The WiFi-7 standard, 802.11be, is almost finalized and will be completed by late 2024. This has prompted early product launches, showcasing the intense competition in the market. This scenario isn’t new. Each new generation of standards sees the emergence of new players while established leaders maintain their positions and others fall behind. Therefore, as licensing discussions are anticipated, understanding these players’ intellectual property (IP) dynamics is crucial.
We have been tracking advancements in Wi-Fi 7 standard technologies to understand the necessary progress for the next generation of wireless technology. As a result, we have identified over 10 enabling technologies for the Wi-Fi 7 standard.
This article delves into the intricacies of the two most crucial Wi-Fi 7 technologies, initially introduced in the Wi-Fi standard. Additionally, the article highlights the leading innovators propelling Wi-Fi 7 into reality.
Fill in the form below for the complete list of 10 enabling technologies for the Wi-Fi 7 standard.
Multi-Link Operation (MLO):
MLO enables Access Points and Mobile Stations to exchange data on two or more bands simultaneously, thus allowing for higher data rates per user. While this concept is new to WiFi standards, it has been a crucial part of LTE and 5G standards, where it is recognized as Carrier Aggregation.
The implementation of Multi-Link Operation in WiFi 7 required advancements in various areas. This includes MLD Link Setup and discovery mechanisms, power-saving enhancements like MLD traffic indication map and MLD TWT, and innovations across MAC architectures and Multi-Link transmission schemes.
Top Innovators Developing Multi-Link Operation Technology
An analysis of patented innovations focused on the TGBe (IEEE 802.11be) standard, starting from 2018, revealed that roughly 40% of filings related to WiFi 7 are centered around Multi-Link operation. The innovations in this space are being led by top innovators like Intel, Huawei, LG, MediaTek, and Canon, which are top filers securing relevant IP around this technology.
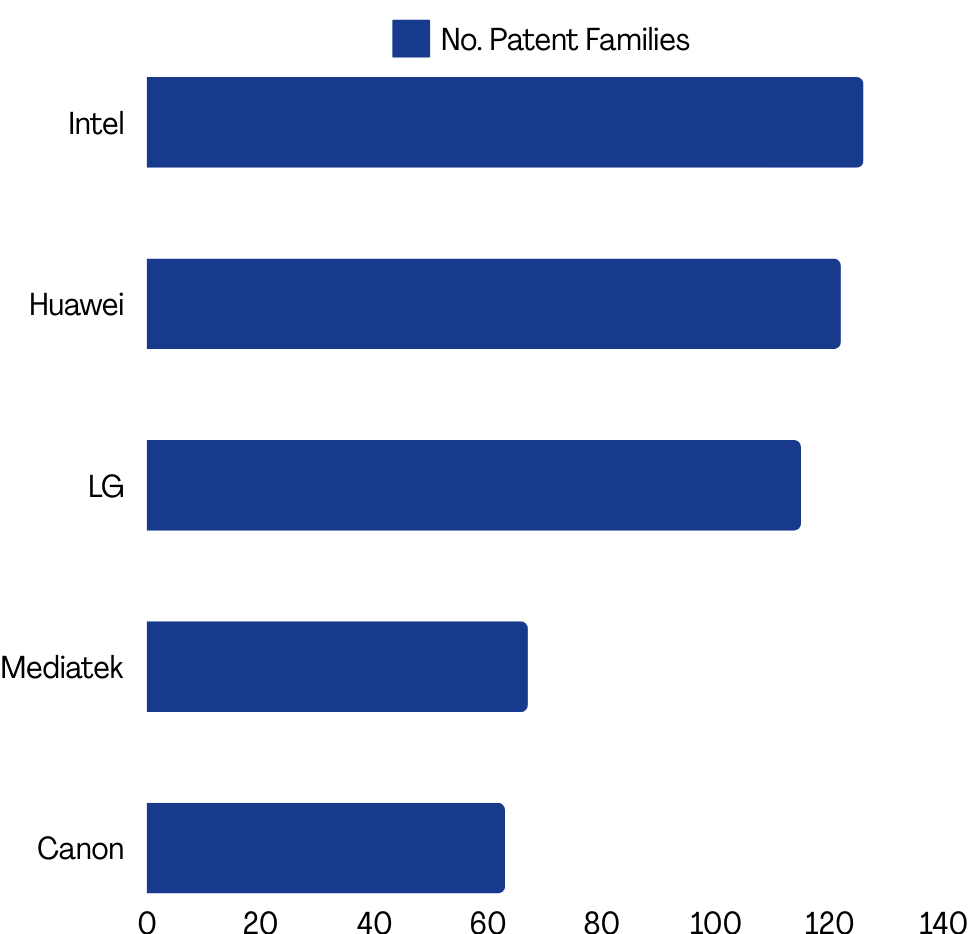
(Source: GreyB’s WiFi 7 Dashboard)
Intel and Canon have heavily invested in this technology. Over 50% of their WiFi 7 portfolios focus on Multi-Link operation, indicating the technology’s potential to realize the WiFi 7 standard.
Upon reviewing the TGBe workgroup contributions, we noticed similar trends. The same companies occupied the top slots, except Qualcomm, which ranked 2nd in MLD contributions despite being 8th in patent filings across MLD.
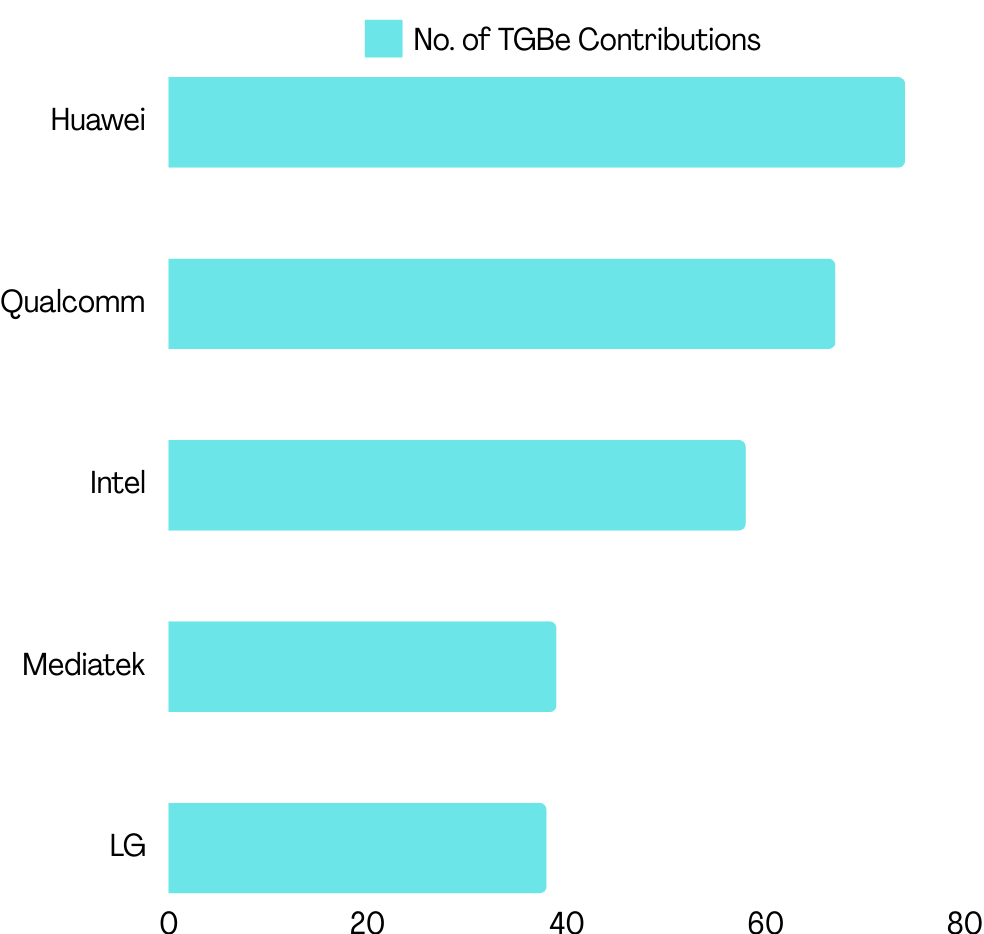
(Source: GreyB’s WiFi 7 Dashboard)
Multi-AP coordination:
Unlike Wi-Fi 6, which is limited to single-AP communication, Wi-Fi 7 introduces Multi-AP Coordination to enhance network performance and availability. This technology facilitates coordinated transmissions between multiple access points (APs), improving user experience in dense deployments.
In the Multi-AP coordination space, WiFi 7 innovations are focused around the following sub-topics:
Coordinated Spatial Reuse (CSR): Wi-Fi 7 builds upon existing interference mitigation techniques like BSS coloring from Wi-Fi 6. However, it adds a layer of coordination between adjusting transmission power dynamically, minimizing co-channel interference, and maximizing network throughput.
Joint Transmission (JTX): This mode leverages multiple APs to create a virtual MIMO system for a single user.
Coordinated Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (C-OFDMA): While OFDMA in Wi-Fi 6 assigns resources to individual users within an AP, C-OFDMA extends this concept across multiple APs. This coordinated resource allocation avoids conflicts and optimizes spectrum utilization for all stations.
Coordinated Beamforming (CBF): Beamforming focuses signal transmission towards specific stations. Previously, each AP did this independently, leading to potential interference. CBF in Wi-Fi 7 coordinates beamforming across APs, ensuring signals are directed precisely and minimizing inter-AP interference.
Top Innovators Developing Multi-AP Coordination Technologies
Patent filings and workgroup contributions in this domain highlight the importance of technology and the key innovators driving its development. A look at patent families related to Multi-AP coordination reveals companies like Huawei, Sony, MediaTek, Qualcomm, and Intel as top filers.
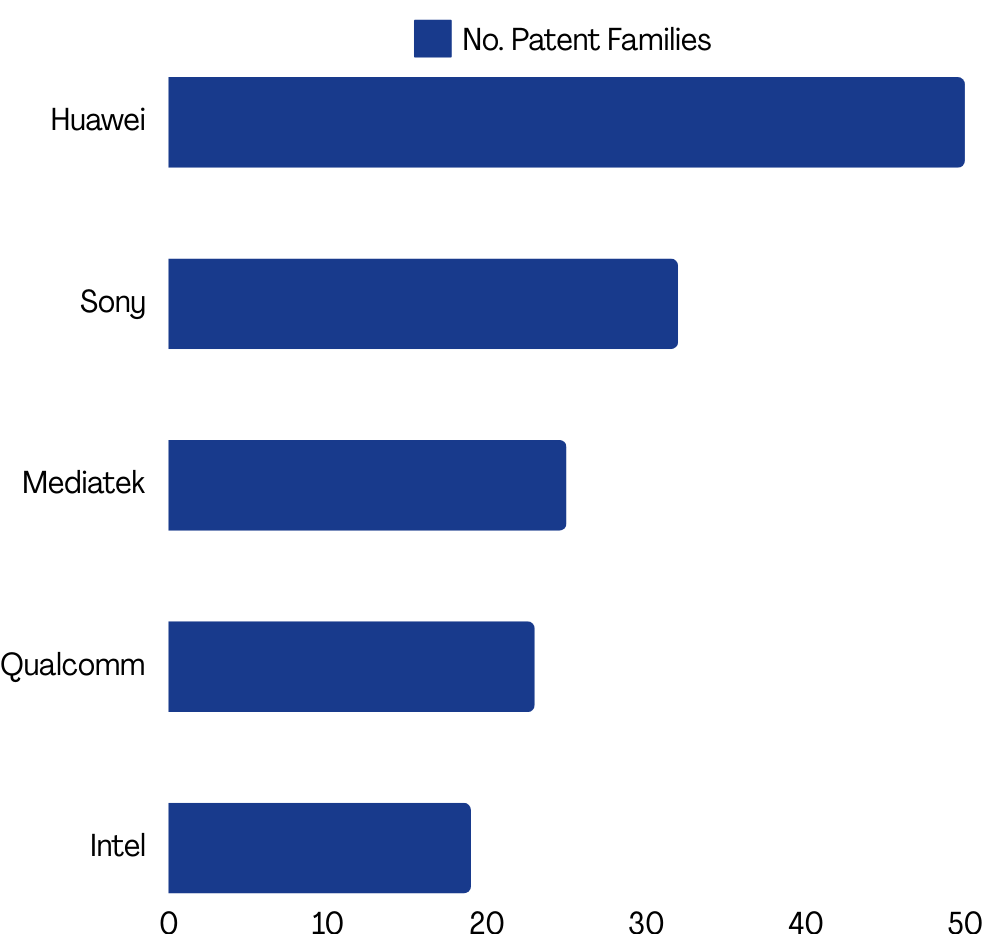
(Source: GreyB’s WiFi 7 Dashboard)
Similarly, an analysis of TGbe workgroup contributions to Multi-AP coordination shows Huawei, Intel, LG, MediaTek, and ZTE as major contributors.
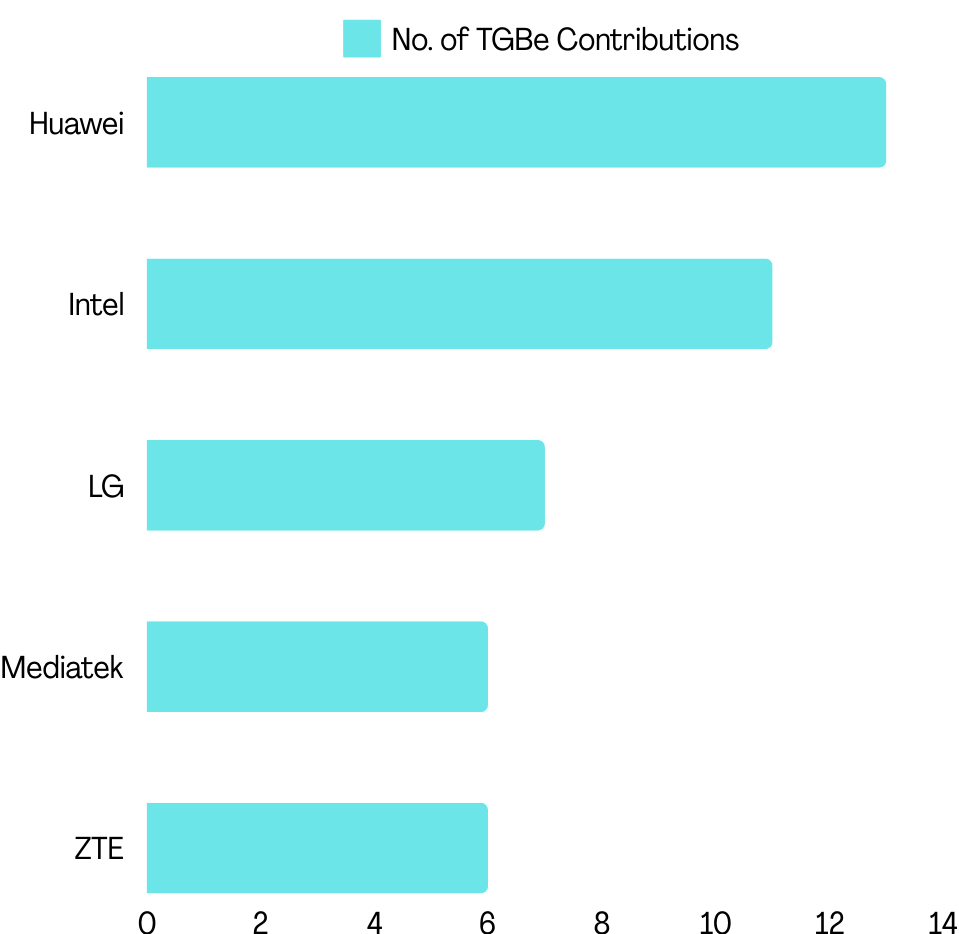
(Source: GreyB’s WiFi 7 Dashboard)
Conclusion
Following the release of initial standard drafts in 2021, the TGBe workgroup is still in development. It continues fine-tuning the WiFi 7 standard (expected to be finalized by the end of 2024).
The market size of WiFi 7 is projected to reach USD 24.2 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 57.2%. Many WiFi 7 manufacturers, such as TP-Link, Huawei, ZTE, Xiaomi, Zyxel, etc., have also started to capitalize on this growing market after receiving certifications from the WiFi Alliance. Therefore, it’s imperative to understand the domain’s patent landscape, top innovators, and technological developments to gain an edge over your competitors in the WiFi 7 space.
Read other expert articles on Wi-fi 7 Technology:
Fill out the form below to develop a flexible monetization strategy that adapts to the evolving Wi-Fi 7 technology. Using data-driven insights, you will gain a competitive edge and capture a significant wireless market share.
Authored by: Aman Kumar, Prior-Art Team
Edited by: Annie Sharma