In recent years, Airbnb, the global hospitality disruptor, has been quietly but persistently venturing into a new domain: social networking. While Airbnb is known for its innovative approach to hospitality, its patent filing data suggests an intriguing pivot toward a more interconnected digital landscape-
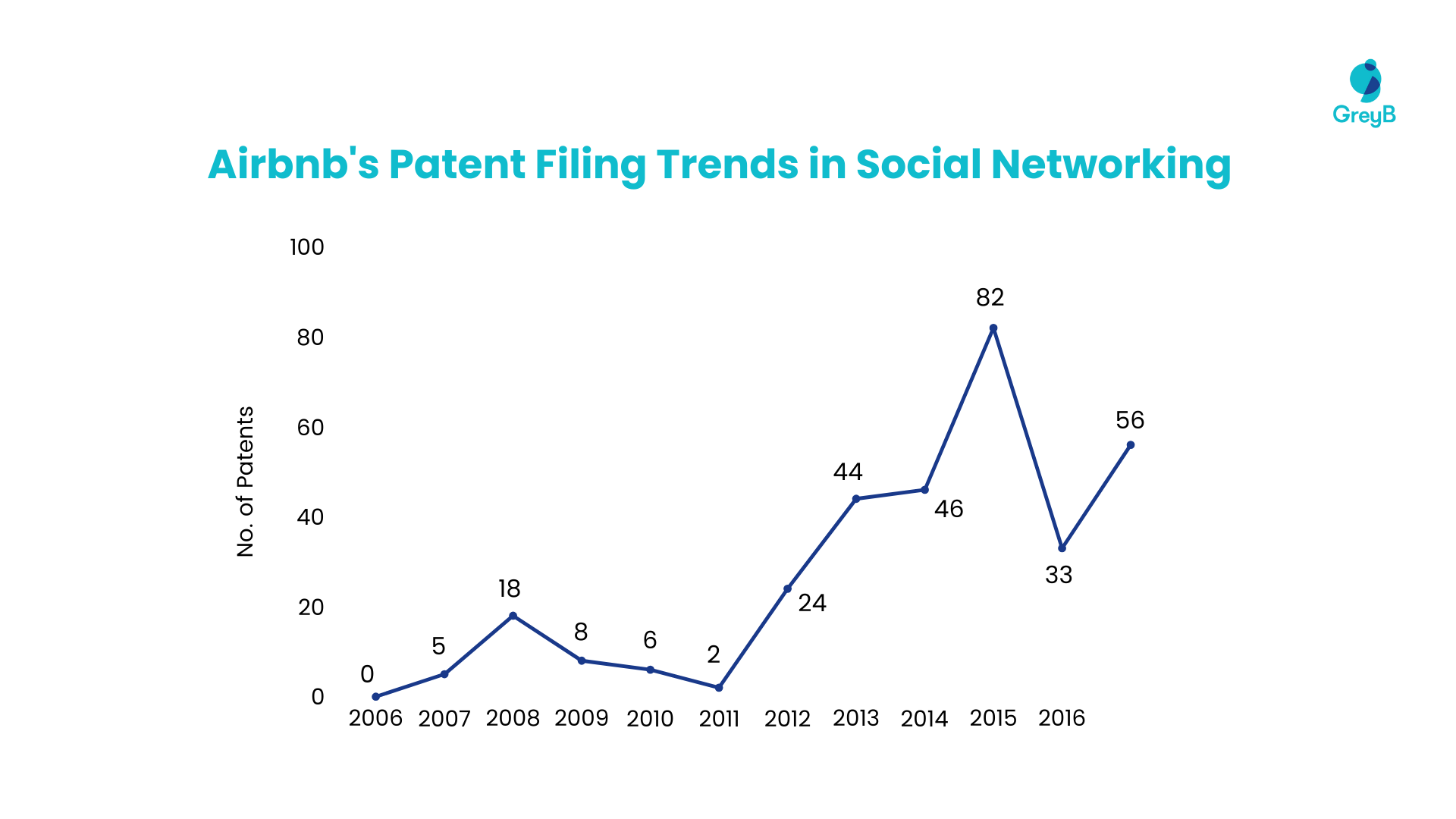
Since 2011, AirBnB has been filing more patents in the social networking domain. An analysis of their activity shows that these patents are blocking the patents of large tech companies such as IBM, Microsoft, Google, and Meta.
Eventually, this study decodes the types of rejections that the patents of these giants face and the abandonment rates over time. There is a clear indication that AirBnB is a significant threat to other players in the social networking space.
How are Airbnb’s patents strategically blocking tech giants?
Airbnb has patents in the social networking domain that effectively lock horns with tech titans like IBM, Microsoft, Google, and Meta (formerly Facebook).
For instance, Airbnb’s patent US8412645B2 discussed the identification of unwanted online users using content analysis, which has blocked IBM‘s US10230677B2 and Sony‘s US11358066B2. Additionally, their patent, US8224755B2, discussed “controlling access levels based on social connections in collaborative spaces” and blocked Google‘s US9465505B1 and Intuit‘s US20150341357A1.
This signifies the strength of Airbnb’s patents and why its substantial transition into an increasingly interconnected digital world cannot be underestimated.
What do rejection trends by Airbnb indicate?
Examining the kinds of patent applications AirBnB’s patents have caused rejection to over time is crucial to fully understanding this company’s venture into social networking. This provides insights into the evolving standards Airbnb sets in this dynamic field and its connections with intellectual property from industry giants.
These rejections position Airbnb as a direct competitor in social networking, offering valuable insights into its strategic position and significance.
One crucial insight emerges from examining rejection types: the divergence between two rejection categories – 102 and 103.
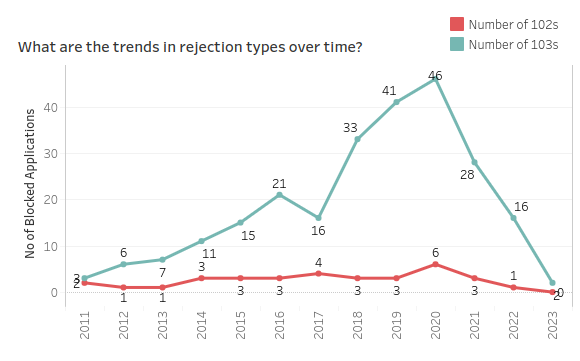
While 102 ensures no innovation overlaps with Airbnb’s existing innovation, 103 stresses the need for inventive ideas that go beyond the obvious for skilled individuals in social networking.
Initially, Airbnb handed out only a small number of rejections in this domain. However, the landscape has changed over time. By 2020, there was a marked increase in rejections under this category by AirBnB’s patents—up to 46. This indicates that Airbnb has elevated the benchmark for what is considered inventive, suggesting a higher industry innovation threshold.
As Airbnb establishes itself more prominently in social networking, its competitors face more stringent examinations and higher standards to prove their innovations. These requirements are not only about novelty but also about being non-obvious to industry experts, a challenge intensified by Airbnb’s presence in the market.
How does Airbnb’s strategy impact patent abandonment rates?
The evolution of the abandonment rates for applications blocked by AirBnB narrates an interesting story. These metrics provide insights into the challenges faced by those trying to innovate in the social networking domain and the threat Airbnb’s patents pose.
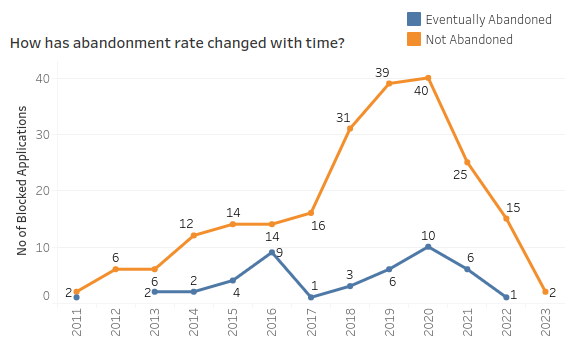
Over the years, consistent abandonments have indicated a pattern of challenges encountered by those seeking to innovate in areas overlapping with Airbnb’s interests.
What challenges and opportunities does Airbnb face?
While Airbnb has sought significant opportunities in the domain, it faces formidable challenges when competing with industry giants like IBM, Microsoft, Google, and Meta.
The first significant challenge is distinguishing itself amidst these giants’ vast, established user bases and advanced platforms. The market has many experienced players, making it tough for newcomers to attract users because of high expectations and the already wide range of social networks.
Nevertheless, Airbnb possesses unique opportunities to innovate. This includes cultivating a niche social network centered around travel experiences and leveraging its global presence. Additionally, integrating seamlessly with its current offerings creates a distinctive, travel-oriented social ecosystem that could resonate with modern, experience-seeking users.
Conclusion
Despite the obstacles, Airbnb persists, signaling its determination to shake up the competitive landscape.
This surprising strategic move promises to impact operations and collaborations across travel and hospitality, driving companies to reevaluate integrating social connections into their platforms.
As we reflect on Airbnb’s bold move, it becomes intriguing to anticipate their next steps. This is a reminder that companies from diverse domains may attempt similar moves, underscoring the importance of being prepared and developing patent-centric business strategies to foster innovation in this evolving landscape.
Strengthen your position in the competitive market by exploring your competitor’s market interests and targets with minimal effort, staying one step ahead in the game.
Authored By – Jogeshwar Singh, Product Development Team
Edited By – Ridhima Mahajan, Marketing