in this space.
- On Sep 6, 2019, Microsoft announced the integration of TomTom’s navigation technology into its Connected Vehicle Platform.
- On Sep 9, 2019, Microsoft updated its automotive strategy, which now clearly outlines the core principles that govern Microsoft’s decisions related to vehicles. Additionally, new partners were announced for Microsoft’s Connected Vehicle Program, and a new program was launched to help startups make autonomous vehicles.
- On Jan 3, 2020, Microsoft reported that it is expanding its partnership with Luxoft — a division of DXC Technology Company. The collaboration is focused to accelerate the delivery of connected vehicle systems and mobility experiences. Luxoft will make use of Microsoft’s Connected Vehicle Platform, which is based on Azure cloud-connected IoT, diagnostic and security solutions to enable automakers with data-centric features.
- On Apr 03, 2020, Microsoft said that it’s continuing to develop a machine learning system capable of making decisions based on visual data. As per the Microsoft Autonomous systems division, these systems train deep neural nets using simulated data before testing them in real-world environments. These systems have been deployed in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge, which centers on using autonomous technology to assist first responders in rescue missions.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Jan 2021, Microsoft established a strategic partnership with GM and Cruise to expedite the deployment of self-driving vehicles. Microsoft united with GM, Honda Motor, and additional institutional investors in a joint equity investment exceeding $2 billion in Cruise. In their announcement, the companies disclosed that Microsoft will be the preferred cloud provider for both GM and Cruise. They also committed to collaborative efforts encompassing software and hardware engineering, cloud computing capabilities, manufacturing, and fostering a partner ecosystem. (Source)
- In Feb 2021, Volkswagen entered into a strategic partnership with Microsoft to bolster Volkswagen’s autonomous driving capabilities by facilitating cooperation between its Cars. Software organization and Microsoft. Together, they will develop a cloud-based automated driving platform using Microsoft Azure, the company’s intelligent cloud platform in Redmond. (Source)
2022
- In Jan 2022, Microsoft announced that the company, in collaboration with institutional investment firm Baillie Gifford and Sir Richard Branson’s Virgin Group, invested $200 million into Wayve, a self-driving startup. Wayve’s approach to self-driving relies on machine learning, artificial intelligence, and optical cameras to empower vehicles to navigate autonomously. This method shares similarities with Tesla’s approach to the development of fully autonomous vehicles, which also harnesses cameras and AI technology. (Source)
- In May 2022, Microsoft partnered with Wayve to leverage the supercomputing infrastructure needed to support the development of AI-based models for autonomous vehicles on a global scale. (Source)
Intel – Mobileye
Intel, of course, has been keen to push into the sector, having been beaten to the punch by companies like NXP and Nvidia to supply automotive silicon and autonomous processing power.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On July 1, 2016, BMW Group and Mobileye joined forces to make self-driving vehicles and future mobility concepts become a reality. The three leaders from the automotive, technology and computer vision and machine learning industries are collaborating to bring solutions for highly and fully automated driving into series production by 2021.
- On November 15, 2016, Intel CEO Brian Krzanich announced that Intel Capital is targeting more than $250 million of additional new investments over the next two years to make fully autonomous driving a reality. This is the first time Intel is keynoting at an automotive conference, signifying how critical the automotive market has become for the company.
- On Sep 18, 2017, Intel announced a collaboration with Alphabet’s self-driving unit Waymo to provide the computing power necessary for Level 4 and 5 autonomous vehicles that can drive in any condition. Waymo’s self-driving Chrysler Pacifica minivans already feature Intel-produced technology for everything from connectivity to sensor-data processing. By working more collaboratively in the future, the two companies say they hope to eventually produce vehicles capable of driving in any condition without human intervention.
- On Jan. 8, 2018, Mobileye and NavInfo, the leading autonomous driving solution provider in the China market with core businesses in HAD mapping and high accuracy positioning, announced a collaboration intended to build and distribute Mobileye’s Road Experience Management (REM®) product in China. Specifically, the partnership’s purpose is to use Mobileye’s REM technology to generate a RoadBook™ in China that is integrated and aligned with NavInfo’s mapping solutions.
- On Jan 9, 2018, Intel showcased its first self-driving test car and announced a number of tie-ups with automakers to take the technology forward. The company introduced the first autonomous car in its 100-vehicle test fleet during CEO Brian Krzanich’s keynote address at the industry expo CES in Las Vegas. The car features 12 cameras, radars, laser scanners, and computing technologies from Mobileye and Intel. There are three high-resolution cameras at the front of the vehicle that allows for a 180-degree field of view and let the car’s image processor see at a distance of up to 300 meters.
- On January 11, 2018, SAIC Motor Corporation Limited took a further step in the development of intelligent driving technologies by cooperating with Mobileye. SAIC Motor will equip its first-generation intelligent driving central controller with the latest vision chip produced by Mobileye. The cooperation, a key element of SAIC Motor’s development strategy, is expected to promote the growth of self-driving cars in China.
- On October 11, 2018, The state of Arizona announced the formation of the Institute for Automated Mobility to advance the safe deployment of automated vehicles. Intel Corporation is a founding partner of the new institute. This unique public-private consortium will focus on the liability, regulatory, and safety implications of automated vehicles. It will also work to develop standards and best practices for the industry to follow.
- On Oct. 29, 2018, Volkswagen Group, Mobileye, and Champion Motors announced plans to roll out Israel’s first self-driving ride-hailing service. The partners are planning to establish a joint venture for operating as “New Mobility in Israel.” The group’s proposal was formally accepted by the Israeli government during a private ceremony at the Smart Mobility Summit in Tel Aviv.
- On July 3, 2018, Baidu announced that it plans to work with Mobileye to integrate and commercially deploy Mobileye’s Responsibility Sensitive Safety (RSS) model in both the open-source Project Apollo and commercial Apollo Pilot programs. Baidu also announced plans to adopt Mobileye’s Surround Computer Vision Kit as the visual perception solution.
- On January 8, 2019, Intel and Warner Bros. demoed a Batman entertainment experience aimed at passengers in a concept for a self-driving car. It is meant to show how we could entertain ourselves in the cars of the future. It’s based on Intel’s concept of a “passenger economy,” which assumes that we’ll have a lot more time on our hands in self-driving cars and will need to find a way to entertain ourselves.
- On 4 Feb 2019, Intel announced that for automated driving solutions the US chipmaker starting to gather data on traffic patterns, roadside behavior, and infrastructure conditions in India. Intel plans to use the data to create algorithms that could also be used overseas to promote automated driving, without any human assistance. Intel is currently carrying out the projects in Telangana and Karnataka, which it plans to expand to Goa, said Jitendra Chaddah, director for strategic development and operations at Intel India.
- On January 11, 2019, Intel’s Mobileye said that it is trialing autonomous vehicles on the streets of Jerusalem in a bid to test safety systems and navigation around heavy traffic and “aggressive” driving, Intel SVP and GM of Network Platforms Sandra Rivera told ZDNet. Speaking with ZDNet at CES 2019 in Las Vegas, Rivera said Intel is working with the Israeli government to ensure a safer environment for autonomous vehicles through Mobileye’s open Responsibility-Sensitive Safety (RSS) software model.
- On July 2, 2019, Intel and a team of automotive companies teamed up to create new guidelines for autonomous vehicles. The intention of the “Safety First Automated Driving” paper, is to establish a framework of universal safety principles that all self-driving cars should abide by. The standards deal primarily with how the industry should monitor and report safety standards when building and operating autonomous cars.
- On July 16, 2019, Intel announced that it has a new deep-learning chip system that is capable of crunching complex AI algorithms up to 1,000 times faster and 10,000 times more efficiently than regular CPUs. The new system, codenamed Pohoiki Beach, is made up of 64 Loihi ‘neuromorphic’ deep-learning chips, modeled after the human brain, and 8-million neurons. The chips are installed on a ‘Nahuku’ board that contains from 8 to 32 Loihi chips. The Pohoiki Beach system contains multiple such boards that can be interfaced with Intel’s Arria 1- FPGA developer’s kit. The system is aimed at making AI-enabled technologies such as autonomous driving, robotic skin, and prosthetic limbs more adaptable.
- On Aug 23, 2019, Nissan enlisted the help of Intel’s Mobileye to work on its hand-off freeway driving feature. Version 2.0 is a collaborative work by the two companies, as announced by Mobileye. ProPilot Assist by Nissan is considered one of the first super-advanced driver-aid suites made available in affordable cars. Several tests of the system concluded that it works well with drivers, but now it’s been made better.
- On Nov 5, 2019, Mobileye partnered with Chinese electric car startup Nio to develop autonomous vehicles. The company’s strategic collaboration aims to bring highly automated and autonomous vehicles to consumer markets in China and other territories.
- On Dec 18, 2019, Intel Corporation acquired Habana Labs for approximately $2 billion. Habana is an Israel-based company that develops programmable deep learning accelerators for the data center. This acquisition is aimed at strengthening Intel’s artificial intelligence portfolio and accelerating its efforts in the AI silicon market, which Intel expects to be greater than $25 billion by 2024.
- On Jan 7, 2020, Intel showed part of the unedited video at a news conference at the tech show CES in Las Vegas. The chipmaker’s demo is notable as self-driving car technology companies generally pair cameras with other sensors, like radar or lidar, to help the vehicle “see” its surroundings.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Feb 2021, Mobileye announced that its collaboration with Transdev Autonomous Transport System and Lohr Group to incorporate Mobileye’s autonomous driving technology into the i-Cristal autonomous electric shuttle produced by Lohr Group. Their objective was to introduce these autonomous shuttles into public transportation networks worldwide, with their initial deployment slated for Europe. (Source)
- In Jul 2021, Mobileye announced that it has embarked on a challenging and uncommon endeavor by conducting tests of its autonomous vehicles (AVs) in New York City, despite the state’s stringent regulations on such testing. According to Amnon Shashua, who serves as the company’s president and CEO, Mobileye is presently conducting trials with two autonomous vehicles in New York City, with intentions to expand that fleet to seven vehicles “over the coming months.” (Source)
- In Sep 2021, Mobileye revealed plans to introduce a robotaxi service in Germany in 2022, marking a significant step in their strategy to differentiate themselves in the autonomous vehicle (AV) industry. They aim to serve as both an AV technology supplier and a fleet and service provider operator. This taxi service was to be executed in collaboration with the German rental car firm Sixt and Moovit, an Israeli startup focused on mobility data, which Intel acquired for $900 million. Passengers will have the option to request rides through either Sixt’s or Mobileye’s dedicated apps. (Source)
2023
- In Mar 2023, as per two reports, Mobileye was recognized as the leader in the development of autonomous vehicle technology by two leading research groups, Guidehouse Insights and ABI Research. (Source)
- In May 2023, Porsche joined forces with Mobileye to introduce advanced hands-free assistance and navigation features in forthcoming sports cars. In this forthcoming partnership, Mobileye’s SuperVision technology platform will underpin the development of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) in Porsche’s upcoming vehicles. SuperVision empowers cars to autonomously follow navigation routes, execute lane changes, and automatically pass slower vehicles on multi-lane roads, as detailed by Mobileye. (Source)
- In May 2023, MAN collaborated with Mobileye Autonomous Buses. This partnership comes after MAN’s recent announcements regarding autonomous bus projects and advancements. Their initial joint objective involves commencing pilot operations for the first autonomous city bus, equipped with a safety driver, starting in 2025. This effort is part of the newly introduced MINGA research project in Munich. (Source)
- In Jul 2023, Mobileye introduced software for AV designed to prevent drivers from exceeding the maximum speed limits on roads. This innovation harnesses the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and a single camera. Unlike existing Intelligent Speed Assist (ISA) technology, which relies on cameras, low-resolution maps, and GPS data, Mobileye’s ISA system utilizes machine learning and a solitary camera to ascertain and enforce speed limits autonomously. (Source)
Waymo (Google)
Waymo is the top contender to be on the list of top autonomous vehicle companies. The company has been working on driverless car technologies since 2009. Initially, the project was named as Google driverless car project. In December 2016, the new unit Waymo was formed as the subsidiary of Google’s parent firm, Alphabet. Waymo’s self-driving technologies have gone through millions of miles of test drives already in US cities. Waymo cars had 1 billion simulated miles of test driving in 2016. However, Waymo’s effort got a regular halt due to the departure of project engineers and leaders including founding member Chris Urmson.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On March 9, 2018, Google said that it plans to use Waymo’s self-driving trucks to deliver cargo to Google’s data centers. The transport tests will take place in Atlanta, where Google-owned Waymo recently expanded its test program of self-driving minivans. Google’s logistics team will work closely with Waymo’s team to give Waymo’s self-driving trucks a chance to operate in a real-world business scenario.
- On Mar 27, 2018, Jaguar Land Rover announced that the company is to supply up to 20,000 of its new electric I-Pace cars to Waymo to be converted into self-driving vehicles for its ride-hailing service. The tie-up, worth up to £1.3bn, is a further mark of Waymo’s ambition in the race with Uber and others to develop a driverless ride-hailing service – as well as a huge boost for Britain’s biggest car manufacturer as it takes its first steps into electric vehicles.
- On July 25, 2018, Google’s sister company Waymo announced a trial in which its self-driving cars will ferry shoppers to and from a nearby Walmart store to pick up their groceries. For now, the pilot is being restricted to 400-plus members of its early rider program in Phoenix, Arizona.
- On May 31, 2018, Waymo announced its preparation to roll out more than 62,000 autonomous Chrysler Pacifica hybrid minivans. The mobility services company is expanding its partnership with Fiat Chrysler in a deal that may include licensing Waymo’s technology and services so they can be incorporated in FCA vehicles.
- On October 10, 2018, Waymo announced that its autonomous vehicles have driven 10 million miles on public roads in the United States. Keep in mind that the company hit 8 million miles in July and had logged just 4 million miles in November 2017. That suggests, Waymo’s pace is quickening.
- On February 5, 2019, The Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi alliance will tie up with Waymo to develop autonomous taxis and other services using self-driving vehicles, the Nikkei reported. The partners are considering the joint development of unmanned taxis using Nissan vehicles and a system that handles reservations and payments.
- On March 6, 2019, Waymo said that it will begin selling the laser-mapping sensors used on its driverless vehicles to other companies—as long as the customers don’t compete with its core robotaxi business. The sensors, known as lidar will be used in the next generation of warehouse robots, security systems, and even autonomous tractors.
- On March 20, 2019, Waymo announced that it is opening another technical service center in the Phoenix area, an expansion that will allow the autonomous-vehicle technology startup to double its capacity in the area as it prepares to grow its commercial fleet. The new 85,000 square-foot centers will be located in Mesa and is expected to open sometime in the second half of the year.
- On April 23, 2019, Waymo announced that it is building a factory to turn regular ol’ dumb cars into smart autonomous cars. Months after announcing that it was bringing its self-driving car operation to Michigan, the company said that it would be opening a repurposed factory in Detroit. In the new facility, Waymo will mass manufacture level 4 autonomous vehicles.
- On May 7, 2019, Lyft announced that the riders in the Phoenix area will soon be able to summon one of Waymo’s self-driving minivans for a ride. It’s the culmination of a partnership that was first announced almost two years ago.
- On May 10, 2019, Waymo announced that it has enrolled 1,000 customers for its ride-hailing service in suburban Phoenix. Chief Executive Officer John Krafcik touted the milestone while revealing plans to allow select Lyft Inc. users in Arizona to hail Waymo taxis.
- On May 29, 2019, Waymo announced the news in a tweet that it is bringing its autonomous trucks back to Arizona.
- On July 2, 2019, The California Public Utilities Commission granted Waymo a permit to participate in the state’s Autonomous Vehicle Passenger Service pilot. A statement from a Waymo spokesperson provides some hints as to how and where the company intends to use this permit.
- On July 26, 2019, Google said that its DeepMind system is using a type of algorithm called population-based training to mimic natural selection. The algorithm shortcuts the learning process by starting with the most efficient units and then basing future adaptations on those. The same thing is happening with self-driving development. DeepMind selects the aspects of the neural network that are most efficient and using those when it needs to retrain or adjust its procedures as new data comes in.
- On Aug 20, 2019, Waymo said that it will start testing on public roads in Florida to better experience heavy rain. The tests would begin in the Miami area and include highway driving to Orlando, Tampa, and Fort Myers. The Florida test vehicles will be driven by humans. They’ll collect data with laser and radar sensors.
- On Dec 12, 2019, Waymo acquired the Oxford artificial intelligence company Latent Logic for an undisclosed amount, giving Waymo its first presence in the UK. Latent Logic, a spinout company from Oxford University, specializes in “imitation learning”, teaching machines how to act by showing them examples of humans doing the same actions.
- On Jan 7, 2020, Waymo announced that their autonomous cars drove 10 million miles on public roads in the past year that was double the company’s self-driving record of the prior 10 years.
- On Jan 30, 2020, Waymo announced that it will partner with UPS to deliver packages across Arizona. Waymo’s automated minivans will transport packages from Phoenix UPS stores to Tempe sorting facilities, while a Waymo employee will monitor the cars’ performance along the delivery route.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Jan 2021, Waymo abandoned the term “self-driving” in favor of “autonomous” when referring to its technology, marking a subtle but significant change. This shift by the Alphabet company provides a clearer definition of the technology’s capabilities and limitations. It’s also seen as an effort to create some separation, not only from Tesla’s terminology of “full self-driving” for its advanced driver assistance system but possibly from the industry as a whole. (Source)
- In Jun 2021, Waymo announced that it had secured $2.5 billion in its second external funding round. In a blog post, the company intended to utilize these funds for the ongoing expansion of Waymo Driver, its autonomous driving platform, and its workforce. (Source)
- In Aug 2021, Waymo invited San Francisco residents to participate in testing its self-driving cars as part of its efforts to establish the city as its second market. The company introduced a research-oriented initiative called “Trusted Tester.” Residents can enroll in this program via the Waymo One app. Those selected could request rides in all-electric Jaguar I-PACE vehicles and subsequently offer feedback on their riding experiences. (Source)
- In Aug 2021, Waymo officially ceased the sale of its custom sensors to third parties in the past. This decision marked the Alphabet-owned self-driving company’s withdrawal from a business operation that existed for just two years. Waymo confirmed this move to Reuters and stated that it had shifted its focus towards deploying its Waymo Driver technology within its Waymo One ride-hailing and Waymo Via trucking divisions. (Source)
- In Nov 2021, Waymo Via, the delivery division of Alphabet’s self-driving unit, expanded its ongoing collaboration with UPS to transport freight using autonomous Class 8 trucks. This six-week pilot program, which commenced last week and ran until the end of the year to accommodate the holiday season, was conducted in Texas along the route connecting Houston and Dallas-Fort Worth. (Source)
- In Dec 2021, Zeekr collaborated with Waymo to create an autonomous ride-hailing vehicle. The electric MPV, as shown in official renderings, was designed to integrate with the emerging ‘Waymo One’ ride-hailing platform. At that time, the Waymo One service was operational in Phoenix, Arizona, and undergoing testing in San Francisco. (Source)
2022
- In Feb 2022, Waymo collaborated with C.H. Robinson, the largest freight-booking platform in North America. This collaboration was part of Waymo’s initiatives to advance its robotic truck technology to transport goods for commercial clients. C.H. Robinson intended to commence trial operations using Waymo Via autonomous big rigs to transport freight between Houston and Dallas within a few months. The identity of the shipper involved remained confidential between the two companies. (Source)
- In Oct 2022, Waymo planned to extend its robotaxi service to Los Angeles, marking the third region where this service would be available. While robotaxi services were slowly being introduced in various U.S. cities, they had yet to achieve widespread adoption. Waymo had strategically priced its service to be competitive with other ride-hailing companies, as confirmed by Chief Product Officer Saswat Panigrahi during an interview. (Source)
- In Nov 2022, Waymo officially introduced residents in downtown Phoenix. Although self-driving cars had been accessible to trusted testers in the region, Waymo One was declared ready for public use following extensive testing involving millions of miles both in real-world scenarios and simulations. (Source)
2023
- In May 2023, Waymo’s expansion transformed Phoenix into the “World’s Largest Self-Driving Car Zone.” The company’s self-driving taxis were set to become accessible in various parts of the metropolitan area, including Tempe, Mesa, and a recently added airport pick-up spot. Following a recent expansion that doubled its coverage area, the Phoenix metropolitan region earned the distinction of being the most extensive contiguous service area for autonomous cars globally, as reported by Corina Vanek in the Arizona Republic. Waymo also intends to expand its fleet in the Phoenix area further, although the exact number of vehicles was unspecified then. (Source)
NVIDIA
Nvidia is one of the leading chip-makers in the autonomous vehicle space today. Many automakers have already announced to use of systems from Nvidia in their self-driving cars. Some of these include Audi, Mercedes Benz, Toyota, and Tesla among others.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On Feb. 7, 2018, Continental announced that it will use graphic processor designer Nvidia’s autonomous driving computing system to help build its own self-driving technology platform. Engineers from both companies will work together to integrate Nvidia’s Xavier DRIVE system-on-a-chip, its DRIVE operating system (OS), and DRIVE software stack with Continental’s ASIL-D security certification, and radar, camera, and LiDAR sensor suite to build an autonomous driving solution.
- On July 10, 2018, German automaker Daimler and electronics company Bosch announced they would join forces to develop a fully automated, driverless car system. And for that, they’ve chosen Nvidia’s Drive Pegasus as their artificial intelligence (AI) computing platform of choice. Both companies will begin testing self-driving cars in California in the second half of 2019.
- On September 12, 2018, Isuzu Motors announced that it is using the NVIDIA DRIVE AGX platform to address an industry-wide driver-shortage issue while making roadways safer and less congested. Isuzu, which makes more than 600,000 commercial vehicles annually, is pursuing autonomous driving by using the NVIDIA DRIVE AV software stack and the energy-efficient DRIVE AGX platform inside the vehicle.
- On September 13, 2018, Nvidia said that it is using the underlying architecture of its Drive autonomous vehicle platform to enable product development in other verticals with AI systems that deal with vast amounts of critical data, such as video surveillance, robotics, and health care. Called Project Maglev, the initiative to transfer the data framework to industries beyond autonomous vehicles started roughly 18 months ago, Nvidia VP of AI infrastructure Clément Farabet told VentureBeat in a phone interview.
- On November 5, 2018, Optimus Ride, an autonomous technology startup based in Boston, revealed Nvidia’s Drive AGX Xavier as its development platform of choice for driverless cars. The company plans to upgrade all of its autonomous vehicles deployed in Boston’s Seaport District and the Union Smart Point development in Weymouth, Massachusetts with Drive AGX Xavier. It is also looking to incorporate the hardware/software framework into future prototypes at yet-to-be-announced sites.
- On November 21, 2018, The Chinese electric car companies XPeng Motors, Singulato Motors, and SF Motors signed a deal with the chipmaker to use NVIDIA’s Xavier AI chip to bring Level 3 autonomous driving. The NVIDIA DRIVE AGX Xavier car computer that comes with the kit is capable of taking care of a self-driving car’s heavy computational load — obstacle recognition, driver monitoring, and other aspects of autonomous driving.
- On January 8, 2019, Mercedes-Benz announced that it has selected NVIDIA to help realize its vision for next-generation vehicles. Both companies agreed that the car of the future must be software-defined — starting from creating the software for today’s requirements, anticipating software for tomorrow’s needs and building the computing architecture to enable it.
- On March 18, 2019, at the GPU Technology Conference, NVIDIA founder, and CEO Jensen Huang announced NVIDIA DRIVE AP2X — a complete Level 2+ automated driving solution encompassing DRIVE AutoPilot software, DRIVE AGX, and DRIVE validation tools. DRIVE AP2X incorporates DRIVE AV autonomous driving software and DRIVE IX intelligent cockpit experience. Each runs on the high-performance, energy-efficient NVIDIA Xavier system-on-a-chip (SoC) utilizing DriveWorks acceleration libraries and DRIVE OS, a real-time operating system.
- On March 19, 2019, Israel-based Cognata, a developer of simulation platforms for self-driving cars, said that it was partnering with U.S. chip supplier Nvidia to speed up testing and validation for autonomous driving. The companies will deliver an array of scenarios and traffic models using large-scale, hardware-in-the-loop simulation, it said. The simulation, Cognata said, will reduce testing time and costs, as well as produce better product quality and increase safety.
- On March 20, 2019, Nvidia said that with NVIDIA DRIVE Mapping software, sensors and onboard computers help self-driving cars see, plan, act, and can also make sure vehicles stay on the right path. DRIVE Mapping allows vehicles to navigate anywhere in the world. It uses maps from partners such as Baidu, HERE, TomTom, NavInfo, and Zenrin to localize vehicles to high-definition maps with unprecedented breadth and accuracy.
- On Mar 26, 2019, the chipmaker announced that its expanded partnership with Toyota Motor. The new collaboration between NVIDIA and Toyota Research Institute-Advanced Development (TRI-AD) in Japan and the United States “builds on an ongoing relationship with Toyota to utilize the NVIDIA DRIVE AGX Xavier AV [autonomous vehicle] computer. The collaboration involves the development, training, and validation of self-driving vehicles.
- On May 23, 2019, NVIDIA built DRIVE AGX as an open platform to seamlessly incorporate new sensors for more efficient autonomous driving development. Sensors are a key component to making a vehicle driverless. Cameras, radar, and lidar enable an autonomous vehicle to visualize its surroundings, detect objects, and implement interior features such as driver monitoring and customized passenger experiences. DRIVE AGX helps speed up this development with the DriveWorks sensor abstraction layer (SAL).
- On May 31, 2019, NVIDIA DRIVE partner and autonomous trucking startup, TuSimple, has hauled mail more than 1,000 miles between Phoenix and Dallas as part of a two-week pilot with the U.S. Postal Service. Halfway through the test, the self-driving prototypes from TuSimple — which is also an NVIDIA Inception member — arrived at the delivery hubs earlier than expected.
- On June 17, 2019, NVIDIA unveiled the world’s 22nd fastest supercomputer — DGX SuperPOD — which provides AI infrastructure that meets the massive demands of the company’s autonomous-vehicle deployment program. The system was built in just three weeks with 96 NVIDIA DGX-2H supercomputers and Mellanox interconnects technology. Delivering 9.4 petaflops of processing capability, it has the muscle for training the vast number of deep neural networks required for safe self-driving vehicles. Customers can buy this system in whole or in part from any DGX-2 partner based on our DGX SuperPOD design.
- On June 18, 2019, at its headquarters in Gothenburg, Sweden, Volvo Group announced that it’s using the NVIDIA DRIVE end-to-end autonomous driving platform to train, test and deploy self-driving AI vehicles, targeting public transport, freight transport, refuse and recycling collection, construction, mining, forestry, and more.
- On Oct 24, 2019, Nvidia partnered with Tel Aviv-based Blue White Robotics Ltd. to develop autonomous vehicle test-beds. The test-bed will enable Israeli automakers and startups to test and certify different types of autonomous vehicle technologies.
- On Dec 18, 2019, NVIDIA announced a partnership with the Chinese mobile transportation platform Didi Chuxing (DiDi). With the collaboration, DiDi would look to leverage NVIDIA GPUs and AI capabilities to develop self-driving tech and cloud computing solutions.
- On Mar 24, 2020, In a recent Leaderboard report, Navigant Research ranked NVIDIA as the leading automated driving computing platform. Navigant ranks companies in this report on 10 criteria: vision; go-to-market strategy; partners; production strategy; technology; sales, marketing, and distribution; product capability; product quality and reliability; product portfolio; and staying power.
- On Apr 17, 2020, The Chinese company Xpeng selected NVIDIA DRIVE AGX Xavier platform for its Xpeng XPILOT 3.0 Level 3 driving automation system. The first model equipped with NVIDIA’s AI computing platform will be the all-electric Xpeng P7 sedan, which is scheduled for market launch on April 27.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Jan 2021, NIO and NVIDIA announced that NIO had chosen the NVIDIA DRIVE Orin™ system-on-a-chip (SoC) for its upcoming line of electric vehicles featuring advanced autonomous driving functionalities. During NIO Day, their annual customer event, the electric vehicle manufacturer unveiled a supercomputer named Adam, powered by NVIDIA DRIVE Orin. This supercomputer was set its debut in the ET7 sedan, scheduled for release in China in 2022. (Source)
- In Mar 2021, Plus revealed its intention to integrate the Nvidia Drive Orin system-on-a-chip into the forthcoming iteration of its autonomous truck driving system. The company had outlined its deployment plans for this advanced system in 2022, spanning regions in the United States, China, and Europe. Hao Zheng, the Chief Technology Officer and Co-founder of Plus mentioned they had already received over 10,000 pre-orders for their system. He also indicated that they would continue to advance their next-generation product based on the Nvidia Drive platform while simultaneously delivering the systems to their customers. (Source)
- In Apr 2021, NVIDIA made announcements regarding its autonomous driving system-on-a-chip (SoC) lineup. They introduced updates to the DRIVE Orin SoC and unveiled the DRIVE Atlan SoC, an AI-powered chip for automakers to incorporate into their 2025 vehicle models. This SoC featured the integration of NVIDIA’s BlueField data processing unit, offering networking, storage, and security capabilities. Regarding computational power, it far surpassed the performance of the company’s earlier autonomous driving-focused chips, such as Drive Xavier (30 operations per second, or TOPS) and Drive Orin (254 TOPS). According to NVIDIA’s claims, DRIVE Atlan boasted 1,000 TOPs on a single chip. (Source)
- In Jun 2021, Nvidia announced its acquisition of DeepMap, a startup specializing in high-definition mapping. The company stated that incorporating DeepMap’s mapping intellectual property would enhance Nvidia’s autonomous vehicle technology division, Nvidia Drive. Ali Kani, the Vice President and General Manager of Automotive at Nvidia, expressed that this acquisition was an endorsement of DeepMap’s distinctive vision, technology, and team. It was anticipated that DeepMap would contribute to expanding Nvidia’s mapping products, facilitate the global scaling of map operations, and further develop their expertise in full self-driving capabilities. (Source)
2022
- In Feb 2022, Jaguar Land Rover entered into a multi-year strategic partnership with NVIDIA to jointly develop and provide advanced automated driving systems, along with AI-enhanced services and experiences for their customers.
Starting in 2025, all newly manufactured Jaguar and Land Rover vehicles will be based on the NVIDIA DRIVE™ software-defined platform. This platform would encompass many functionalities, including active safety features, automated driving and parking systems, and driver assistance systems. (Source)
- In Sep 2022, Nvidia introduced its novel computing platform, DRIVE Thor, which aimed to centralize various functions, including autonomous, assisted driving, and in-car entertainment. Danny Shapiro, who led Nvidia’s automotive business then, highlighted DRIVE Thor’s potential to replace multiple chips and cables within the vehicle, thereby reducing the overall system costs. However, specific figures regarding the extent of these cost savings were not disclosed. (Source)
2023
- In Feb 2023, Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) and Nvidia planned to establish three autonomous vehicle hubs in Europe. This initiative stemmed from a long-term partnership formed by the two companies the previous year, illustrating the growing collaborations between automakers and the technology sector. (Source)
Samsung
In May 2017, Samsung received approval from the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport to test autonomous vehicles on Korean roads. Samsung’s self-driving cars are based on Hyundai vehicles equipped with cameras and sensors. In the autonomous car segment, Samsung’s primary competitor is Apple.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On September 1, 2017, Samsung got permission to test self-driving cars on public roads in California. The permit means its driverless vehicles will be able to travel on the same routes as cars driven by humans. The firm said that it had no plans to make its own driverless cars instead it will make control systems for autonomous vehicles.
- On Aug 30, 2018, Renault Samsung Motors said that it received temporary approval from the country’s transportation ministry to test its self-driving cars on roads in South Korea. The permission allows the South Korean unit of French carmaker Renault S.A. to test its autonomous vehicles under development on designated expressways and test sites. Currently, Renault Samsung is working on a traffic jam assist system that can be used to drive cars on crowded roads at low speeds. With its newly granted permit, the carmaker plans to test this feature with a self-driving car equipped with side radar, cameras, and sensors on crowded streets at speeds below 50 km.
- On November 14, 2016, Samsung Electronics acquired Harman International Industries, for $112.00 per share in cash, or a total equity value of approximately $8.0 billion. The acquisition will immediately give Samsung a significant presence in the large and rapidly growing market for connected technologies, particularly automotive electronics, which has been a strategic priority for Samsung.
- On August Jan 8, 2018, Samsung unveiled DRVLINE, a hardware and software platform that will allow car makers to create customized, technologically advanced autonomous vehicles. Many platforms are an all-or-nothing solution, which forces users to adopt the entire package en masse, without any sort of customization. DRVLINE, however, allows vendors to swap and customize individual components, building the vehicle to their specifications, as well as allowing for rapidly evolving technology.
- On August 08, 2018, Samsung Electronics created a new team to study autonomous driving at its research lab Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology. Along with the firm’s automotive parts business unit, the team is expected to play a key role in leading Samsung’s renewed push for connected cars. The research lab usually studies early-stage technologies before their mass-market adoption.
- On September 14, 2017, Samsung announced that it has launched Samsung Automotive Innovation Fund, a $300 million fund to back startups and other interesting bets in the automotive market. And as a first investment out of that fund, Samsung has put €75 million (nearly $90 million) into TTTech, an Austria-based developer of platforms and safety software for connected cars, alongside a corresponding investment from Audi.
- On January 2, 2019, according to a report released by the European Patent Office (EPO), Samsung Electronics has filed the largest number of patent applications related to autonomous driving in Europe. Samsung was followed by two other semiconductor companies, which indicates that autonomous driving is emerging as a new battleground for semiconductor companies. According to the EPO’s latest report on patents and self-driving vehicles, Samsung Electronics filed 624 applications for patents related to autonomous driving between 2011 and 2017. It was followed by Intel (590), Qualcomm (361), LG Group (348), Bosch (343), and Toyota (338).
- On Dec 10, 2018, Samsung said that it is aggressively hiring software engineers specialized in autonomous driving technologies. The South Korean tech giant has been seeking experts in autonomous driving, an industry source said, with Samsung thought to be planning to kick-start new business officially as early as 2019.
- On December 6, 2018, Samsung announced that it has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Korea Transportation Safety Authority (KOTSA) to collaborate on next-generation telecommunication technology which will enable autonomous driving innovation across the country. Through the partnership, both entities will build 4G LTE, 5G, and Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) telecommunication networks and related IT infrastructures at K-City, a testbed for autonomous driving technology in Korea.
- On May 13, 2019, Samsung Electronics, a world leader in advanced semiconductor technology, announced that it has received the ISO 26262 certification for functional safety in automotive components from TÜV Rheinland, a globally renowned third-party testing, inspection, and certification company. The accreditation of Samsung’s new functional safety management system ensures that the company’s advanced automotive semiconductors, such as processors, image sensors, memory, and light-emitting diode (LED) solutions, satisfy the industry’s rigid safety standards throughout the product development process.
- On Dec 11, 2019, SK Telecom and Samsung announced the development of a 5G-based autonomous platform for testing the technology. Also featuring remote control capabilities, the test ship built by Samsung features 5G-based light detection and ranging (LiDAR), a cloud-based IoT platform, and real-time video monitoring from SK Telecom.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Mar 2021, Samsung was reported to have taken on the task of producing self-driving car chips for Waymo. Samsung’s involvement centered around developing a chip designed to process data gathered from the sensors integrated into self-driving vehicles. Additionally, this chip was expected to facilitate real-time communication with Google data centers, enabling centralized control over various functions. (Source)
- In Jul 2021, Samsung achieved the initial milestone in the creation of its inaugural lidar technology designed for autonomous driving purposes. This technology, previously undisclosed until that moment, was reportedly progressing toward a planned commercial release in 2026, as indicated by a new report from South Korea. (Source)
- In Oct 2021, reports indicated that Samsung had been identified as Tesla’s supplier for developing next-generation self-driving chips. According to industry sources, both companies were said to be collaboratively involved in the design and production of Tesla’s HW 4.0 chip, which was intended to enable advanced self-driving features in their upcoming vehicles. (Source)
2023
- In May 2023, according to local reports, the Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology (SAIT) conducted a successful “driver-free” test, covering the distance between Suwon and Gangneung in South Korea, which totaled nearly 200 kilometers. This test was made possible by creating a self-driving algorithm by Samsung’s R&D team, enabling the vehicle to operate without needing driver intervention. It’s significant progress toward developing a self-driving system that approached, or possibly achieved, Level 4 autonomous driving capabilities. (Source)
Huawei
Chinese telecommunication giant Huawei has shifted resources toward the development of autonomous vehicles in recent years. It has published a white paper explaining the ways in which mobile network operators could prove to be valuable to the connected car space. Some of these areas include smart parking, fleet management, data related to in-car entertainment, LTE-based emergency services, and more.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On Oct 12, 2018, Huawei announced that it will develop self-driving technology with Audi for cars that will be sold in China. The partnership will focus on creating so-called Level 4 technology, which the Society of Automotive Engineers defines as a car that completely drives itself from start to finish within a specifically designated area.
- On Dec 10, 2018, Huawei Technologies, its semiconductor subsidiary HiSilicon and RoboSense, a maker of lidar sensors used in driverless cars, became the first Chinese company to help establish an international non-profit group that supports open-source autonomous driving projects. The three firms are among the more than 20 founding members of the Autoware Foundation, which aims to promote collaboration between corporate and academic research efforts in autonomous driving technology.
- On Jan 25, 2019, Huawei submitted a patent for autonomous vehicles that could detect whether drivers are drunk or sleepy when getting behind the wheel. The patent was submitted to the European Patent Office and published on January 17, with an abstract of the submission suggesting that Huawei’s system can detect the condition of the driver and make a decision whether they can take control of the car or not.
- On April 27, 2019, China’s Huawei Technologies launched the world’s first 5G communications hardware for the automotive industry. The hardware signs its growing ambition to become a key supplier to the sector for autonomous driving technology. Huawei said in a statement that the MH5000 module is based on the Balong 5000 5G chip, which it launched in January. Based on this chip, Huawei has developed the world’s first 5G car module with high speed and high quality.
- On June 3, 2019, Huawei officially announced the establishment of its new department working on smart car solutions for vehicle manufacturers. The newly formed department will operate under the ICT Management Committee, and offer end-to-end smart mobility solutions including information and communication technology (ICT) equipment and applications to car manufacturers.
- On Jul 9, 2019, Huawei obtained a permit allowing the tech giant to draw up high-definition navigation maps in China, a move that will aid the development of simulation software for autonomous vehicles.
- On Oct 22, 2019, Huawei said that it will utilize its 5G technologies to develop radar for self-driving cars. As the Chinese manufacturer looks to play a bigger role in the auto industry, it seems to build an “ecosystem” of car-equipped sensors.
- On Nov 26, 2019, Huawei announced that it would use NavInfo Co. Ltd.’s high-definition map data in its autonomous cars. The prime reason for using their maps is to avoid a major hurdle. The main issue is Beijing considers the digital cartography of the country’s roads and infrastructure a threat to national security. As, the Chinese Communist Party doesn’t want private firms collecting data on bridge heights and road gradients. As such, only a handful of companies backed by huge Sino conglomerates like Alibaba and Baidu have been granted licenses to create high-precision maps. NavInfo also has a digital cartography license and can provide local firms with map data. Since having detailed topographical information is essential to compiling a functional self-driving artificial intelligence, Huawei needed a partner. Otherwise, it would need to endure a lengthy bureaucratic process to secure its mapping license. In this instance, the Sino handset maker chose the path of least resistance.
- On Nov 28, 2019, Huawei released its white paper on autonomous driving based on its core 5G network to advance the development and integration of 5G in the field of self-driving technology. Huawei aims to establish a set of standards for classifying autonomous driving levels by conducting an extensive analysis of customer experience, labor, and network complexity.
- On Jan 16, 2020, Huawei said that it’s deriving inspiration from Tesla for driverless car technology. Huawei has been working with various car companies to launch autonomous vehicles and could roll out in 2021. This could be the Chinese company’s move beyond the traditional telecom equipment industry to venture into a broader range of AI-based products.
- On March 19, 2020, Huawei made its autonomous driving cloud service platform (Octopus) operational at Xiangjiang New Area, Hunan province. Octopus offers driving data, training, and simulation services that can help automakers and other developers more rapidly develop autonomous driving applications, so as to speed up the commercial use of autonomous driving technologies.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Apr 2021, Huawei Technologies announced a significant investment of $1 billion dedicated to the research and development of self-driving and electric vehicle technologies. This move aimed to expedite Huawei’s competition with industry leaders such as Tesla Inc and Xiaomi Corp in the global automotive sector, the largest of its kind. During a briefing with analysts in Shenzhen, the rotating chairman at the time, Eric Xu, revealed that Huawei’s autonomous driving technology had already surpassed certain aspects of Tesla’s capabilities. For example, it enabled vehicles to autonomously travel over 1,000 kilometers (621 miles) without human intervention. Additionally, Eric Xu mentioned that Huawei had plans to collaborate with three automakers initially, intending to produce self-driving vehicles bearing the Huawei name as a sub-brand. (Source)
- In Apr 2021, the initial commercial passenger vehicle equipped with an autonomous driving system created by Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd. entered the pre-order phase. This marked Huawei’s determined entry into the automotive sector, a strategic move aimed at mitigating U.S. sanctions’ repercussions on its primary smartphone business. (Source)
- In May 2021, Chongqing Changan Automobile Co. Ltd. revealed a new identity for its subsidiary, which was set to collaborate with telecommunications and battery industry leaders Huawei Technologies and CATL to develop smart vehicles. This move reflected Huawei’s assertive entry into the smart car sector. The subsidiary, which was predominantly owned by Changan with a 95.38% stake and had a 4.62% ownership by Nio Inc., underwent a new name, i.e. Avatar Technology Co. Ltd. (Source)
- During Auto Shanghai 2021, Huawei unveiled its next-generation intelligent components and solutions, which included the 4D imaging radar, AR-HUD, and MDC 810. This announcement was made as part of Huawei’s product launch event titled ‘Focused Innovation for Intelligent Vehicles’ under the banner of Huawei Inside (HI). The primary objective of these products was to assist original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in constructing cutting-edge intelligent vehicles and to facilitate the Chinese automotive industry’s technological advancement, positioning it as a leader in new energy and autonomous driving. Huawei viewed intelligent automotive components as a long-term strategic opportunity and expressed its commitment to increasing investments in this domain, on advancing autonomous driving software development to establish a sophisticated autonomous driving system. (Source)
- In Aug 2021, Chinese automaker GAC Group and Huawei collaborated to develop a smart SUV scheduled for release in 2023. This electric vehicle deemed the “inaugural joint project” between the two companies, was designed to feature level 4 autonomy and innovative new energy capabilities. GAC was responsible for supplying the chassis, while Huawei focused on contributing expertise in computing and communication. Additionally, the partnership outlined their plans to introduce “eight models and multiple series” of electric vehicles in the future. (Source)
2022
- In Dec 2022, Huawei established lucrative agreements with several automakers, including Mercedes-Benz, Audi, BMW, Porsche, Subaru, Renault, Lamborghini, and Bentley. These agreements involved the licensing of Huawei’s technology patents. As a result, Huawei anticipated substantial revenue from these deals, with its technology projected to be incorporated into approximately 15 million of the 70 million cars manufactured worldwide. (Source)
2023
- In Apr 2023, Huawei introduced its second-generation automated driving system, ADS 2.0. A noteworthy technical aspect of this system was its capability to operate independently without requiring high-precision maps. Richard Yu, the CEO of Huawei’s Intelligent Automotive Solution Business Unit, emphasized that maintaining high-precision maps covering the entire country was unfeasible due to the continuously evolving nature of Chinese road conditions in real time. Consequently, an intelligent driving system without such maps was deemed more practical for widespread implementation. (Source)
- In May 2023, Based on data disclosed by IDC, Huawei, with automotive companies as its primary collaborators, emerged as the second-largest autonomous solution provider in the past. In 2022, it achieved an impressive revenue of 175 million yuan (approximately 25.3 million USD) and a substantial market share of 29.7%. This remarkable growth demonstrated Huawei’s progress in this field, and the company was actively advancing with its latest solutions. (Source)
Baidu
Baidu, which is also known as Chinese Google ramped up its autonomous car initiatives since 2014 when it opened its first AI lab in Silicon Valley. It has a dedicated Autonomous Driving Unit (ADU) that is based in Beijing and Silicon Valley and takes care of the company’s autonomous car efforts.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On September 22, 2017, Baidu put some serious cash behind its self-driving car push after it announced a $1.5 billion fund that’s focused on backing autonomous driving tech companies.
- On March 23, 2018, Automotive group Jaguar Land Rover and Chinese technology giant Baidu began new self-driving car tests this week, despite an autonomous Uber car killing a pedestrian in Arizona last weekend.
- On June 15, 2018, Honda Motor joined a consortium led by Chinese tech giant Baidu aimed at advancing autonomous driving technology, hoping to carve out a share as China races to become the world’s largest market for self-driving vehicles.
- On July 03, 2018, Chinese internet search leader Baidu tied up with SB Drive, a subsidiary of SoftBank Group, to enter Japan’s autonomous vehicle market. Both have been investing in autonomous driving and aim to marry their systems in a bus model that would go into testing by year-end. China’s Xiamen King Long United Automotive Industry will build the bus, currently called Apolong. The companies aim to ship 10 buses to Japan by 2019 and to begin commercialization later.
- On Oct 30, 2018, Baidu signed a partnership agreement with the Changsha municipal government to reshape the city’s transport infrastructure. The internet giant has announced plans to roll out a self-driving taxi and bus service in Changsha, the capital of southern Hunan province.
- On October 31, 2018, Ford and Baidu teamed up to develop self-driving cars in China. The US automaker and Chinese internet company said that they plan to start testing autonomous vehicles together on Beijing roads by the end of the year.
- On November 01, 2018, Chinese tech giant Baidu said that it will launch a fully autonomous passenger car next year in a partnership with Hongqi, or Red Flag, a brand used by China’s political elite.
- On Nov 1, 2018, Baidu announced that it is continuing its partnership spree for Apollo, its open development platform for autonomous driving after it inked a deal with Swedish automaker Volvo to develop level four self-driving passenger cars.
- On December 18, 2018, Baidu teamed up with the Unity gaming engine to help speed along with the development of self-driving cars, using simulations to gather test data on how the vehicles perform in 3D environments.
- On January 9, 2019, Baidu made several big announcements about Apollo, its open-source autonomous vehicle technology platform, at CES 2019. The first is the launch of Apollo Enterprise for vehicles that will be put into mass production. The company claims that Apollo is already used by 130 partners around the world. One of its newest partners, Chinese electric vehicle startup WM Motors, plans to deploy level 3 autonomous vehicles by 2021.
- On June 19, 2019, Baidu announced its new Apollo Lite system, which it says uses 10 cameras and no lidar or radar to achieve Level 4 autonomy. Baidu also claims that its cameras can detect and identify objects at distances of over 700 feet from the vehicle.
- On July 2, 2019, Baidu revealed that its fleet of 300 level vehicles across 13 cities recently achieved a major milestone: 2 million kilometers (1.2 million miles) driven autonomously in urban environments.
- On July 8, 2019, Baidu teamed up with Toyota and Geely to work on both self-driving tech and artificial intelligence, according to Reuters.
- On Aug 9, 2019, Baidu and Elektrobit (EB) signed a strategic partnership in which EB will provide automotive infrastructure software for the Apollo Computing Unit (ACU), Baidu’s advanced in-vehicle computing platform for autonomous driving. The ACU, an autonomous driving in-vehicle computing platform for mass production, is one of the most important products of Baidu Apollo, which is being developed with 156 industry partners including Chinese automakers.
- On Sep 27, 2019, Baidu launched Robo taxi services in the city about two years after Google’s self-driving unit Waymo started its pilot project in Phoenix, Arizona. The taxi services consisted of 45 autonomous cars expected to run initially on 50-kilometer-long open roads.
- On Dec 27, 2019, Baidu announced that it secured 40 licenses to test driverless cars carrying passengers on designated roads in Beijing, making it one of the first to do so in the Chinese capital. It also revealed that its self-driving cars have traveled more than three million kilometers (or about 1.8 million miles) during tests in 23 Chinese cities to date.
- On Jan. 7, 2020, Wind River®, a leader in delivering software for the intelligent edge, announced its collaboration with Baidu to develop an autonomous vehicle solution. A joint proof of concept has been developed to include an AUTOSAR Adaptive–based software architecture with Baidu’s Apollo autonomous driving open platform, designed to meet the specific challenges of the next generation of software-defined automobiles.
- On Mar 25, 2020, Baidu announced it received an RMB 52.8 million ($7.3 million) government contract to build an autonomous vehicle testing site within the Chinese municipality of Chongqing. The Chinese city of 30 million residents plans to be a leader in smart city technology that is powered by 5G networks. The 20-kilometer square test region will be fully equipped with vehicle-to-infrastructure communication technology using 5G networks.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Jan 2021, Baidu received approval to conduct testing of fully autonomous vehicles on public roads in California. Baidu became the sixth company to obtain a permit for conducting fully autonomous tests, joining others such as Cruise, Waymo, Nuro, Zoox, and AutoX. It was worth noting that, at that time, California’s Department of Motor Vehicles had issued active permits for autonomous vehicle testing with a safety driver to 60 companies. (Source)
- In Apr 2021, As per Global Times, Baidu initiated China’s inaugural self-driving bus initiative in Yongchuan, located in Southwest China’s Chongqing Municipality. This marked a significant milestone in China’s efforts to commercialize autonomous driving technology. The Robobus, measuring 5.9 meters long, was designed for autonomous operations on open roads. It could autonomously halt, navigate intricate urban road scenarios, and effectively fulfill the requirements for standard bus services. (Source)
- In May 2021, Baidu introduced fully driverless robotaxi services to the public in Beijing. This marked a significant milestone as it became China’s first paid autonomous vehicle service, allowing users to hail a robotaxi without the presence of a safety driver in control. The launch of the Apollo Go Robotaxi service in a fully driverless mode initially occurred in Beijing’s Shougang Park, designated as one of the 2022 Beijing Winter Olympics venues. Subsequently, this service was extended to transport visitors during the games, representing a noteworthy advancement toward commercializing autonomous driving technology. (Source)
- In Sep 2021, DeepWay, a company supported by Baidu, introduced Xingtu, an intelligent heavy-duty truck powered by new energy sources. This innovative truck boasted an impressive computing capacity exceeding 500 teraflops per second and exceptional long-distance sensing capabilities of over 1 kilometer. This launch had signaled Baidu’s entry into the expansive global freight market, valued in the multi-trillion dollar range. (Source)
- In Nov 2021, Baidu declared itself the world’s leading autonomous driving service provider following years of research and development in autonomous driving technology. The company planned to extend its autonomous services to additional cities. Baidu’s autonomous ride-hailing platform, Apollo Go, successfully completed 115,000 rides during the third quarter, solidifying its position as the world’s largest autonomous mobility service provider. Baidu CEO Robin Li made this announcement in an internal communication addressed to the company’s staff. (Source)
- In Nov 2021, Swiss Re partnered with Baidu to deliver risk management expertise and innovative insurance offerings tailored for Baidu’s autonomous driving ventures. The primary objective of this partnership was to advance the autonomous driving sector and establish a fresh industry framework. It allowed reinsurers like Swiss Re to customize insurance products specifically designed to cater to the requirements of technology companies operating in the autonomous driving space. (Source)
2022
- In Dec 2022, Baidu secured the first license permitting the testing of autonomous vehicles without a safety operator on board in Beijing. This development paved the way for introducing a paid, fully driverless robotaxi service in the capital city of China, following its successful implementation in Wuhan and Chongqing. Baidu has been actively expanding the operational area, fleet size, and operational hours of its commercialized fully driverless robotaxi service in the central Chinese city of Wuhan. The company had ambitious goals to establish the world’s largest fully driverless ride-hailing service area by 2023. To achieve this, Baidu had plans to deploy an additional 200 fully driverless robotaxis into operation during the same year. (Source)
2023
- In Mar 2023, Baidu’s Apollo obtained authorization to become one of the initial companies allowed to conduct tests of fully autonomous vehicles in Shanghai, which is China’s largest city. At that time, Apollo was already operating driverless robotaxi services in specifically designated regions within Wuhan, Chongqing, and Beijing. (Source)
- In Apr 2023, Baidu successfully obtained permits to provide a fully driverless robotaxi service in Beijing’s Yizhuang district. Notably, these vehicles did not necessitate the presence of human staff in the front seats to supervise their operations. This achievement represented a significant advancement in China’s endeavors to commercialize driverless technology. (Source)
Zoox (Amazon)
Founded in 2014, Zoox aims to provide self-driving ride-hailing services. Operating at the intersection of design, computer science, and electro-mechanical engineering, Zoox is a multidisciplinary team working to imagine and build an advanced mobility experience that will support the future needs of urban mobility for both people and the environment.
In 2018, Zoox became the first company to get approval to provide self-driving transport services to the public in California.
Zoox was able to collect $1 billion in funding with a valuation of more than $3 billion before Amazon bought the startup for $1.2 billion. And with this acquisition, Amazon suddenly became a reckoning force in the self-driving industry.
In Dec 2020, Zoox showcased its autonomous robotaxi. The car can travel up to 75 miles per hour and can run up to 16 hours on a single charge.

Source: CNBC
Further, it also has few features that set it apart from its competitors such as Waymo, Cruise, etc. It has bidirectional driving capabilities and four-wheel steering, which allows it to change directions without the need to reverse and navigate in compact spaces. Further, all its four seats are equipped with an airbag system.
The company plans to launch an app-based ridesharing service, with its first target markets being San Francisco and Las Vegas, according to a statement by Zoox executives.
With 1063 employees, Zoox is the 4th largest company working on self-driving technologies in the Bay Area.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Oct 2021, Amazon’s Zoox initiated testing of self-driving cars on the streets of Seattle. Jesse Levinson, the co-founder and Chief Technology Officer of Zoox, explained two primary reasons behind selecting Seattle as the new testing location. Firstly, Seattle was known as a hub for computer scientists, making it an attractive destination to attract local engineering talent.
Secondly, Seattle’s renowned inclement weather conditions were another factor in the decision. (Source)
2022
- In Oct 2022, Zoox’s CTO, Jesse Levinson, revealed that Zoox vehicles were equipped with four thermal cameras, each with a resolution of 640×480 pixels, positioned at the corners of the vehicle. These thermal cameras provided night vision capabilities and offered a vision that didn’t rely on ambient light from the sun or streetlights but emitted light from headlights or LIDAR technology. This unique feature endowed them with the ability to excel at detecting warm objects, including pedestrians, animals, automobile tailpipes, and warm tires. (Source)
2023
- In Jun 2023, Zoox announced increasing its workforce to expand its testing operations in Las Vegas. This expansion occurred when regulatory considerations had gained significant importance in the development of autonomous vehicle technology. Since June 16, Zoox has been actively conducting tests of its driverless robotaxi on the public roads of Las Vegas. The company’s headcount had grown to approximately 2,200 employees, up from 1,900 at the beginning of that year. (Source)
- In Jul 2023, Zoox initiated testing of its purpose-built, electric, autonomous robotaxis on public streets in Las Vegas. According to the company’s announcement, this event marked the first instance where an autonomous vehicle, designed without pedals or a steering wheel, had been operational on public roads in Nevada. (Source)
Aurora
Aurora was already a well-known autonomous vehicle startup but after it acquired Uber’s self-driving unit, the startup’s position further bolstered as it gained the experience of its top autonomous contenders. Aurora’s co-founders were the ex-employees of Waymo, Tesla, and Uber, which is one reason why the startup collected $1.1 billion in funding. Moreover, Amazon also backed the startup before acquiring Zoox.
One of the highlights of Aurora is its hardware and software that can be custom-fitted to present non-autonomous vehicles to turn them driverless. Unlike Zoox, Aurora is not aiming to make a self-driving car from scratch.
Other than cars, its hardware and software combo also work for mobility, and logistics services.
Aurora’s full-stack solution called “Driver” that allows vehicles to be autonomous isn’t the only solution they plan to offer. In July 2020, Aurora announced their plans for its autonomous truck.

Among many partnerships the startup has, its most important one is with Fiat Chrysler to build autonomous platforms for commercial vehicles.
Post-COVID Activities
2021
- In Feb 2021, Aurora entered into an agreement with Toyota and the automotive parts supplier Denso to collaborate on developing and testing vehicles integrated with the self-driving technology offered by the startup. The initial focus was on a fleet of Toyota Sienna minivans. Engineering teams from both Aurora and Toyota collaborated closely to design and manufacture these self-driving Sienna minivans. The goal was to commence testing this fleet by the conclusion of 2021. (Source)
- In Feb 2021, Aurora acquired OURS Technology, marking the second lidar startup it had purchased in under two years. The earlier acquisition had been Blackmore, a lidar startup based in Montana, which Aurora had acquired in May 2019. (Source)
- In May 2021, Aurora announced its intentions to extend its testing efforts across Texas in the past. This move was part of the company’s ongoing efforts to bring self-driving trucks closer to commercialization. In a blog post, Aurora revealed its plans to enhance collaborations with shippers and motor carriers, intending to refine its autonomous Aurora Driver technology to meet their specific requirements and effectively navigate highway traffic. (Source)
- In Sep 2021, PACCAR entered into a partnership with Aurora and FedEx to initiate a commercial pilot program involving autonomous trucks for linehaul trucking operations. This collaboration was notable as it marked the first of its kind, bringing together a truck manufacturer, an autonomous technology developer, and a logistics provider. (Source)
- In Oct 2021, Aurora introduced its inaugural commercial beta version of the Aurora Driver, comprising the necessary hardware, software, and data services for the secure operation of autonomous vehicles powered by Aurora technology. The Aurora Driver Beta had been actively transporting cargo between Dallas and Houston, Texas, as part of a commercial pilot program for Aurora Horizon. Aurora Horizon offered a range of subscription services aimed at assisting carriers and fleet owners in the safer and more efficient transportation of goods. (Source)
- In Dec 2021, Aurora announced that its self-driving trucks had been transporting goods for Uber Freight customers in Texas as part of a multi-phase commercial pilot program. This initiative aimed to achieve a deeper level of integration between the two companies. Aurora’s self-driving trucks, which always operated with two vehicle safety operators onboard, had been collaborating with Uber Freight for approximately a year before the announcement, as confirmed by a spokesperson. (Source)
2023
- In Jun 2023, Aurora publicly unveiled the Aurora Multi-Sensor Dataset, a comprehensive dataset developed in collaboration with the University of Toronto. This dataset included valuable localization ground truth information. It featured extensive metadata, encompassing diverse weather conditions across all four seasons, such as rain, snow, overcast, and sunny days, along with various times of day and traffic scenarios. Notably, it surpassed the scale of other publicly accessible localization datasets by one to two orders of magnitude, serving as a valuable resource for developing and assessing large-scale, long-term autonomous vehicle localization techniques. (Source)
- In Jul 2023, Aurora completed a stock sale amounting to $820 million to bolster its initiatives aimed at commercialization. This capital raise occurred approximately two years after Aurora had made its public debut on the Nasdaq by merging with a SPAC. (Source)
AutoX
Founded in 2016 by Jianxiong Xiao, AutoX made quite a name as it hit the road in China. AutoX aims to provide autonomous ride-hailing transportation services with its AI drivers capable of driving a vehicle.
The startup is backed by Alibaba Group and collected $160 million in funding from investors like Dongfeng Motor.
AutoX has been operating self-driving taxi pilots in both the US and China. In July 2020, it got the driverless testing permit in California without a human driver making it the third company to get the permit besides Waymo and Nuro.
In 2021, it became the second company to offers its driverless robotaxis for the public (in Shenzhen) without a driver in the vehicle.

Source: AutoX
AutoX opened an 80,000-square-foot Shanghai Robotaxi Operations Center in April 2020, following a 2019 agreement with municipal authorities to deploy 100 autonomous vehicles in the Jiading District.
AutoX is involved in multiple partnerships with automakers, lidar, semiconductor, and other self-driving solution companies. Some of its important partnerships are with Fiat Chrysler, BYD, SAIC Motors, Mediatek, Nvidia, etc.
Its most recent collaborations include its partnership with Honda to develop self-driving tech for China’s road and traffic in April 2021. In the same month, it also partnered with an Israeli company Arbe Robotics to integrate its 4D imaging radar chipsets for ADAS in AutoX’s Level 4 vehicles.
Yandex
Touted as the Russian rival to Google for its search engine and other capabilities, Yandex also has a self-driving wing that is working on a Robotaxi project. The company launched its robotaxi prototype in 2017 and in 2018, it got the license to use its self-driving cars on public roads in the US (Nevada) and Israel.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- In 2019, Yandex announced that it has covered 1 million miles in autonomous driving mode, making it the 5th company to achieve this milestone.
- In December 2019, Yandex introduced in-house lidar systems for its self-driving vehicles. The company is supposedly working on two types of lidars. The first is a solid-state lidar, which has a 120-degree field of view and can provide a highly detailed view of objects in front of the vehicle. The other lidar provides a 360-degree view to create a detailed model of the car’s entire environment.
- In March 2021, the company announced that it completed the milestone of driving 6 million miles in fully autonomous driving mode.
Service Providers Working on Autonomous Vehicles
Didi Chuxing
Didi Chuxing is one of the largest transportation networks in China. The company is also expanding its business in other parts of the world such as Southeast Asia, India, and Brazil. Presently Didi Chuxing is shifting its gear towards self-driving cars.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On May 2, 2018, Chinese ride-hailing giant Didi Chuxing approached an agreement with Volkswagen to deploy a “purpose-built” fleet of VW vehicles in its home country. As part of the joint venture, the German carmaker would provide around 100,000 vehicles, electric and autonomous vehicle technology, and manage the fleet.
- On May 14, 2018, Chinese ride-hailing group Didi Chuxing was given the go-ahead to start testing self-driving cars in California, as it looks to catch up with its Silicon Valley rivals’ earlier start in autonomous systems.
- On 26 Jun 2019, Chinese ride-hailing giant Didi Chuxing said that it would expand its partnership with Guangzhou Automobile Group Co Ltd (GAC Group) to areas such as ride-hailing operations and autonomous driving. China’s largest ride-hailing firm and Guangzhou-based GAC Group will work on fleet expansion and management, development of new mobility products, and collaboration on smart driving, including autonomous driving technology, Didi said in a statement.
- On Jul 25, 2019, Didi Chuxing announced that it has closed a $600 million investment deal from Toyota Motor Corporation to jointly offer auto services for ride-hailing drivers on Didi’s platform. The deal marks a big step forward for Didi, which seeks closer ties with traditional automakers to extend its dominance in the Chinese ride-hailing market.
- On Aug 5, 2019, Didi Chuxing announced that it had spun off its autonomous driving unit into an independent company. The move may be part of efforts to refine its business structure ahead of a much-rumored IPO.
- On Mar 24, 2020, Softbank reported to be expanding its commitment to Didi and is on the edge for a deal of $300 million investment into the ride-hailing startup’s self-driving unit for an undisclosed valuation.
- On Apr 16, 2020, Didi Chuxing joined AutoX to launch its own autonomous ride-hailing pilot projects. According to a TecNode report, two sources familiar with the matter hinted that the pilot projects will commence in late May on the outskirts of Shanghai.
RideCell
RideCell offers transit software to the mobility industry. The company provides a software platform for companies offering service and applications on autonomous vehicles.
Strategic Initiatives and Achievements:
- On Oct 9, 2017, Ridecell, the leading global platform for carsharing and ridesharing operators, announced the acquisition of Auro, a California-based developer of autonomous vehicle technology, in an all-stock transaction. Ridecell also announced the public availability of its autonomous operations platform which has successfully been used in autonomous pilot programs. With these two initiatives, Ridecell now offers the industry’s first complete autonomous new mobility solution that enables on-demand autonomous shuttle mobility service in low-speed, private-road settings.
- On 26 Oct 2018, Ridecell announced that its self-driving vehicle division, Auro, is now licensed to test autonomous vehicles on public roadways in California.
- On November 13, 2018, The San Francisco startup, Ridecell, announced an extension of the $28 million Series B round it completed in May that more than doubles the amount raised to over $60 million.
- On Dec 10, 2018, DeepMap, a leading provider of high-definition (HD) mapping and localization technology for autonomous vehicles announced licensing deals with Swedish trucking company Einride and Ridecell. Both companies are integrating DeepMap’s software into autonomous fleets.
- On April 30, 2019, Ridecell Inc., the leading platform for shared and autonomous mobility operators, and Dataspeed Inc., a globally established drive-by-wire solution provider, announced a strategic partnership to enhance autonomous vehicle (AV) safety. The companies will begin leveraging each other’s technology and testing new technologies in real-world conditions to improve vehicle safety.
Autonomous Vehicle Patent Landscape
It has been more than a decade since autonomous driving vehicles became a topic of research, not only for automakers but for tech companies as well. To find the amount of innovation done by a company, market research is a natural choice. However, when combined with patent analytics, it can give you hidden insights that are difficult to find solely in market research.
With this logic, we analyzed the patents of autonomous driving solutions for the last 12 years. The figure below illustrates the patent filings of autonomous driving solutions from 2007 to 2018.
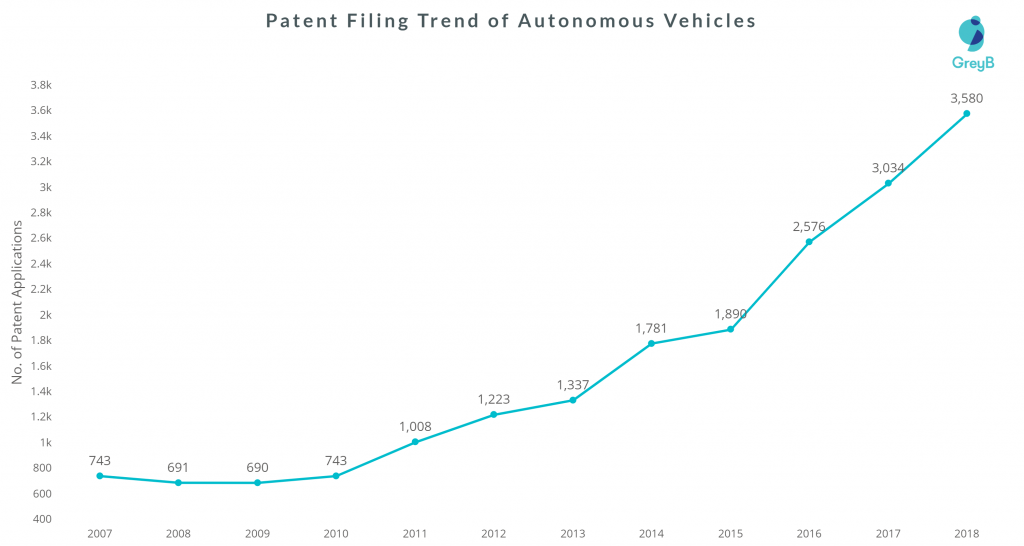
It is evident from the figure that the trend is going upward as companies are getting more aggressive in securing their autonomous driving inventions.
Like the Telecom industry, Autonomous driving is also a domain that involves SEPs. So, it’s only natural that companies would want to secure as many patents as they could. Although, in this case, the criteria might be different than what Telecom standard bodies use, the concept of SEP would be the same, i.e. as a great source of revenue.
Companies with most Autonomous Driving Patents
Toyota and Ford are having tough competition while GM is slightly behind them. The top three companies have considerable patents in their portfolio while the rest of the top ten companies are quite behind.
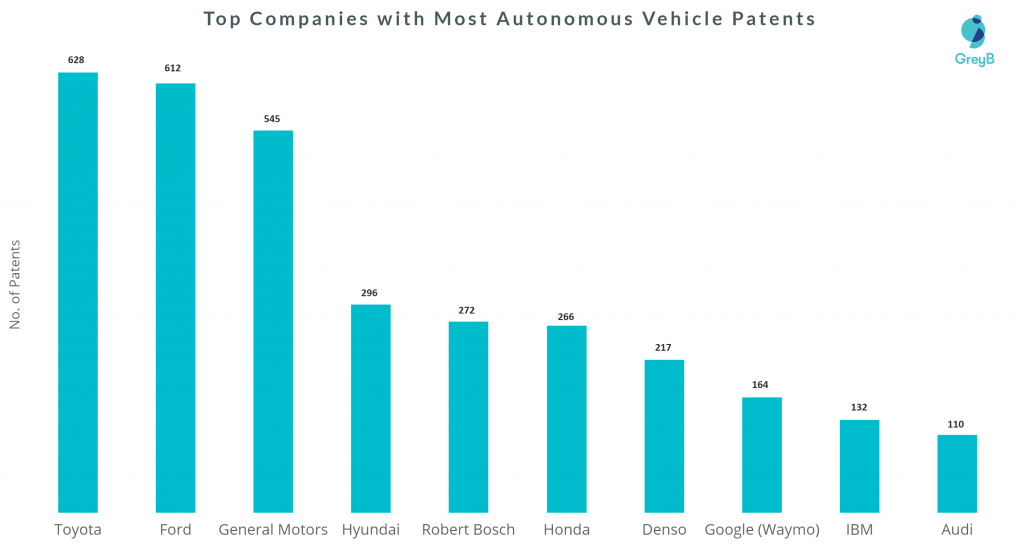
The list contains only two technology companies, i.e. Google (Waymo) and IBM. While Google being on the list makes sense yet IBM doesn’t seem much in the news related to autonomous vehicles. But being a pioneer in AI, it is safe to assume that IBM has the capability to research the technology and thus secured a good number of patents related to driverless technology.
However, it is safe to say that the patent landscape is largely dominated by car manufacturers and tech companies are struggling to make their place in the top players’ list.
Car manufacturers learned from the mistakes of others and thus are able to prevent other industries from infiltrating the autonomous driving industry. But given that the industry is still developing there is a chance for the tech companies to secure a profitable position in the driverless market.
There are a number of notable startups working on autonomous driving solutions that car companies can and have been utilizing. But tech companies still need pioneer car companies and their advanced vehicles for trials and testing.
We have seen many partnerships where tech companies work together with automakers but those tech companies are small in numbers.
So, it is crucial for tech companies to know the strength of others to make a fool-proof strategy that can help the company to get recognition in the autonomous driving field.
The same can be said for service providers that are working on autonomous vehicles and solutions.
Note: This is just an overview of the patent landscape of the autonomous driving solutions. To get the actionable insights, you would need a deeper patent landscape study along with the market research that can help you know your position in the market compared to others and what actions could make you geared up to the list of top players..
For a more detailed description:

Autonomous Vehicle Leaders
A Guidehouse Insights report examines global participants’ capabilities in the emerging automated driving systems (ADS) market. It explicitly assesses companies working on Level 4 ADS for light to medium-duty vehicles. According to a Leaderboard report from Guidehouse Insights, Mobileye, Waymo, Baidu, and Cruise are respectively leading ADS.
Government Regulations
United States
The federal government has released its first rulebook on the manufacturing and sale of autonomous vehicles in 2016, September. Under the rule, the federal government has precisely mentioned to autonomous car manufacturers to share a wide amount of statistics with the federal government. On the other hand, it is uncertain whether the companies will share data with the government. The government also has stated to address 15-points on security assessments including how the vehicle’s software will address on road during accidents and ethical situations and other basic details like how these cars function, how they record statistics, what happens when a car crash, what will be the protective measure against hacking, and so on.
Driverless and semi-autonomous cars have already entered the US market which is compelling the federal government to set up a law on autonomous vehicles. Companies like Tesla have already sold around ten thousand electric cars with a self-driving feature called autopilot. Uber started its test run rides from driverless cars by their smartphone application. Big technology giants like Google and Apple engaged in a test of self-driving cars.
Below are the few points which an eventual bill might do:
- The existing automotive laws and regulations revised where a driver is behind the wheel operating the motor vehicle. The updated vehicle standards may no longer require a driver behind the wheel. It is possible that the new rule would remove the requirement of pedal or steering of cars.
- There is a constitutional confusion raised in distinguishing fully vs. semi-automatic vehicles. In recent times Uber went into a clash with the State of California over the description of “autonomous”, where the state precisely mentioned that Uber’s test is unlawful. Clearing up such terminology-based communication would avert any confusion on both semi and fully autonomous vehicles.
- The government might make standard rules and regulations on a physical and technological standard for autonomous vehicles, related to the laws currently implicit on traditional vehicles.
Europe
Research has been commissioned by the German Federal Ministry of Economics, where it is projected that the driver assistance system and automated vehicles market value would be EUR 8.8 billion and shall generate 130,000 jobs by 2025 in Germany.
Considering the advantage forecasts the law is turning towards the use of automated vehicles in Europe. As a result, the British government is designed to change the national law by summer 2017, to enable the development of autonomous vehicles. The British government is also looking forward to improving internal law by the end of 2018.
The basic requirements of automated vehicles are legal permits on the use of public roads. Any vehicles sold in the EU member state needs EC type approval. The latest ECE 79 guideline contains the necessity of steering in a vehicle which an issue for automated vehicles. The regulation states in paragraph 2.3.4 that an “Advance Advanced Driver Assistance Steering System” is only permitted to control the steering as long as the driver remains in primary control of the motor vehicle at all times. Also in paragraph 5.1.6, it is stated that such systems “shall be designed such that the driver may, at any time and by cautious action, override the function”. The future ECE Regulation 79 may have five primary specifications on automatically commanded steering function (ACSF).
- Automatic parking system
- Automated steering function
- Extend the functionality covered by B, such as single maneuver
- System function that can be initiated and executed after the driver’s confirmation
- System function initiated and executed by a driver will continuously determine the maneuver and complete them
Among the other countries in Europe, Germany and the UK intend to take pioneer in an autonomous vehicle. However, it remains to be seen when and how quickly the amendment of ECE Regulation 79 is amended for an autonomous vehicle.
Asia
Asia is one of the rising testing grounds for autonomous vehicles. Countries like Singapore and other developed Asian countries support such initiatives by providing logistical, financial, and operations support for automated vehicle investors.
In February 2017, the Singapore Road Traffic Act (STA) was amended and authorized the Land Transport Authority (LTA) to keep pace with automated vehicle trials. According to the second minister of Singapore transport Ng Chee Meng, the government will create new rules on artificial vehicle trials, standard car design, and data sharing from the trials.
In China, the Ministry of Industry and Information and police is formulating rules on autonomous vehicles. However, the government has warned the car makers not to test any self-driving vehicles on the highways before the regulations are released.
The Japanese government plans to draw regulations on the use of autonomous vehicles. However, the National Police Agency will consider who will be responsible if any accident happens with driverless cars. The government is also planning to release the legal policy quickly so that the car manufacturers can initiate test runs on the road. The government has classified autonomous cars into five categories, including self-driving cars that do not require any driver or steering wheel and assist a few functions, such as acceleration and braking, during autonomous driving. The car manufacturers and the government are working together to set up a platform for driverless cars that would eliminate accidents caused by human errors or reduce traffic issues.
Future Outlook
Covid-19 Impact
The pandemic was not only harsh for self-driving but also for the automotive and ride-hailing industry. Even Pilot testing was stopped for more than 6 months. However, there was a blessing in disguise for the AV industry.
In the pandemic, taxi services saw a huge decline as people remained indoors. Even after people started going outside, most opted for personal vehicles.
As per McKinsey, “20% of people in the United States who do not currently own a vehicle are now considering purchasing one. This group largely includes city dwellers who often move around town on buses, trains, and through taxi-cabs or rideshares.”
But in the same period, the delivery services saw a huge spike as people shopped online for food, groceries, and other items.
AV technology can fundamentally change how goods move from warehouse to storefront, meals from restaurants to our front door, and how our packages get delivered from retailers to our mailboxes.
While COVID-19 may have interrupted the development of AV technology, it has also increased the potential for further adoption of this technology in other spaces.
Fully Autonomous Vehicles are Years Away
Industry heads, including Elon Musk, have promised to provide fully autonomous vehicles many times. But it is obvious that Fully Autonomous or Level-5 autonomous vehicles are years away.
Companies have poured over $100 billion in R&D but the success is nowhere to be seen. Even leaders such as Waymo are providing their services in very limited cities.
There are over 60 companies that applied to get the permit to test their driverless vehicles in California. Still, only 6 companies got the license to test their vehicles without drivers on public roads.
So while the testing is still ongoing, it would take more than a decade for these vehicles to adapt to public roads of different cities. Because different cities have different traffic situations.
China is Growing at a Faster Pace
Unsurprisingly, China is giving tough competition to the US for every major technology- AI, 5G, or self-driving.
Chinese companies are growing at a faster pace, and some of these companies don’t have big funding and resources like Waymo (Google), Zoox (Amazon), and Cruise (GM). Among them is AutoX, a China-based startup headquartered in San Francisco. The startup is one of the 6 companies that got the permit to test its vehicle on public roads in California. With Baidu, there are 2 Chinese companies to have that permit.
Further, Chinese government policies provide support and a framework to facilitate the development of the AV industry in China. The National Development and Reform Commission published a report on smart vehicle development strategy in February 2020, targeting mass production of L3 autonomous vehicles by 2025.
China is leading in 5G, which is a fuel for connected vehicles. Thus, the country has the infrastructure to develop better in this tech compared to other nations.
Chinese startups are the backbone of its AV market, and with the amount of funding they have got, it seems investors are optimistic about them.
Tough to Survive Industry
The autonomous vehicle has become a tough industry to survive in. Even big companies like Uber and Lyft were forced to sell their self-driving units as bringing investment becomes harder and the cash flow is limited.
Despite billions in investment, they haven’t had much success. And the most affected are startups even if the research is going well. Waymo, which once valued at $200 billion now has a valuation of $30 billion.
Zoox despite having a valuation of more than $3 billion sold to Amazon for $1.2 billion just because they couldn’t bring more investors. And with the ongoing pandemic, Zoox was forced to sell itself for the mutual benefits of both entities.
Autonomous Trucks has a Better Chance of Becoming A Reality than Cars
Most of the autonomous vehicle companies are planning to launch robotaxi services. Over the years, the industry and experts realized that driverless taxi is a tough market to crack. The involvement of urban areas makes the challenge more complex for self-driving cars. Further, taxis are time-bound as customers are often in a hurry, and self-driving will surely lose customer attraction if self-driving fails to reach the destination in time.
On the other hand, trucks are mostly used for cargo deliveries and use highways. Trucks normally restrict themselves to stay on a lane and can make smart and necessary decisions on highways. Also, the highways are the same unlike the urban environment of different cities, so there won’t a need for pilot testing for different cities’ highways. And most importantly, they are not time-bound as taxis so, there would no 1-star rating from the customer side.
Car Companies haven’t Lost the Battle to Tech Companies
If you have seen many leaderboards, you would see that tech companies are leading the autonomous driving market. It makes one wonder if the car companies have lost the AV race. Well, no.
ITech companies and some startups have a good share of the AV market, but plenty is left for car companies.
Car companies know that the progress is slow, so most opt for partnership and acquisition rather than working on themselves. And with the speed at which companies and startups are leaving the battlefield, car companies would have enough spoils of the war.
Moreover, tech companies can’t manufacture cars on a large scale. And very few startups are making their vehicles from scratches, such as Nuro and Zoox. So, car companies will always need to provide vehicles, and tech companies can provide their AI drivers to run those.
Car companies are focusing on EVs rather than AVs
Unlike tech companies, Automakers need car sales to stay in the game. And knowing that a fully autonomous vehicle is years away, car companies are focusing on the next big thing in the automotive industry, i.e., the Electric Vehicle. With the success of Tesla and other EV startups, traditional automakers are finally ready to big their Electric vehicles in the market.
These automotive companies are focusing intensely on EVs rather than AVs, which makes sense considering their business model. EVs are a bigger necessity than AVs, not just for automakers but even for the general public.
With the global temperature rising every year, carbon consumption is increasing, and the amount of fuel is decreasing, electric vehicles do not just save the environment but the general public money as well. Fuel and gas price has surged throughout the world, especially in Asia. The EVs are one of the few solutions to this problem.
Automotive companies have already shared their motives to invest billions in EVs and their mission to make their vehicles’ carbon-neutral. Some of them even launched EVs, too.
Source: Forbes
Conclusion
It is fair to say that companies must make much progress to keep investors optimistic. Because even big companies like Google or Amazon can’t spend billions yearly. Ultimately, they would need external investments to keep the research going.
Waymo is one example seeking to raise $4 billion from outside investors. And if Waymo needs external help, you can guess how others would be doing.
Whatever the future holds for the AV industry, it is clear that in some areas, such as logistics and food & grocery delivery, autonomous delivery makes more sense, especially after the post-Covid world.
Have a query related to the Autonomous Vehicle industry or want exclusive information, contact us.