The development of VVC and next-generation video codecs focuses on two key issues: enhancing bitrate efficiency and reducing device dependency. By improving bitrate efficiency, these new codecs aim to deliver high-quality videos with better resolution, using less internet bandwidth. Additionally, they seek to minimize decoder-level dependencies, enabling the seamless integration of new algorithms across various devices.
As a solution, AI has become crucial in maintaining video quality after decoding, particularly with the integration of neural networks (NN) in next-generation video codecs. However, the uneven adoption of NN technology across companies poses significant challenges. Without a clear understanding, businesses risk unforeseen product infringements, increased litigation, weakened patent portfolios, and missed opportunities for patent licensing.
With the analysis of recent JVET meeting contributions and parallel patent filings related to NN implementation in next-generation video codecs, we identified the areas where innovation is concentrated and the companies leading these efforts. By understanding these developments, you can tackle potential patent infringements and litigation risks while also strengthening your patent portfolio, enhancing licensing strategies, and securing a competitive edge in the VVC.
Hot Zones of NN-implementation in Video Codecs
In our study of ITU-T standards, particularly JVET meetings from 2020 onwards, we identified two major directions in NN-based implementations: Loop Filtering Techniques (NNLF) and Post-Processing Techniques (NNPF). These implementations can be broadly categorized into NN-Based Loop Filtering and NN-Based Post-Processing Filtering.
While other NN-based implementations, such as enhanced compression, CNN-based super-resolution, motion estimation, and buffering management, are being explored, NNLF and NNPF have emerged as the most extensively discussed and experimented topics. Companies like Qualcomm, Tencent, Bytedance, Alibaba, Oppo, Nokia, and LGE have actively participated in these experiments. By examining their patent portfolios, we identified relevant NN-implementation patents and the jurisdictions where they were filed.
These patents primarily focus on NNLF, NNPF, and motion compensation or prediction techniques. Our analysis revealed disparities in filing trends, with China and the US emerging as the top jurisdictions for patent filings in this domain since 2020. Let’s look at the companies driving innovation in these regions.
China’s Dominance in NN-implementation in Video Codecs
Chinese companies, including Tencent, Bytedance, Huawei, and Sharp, have invested significantly in developing NN-based video coding technologies. Some companies, such as Lemon Inc. (a Tencent subsidiary) and Beijing Dajia Internet Information Technology (a Bytedance subsidiary), have parallel filings, further strengthening China’s position.
Over time, these codec software companies have collaborated with universities for research. For example, Tencent has partnered with institutions like Tsinghua University, Harbin Institute of Technology, and Huazhong University to enhance processing capabilities and gather video datasets. These collaborations have led to research papers on topics such as A Neural Network Enhanced Video Coding Framework beyond ECM, Neural Network Based Rate Control for Versatile Video Coding, Interweaved Prediction for Video Coding, etc.
In the US, Qualcomm, Interdigital, and Alphabet are the leading players, highlighting a competitive landscape in video coding innovation. Qualcomm, in particular, has made significant contributions to NN-implementation patents. Our rough estimation indicates that Qualcomm accounts for 60% of the top 10 companies filing US applications in this domain.
Despite multiple university collaborations in the US, such as those involving Qualcomm’s 5G research and Google’s Developer Student’s Club, there appears to be fewer targeted collaborations specifically for video codec development. However, deeper networks and collaborations may still be in the pipeline, poised to drive future innovation.
Our analysis of patent filings since 2020 shows that over 60% of the patents have been filed in China, compared to the US. The strong association with universities could be a contributing factor to this distribution.
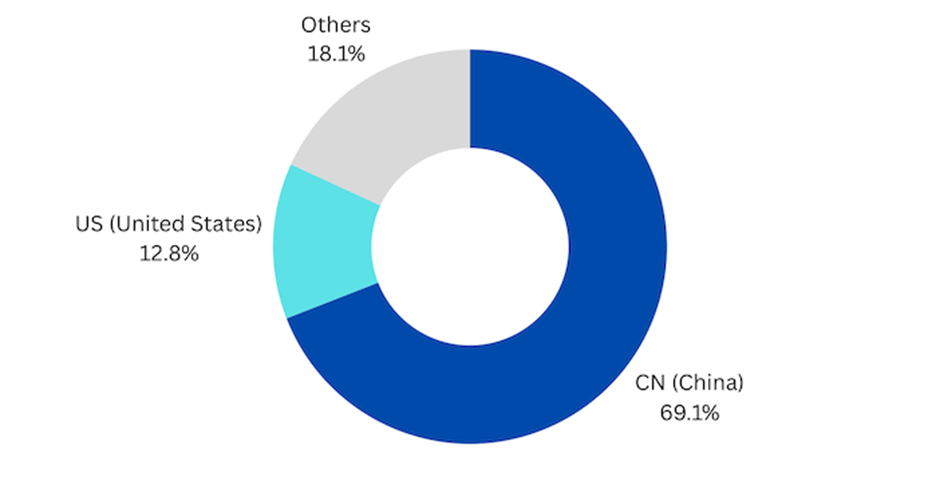
Additionally, Chinese companies’ focus on video-based products, such as Tencent and Bytedance, underscores their priority on providing low-bitrate, high-quality videos while reducing device dependency and processing power consumption.
US-based companies that depend on video codecs are streaming platforms like Netflix, Amazon, Apple, etc., which are steadily developing their own set of royalty-free video codec methods.
Future Scope
As we look ahead, industries such as gaming, streaming, and video conferencing will likely adopt royalty-based and royalty-free video codec standards. However, companies that actively contribute to these standards will maintain a significant advantage in areas such as litigation, licensing, and product implementation.
For other video coding companies, the key strategy is to stay updated about the ongoing changes in the foundational elements of next-generation video coding.
Conclusion
China’s strong presence in patent filings, supported by collaborations and a focus on video-centric technologies, positions its companies as potential leaders in standard-setting and declarations. However, it’s important to note that the volume of patent filings does not always equate to their quality.
Request a detailed analysis of patent validity and essentiality to ensure your portfolio includes only the most valuable patents.
Fill out the form below to identify high-value patents to pursue, areas to strengthen, or opportunities to challenge competitors’ patents.
Authored by: Raima Ghosh and Supreet Kaur, Prior-Art Team










