With the IoT devices projected to surpass 24 billion by 2025, the importance of enhanced connectivity has never been more evident. This is where 6G emerges as the zenith. With speeds 100 times faster than 5G and significantly reduced latency, 6G offers significant improvements. Its expanded data capacity and heightened connection density are critical for handling the surging IoT data flow and securing robust networks.
As 5G’s deployment advances and industry standards solidify, it’s worth pondering: What cutting-edge technological innovations will pave the way for the 6G revolution?
In this article, we present a comprehensive answer by leveraging our extensive research and analysis of global patent data, offering insights derived from our observations.
How did we identify 6G enabling technologies?
Unlike 5G, which has been globally accepted and is being governed by the standardization body 3gpp, there are no standards per se that have been designated for 6G. While standards are expected to be established eventually, 6G is still largely based on speculation. Although the aim is to deploy 6G worldwide by 2030, certain complexities must be addressed beforehand.
GreyB identified several companies actively pursuing 6G technology, including major players in the global telecommunications industry who have already led the way in 4G and 5G innovations, demonstrating a strong commitment to advancing 6G.
Our approach closely monitored these companies’ patent filings over the past three years. This approach gave us insights into novel and significant improvements beyond conventional 5G communication protocols.
Analyzing over 35,000 patents filed during this period, we have developed a methodology for identifying technologies that we believe will play an essential role in the global implementation of 6G.
Although we’ve discussed the top three technologies that will shape 6G, our analysis has identified 10+ crucial 6G enabling technologies.
Gain an edge over your competitors in the 6G space. Request a comprehensive industry landscape analysis tailored to your needs.
6G Enabling Technologies
According to GreyB, the three 6G enabling technologies are Terahertz Communication, Massive MIMO, and Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces.
The graph below represents the patent filing trends for these key technology areas –
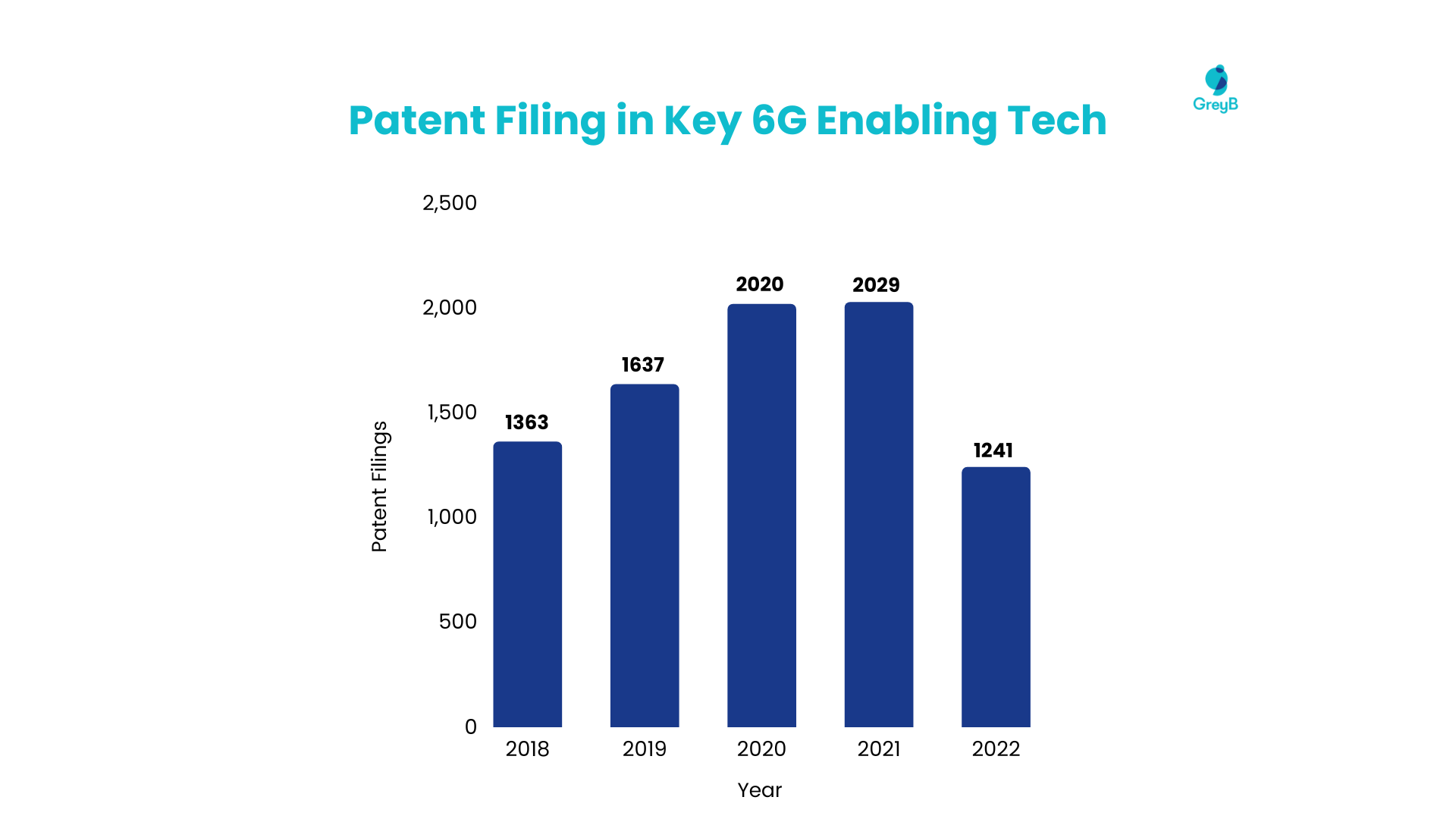
2,452 companies contributed to filing these patents, resulting in a combined count of 8,317.
1. Terahertz Communication (THz)
6G will bring in an ecosystem of seamless interconnectivity that demands continuous, uninterrupted communication with virtually no downtime. To enable reliable, high-speed communication channels, researchers are actively exploring the development of novel metamaterials capable of generating and sustaining terahertz signals.
This technology functions within a frequency range of 0.1 to 10 THz, higher than those used in 4G and 5G networks, enabling high data transfer rates, low latency, and the capacity to accommodate numerous connections.
A collective of 532 companies actively participated in patent filings related to THz technology, yielding a count of 1,480 patents. The graph below depicts the trend in this domain over the past six years.
Insights Unveiled by Patent Data Analysis
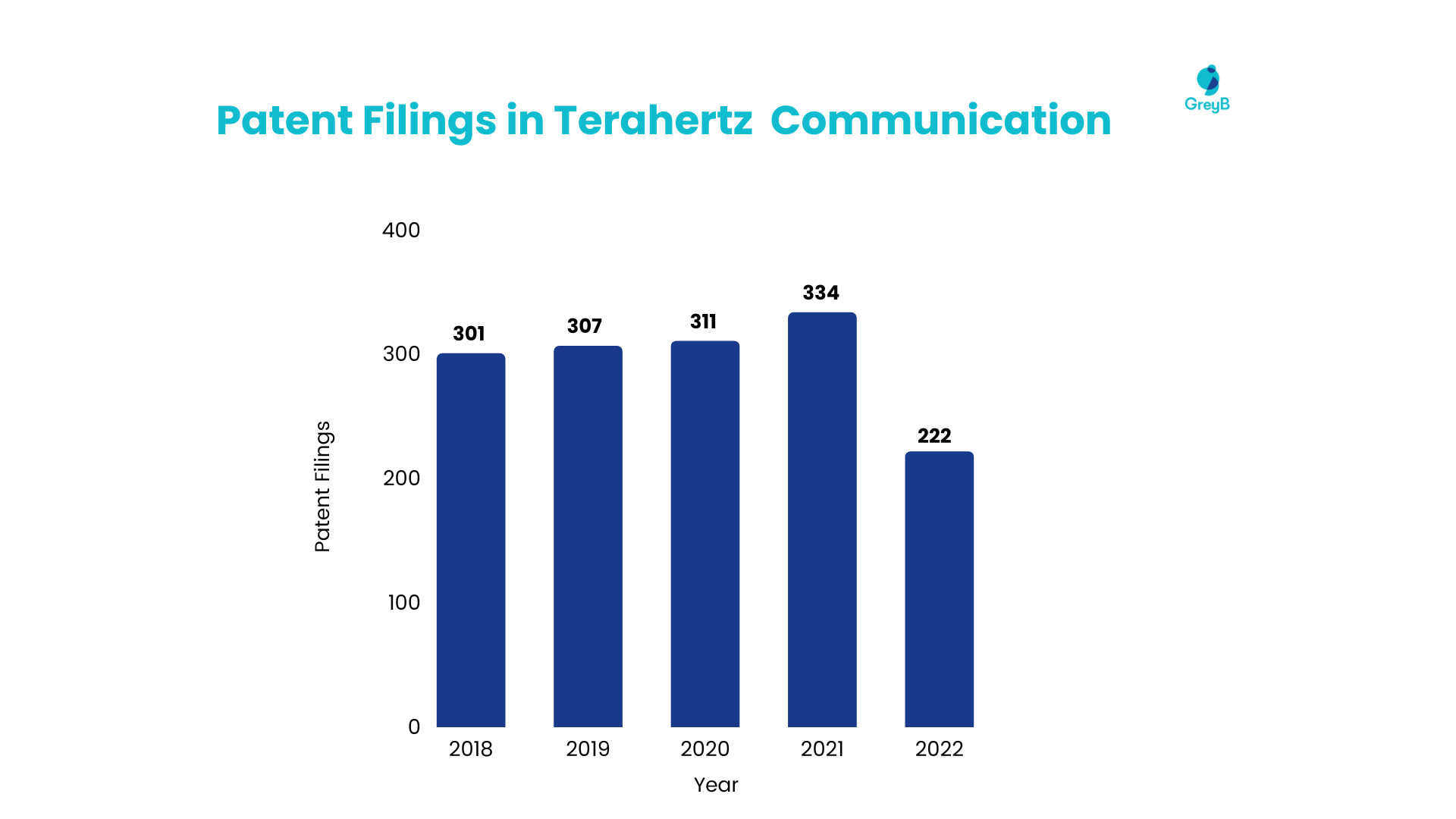
We have previously conducted research on terahertz (THz) technology. Building upon our previous article, let’s now explore the latest developments and key players in this field –
- Terahertz forms a 3% share of patent filings in all of the predicted 6G technologies.
- While major players like Huawei, Qualcomm, and Ericsson seem to be less active in this area, research institutes and universities, including Brainware Terahertz (a subsidiary of China Electronic Technology Group Corporation (CETC)), the Chinese Academy Of Science, Tianjin University, and Tsinghua University, are making significant contributions. This indicates that the technology is still in the research and development phase before corporations become more involved.
- Contributions to the 3GPP standards under the governance of ETSI have begun, with a total of 145 submissions received thus far. Leading the way are TUB (Technische Universität Braunschweig) with 43 contributions, followed by ETSI with 36, and Apple with 28.
One of the noteworthy companies contributing to patent filings in this area is Canon. This interest arises because Terahertz communication has considerable potential in the field of sensing and imaging, including applications like the detection of concealed weapons at security checkpoints.
– Gaurav Sahni, Intelligence Team
2. Massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO)
Massive or Giga MIMO technology employs an exceptionally high number of antenna elements in both base stations and terminals. To put this into practical terms, antenna arrays of up to 1-2K elements at base stations and even larger arrays at the terminals will be utilized.
Approximately 151 companies participated in patent filings related to Massive MIMO technology, resulting in 299 patents. The graph below illustrates the patent filing trends in this industry over the past six years.
Insights Unveiled by Patent Data Analysis
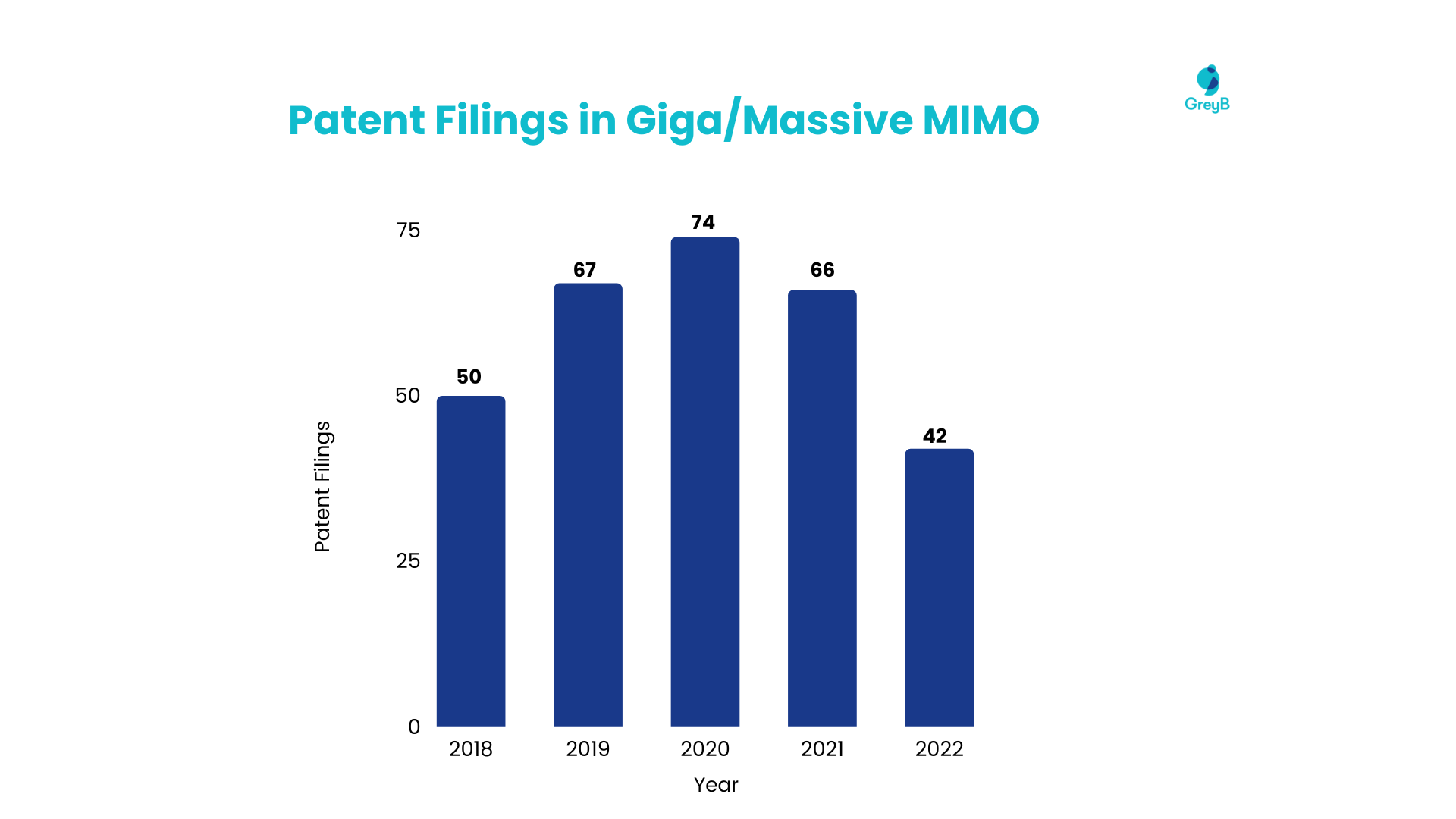
Let’s explore the current developments in the domain –
- It seems that industry giants Ericsson and Qualcomm aim to maintain their leadership by taking the initiative in patent and research filings in this domain. While LG had a slow start, it has recently shown increased activity in this area.
- In terms of filings by research institutes and universities, a considerable contribution has been made by the Southeast University and Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications.
- Qualcomm has reaffirmed its focus on Massive MIMO for 3GPP proceedings, set to commence in mid-2024. Even its R&D Hub in China is leading other Chinese telecom giants in Massive MIMO research.
While emphasizing the importance of deploying many antennas for achieving genuine 6G speeds, another crucial aspect that must align is the effective implementation of beamforming to ensure seamless connectivity.
This concept is called “Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces” (RIS). Let’s discuss this further in detail.
3. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS)
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) is a key technology for enabling 6G wireless communication networks. It involves using small elements, such as antennas and sensors, to finely tune the reflection and scattering of radio waves, enhancing signal strength and energy efficiency.
The research areas of interest in RIS include RIS design (e.g., material), RIS control algorithms, RIS channel modeling, RIS integration with other network components, etc.
845 companies have shown interest in RIS technology by filing patents in this field, resulting in 2,278 patents. The graph below represents the patent filing trends within this domain over the past six years.
Insights Unveiled by Patent Data Analysis
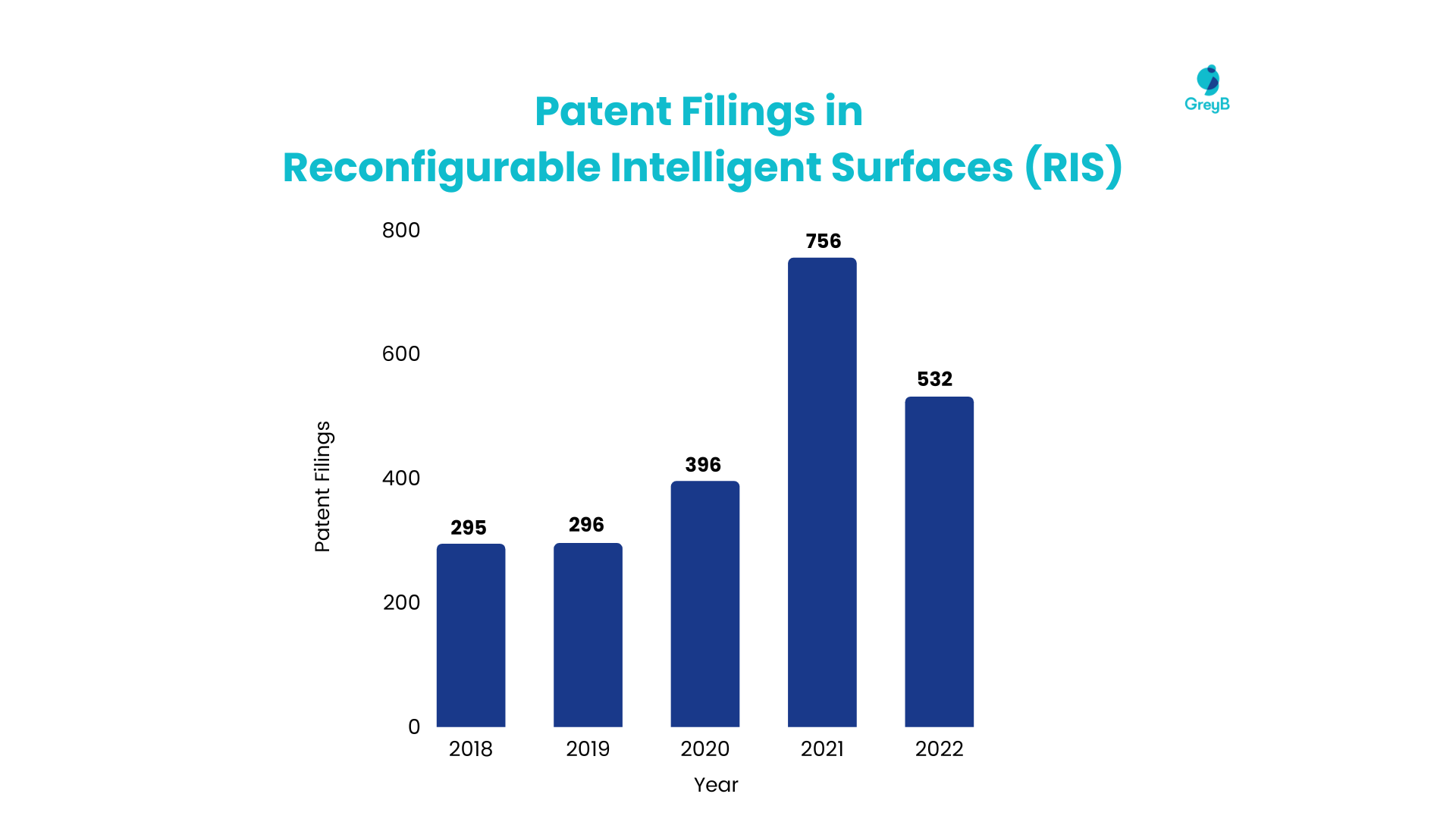
Let’s take a look at the current happenings in this domain –
- Around 4% of patents filed in potential 6G technologies are categorized under this domain. Qualcomm is leading among the major players, filing more than four times as many patents as the closest competitor, China Telecom Corp Ltd. Some of their patents include US20220322321A1 and WO2022193045A1.
- Southeast University, with patents like CN114039706A, appears to be leading the patent filings among research institutes and universities.
- Additionally, startup activity is gaining momentum in this field, with companies like Deepsig and Metawave making notable progress in enhancing beamforming capabilities. An exemplary invention in this context is WO2023094533A1 by Metawave.
- ETSI has expressed interest in this technology area, highlighting its potential significance as a research field. This notion is further supported by the publication of over 66 recent research papers in IEEE.
Author’s note: Aligning with their 5G vision, China maintains a significant lead in this field, exceeding the United States by at least five times in patent filings.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that 6G is still in its developmental stages. While some companies invest in the next-generation wireless standard, establishing industry specifications for 6G-enabled network products will take several years.
We’ll continue to share such insights in future articles. In the next part, we’ll explore the “material” aspect, considering that standard materials might not meet the demands of 6G, potentially requiring specialized “metamaterials.”
Stay tuned for a deeper understanding of these advancements and their potential impact on various industries.
Gain an edge over your competitors in the 6G space. Request a comprehensive industry landscape analysis tailored to your needs.
Authored By: Gaurav Sahni, Intelligence Team
Edited By: Ridhima Mahajan, Marketing










