Note: The article was first published on Nov 11, 2020. It has recently been updated on Mar 16, 2022.
In our previous article, we talked about the 5G chipset market. In this article, we will particularly discuss the top 5g chip makers leading the 5G semiconductor market.
There are many companies participating in 5G chipset manufacturing, however, there are only four companies that are doing exceptionally well in the current times. However, considering that the 5G chipset market is yet to mature, there is a lot of space to grow for other companies. Over time, it is possible that we could observe drastic changes in the position of some of the semiconductor companies in the 5G chipset market.
Acquiring companies and startups can position a company from bottom to top. And currently, we are witnessing such types of big acquisitions in the industry by companies to gain or strengthen their position in the 5G chipset market. AMD’s acquisition of Xilinx for $35 billion is one such example.
It’s forecasted to be a $300 billion industry by 2025, so no wonder, companies are throwing money to get a huge piece.
There are many players working on 5g chipsets but we discussed the top players and the recent work that could help them make a strong foothold in the 5g chipset market.
So, let’s have a look at the research and other activities of the 5G chip makers and find what the top 12 companies are doing differently.
But before we set on our path, let me tell you, my research revealed a lot more. On my quest to get a handle on the research activity and other variables by the players, I decided to explore every aspect and conduct detailed research on the 5G chipset domain, which resulted in a report.
Just like the future of this market, our insight-rich report ended up being pretty long(30,000+ words). To make it easy to consume, we converted it into a PDF copy for later reading. This PDF covers the state of the domain and a lot of aspects in detail, and if you’re working in or are interesting in getting into the 5G Chipset domain, trust me, you will need this report. Want to get your hands on it?
Grab a copy by filling this form below.
What are the Top 5G Chip Makers up to?
There are 12 companies researching on 5G chipsets but only four 5G chip makers are currently leading the 5G chipset market, i.e. Qualcomm, Samsung, Huawei, and MediaTek.

Let’s have a look at the activity of these 4 players and try to understand a bit more about them.
Qualcomm
Qualcomm Technologies and a group of the world’s leading mobile network operators including AT&T, Verizon, China Mobile, Deutsche Telekom, NTT DoCoMo, SK Telecom made a declaration in February 2019 of how far along they are in realizing the vision for 5G.
As the companies planned to begin the first trials of standards-compliant mobile 5G NR networks, at the heart of the mobile test devices, they will use the Qualcomm Snapdragon X50 5G modem to ascertain the performance of these emerging networks. After 3GPP set 5G standards in 2016, Qualcomm started working on the next wave of 5G NR technologies that would pave the way to the subsequent 5G NR standard releases. At MWC 2018, Qualcomm demonstrated three of these 5G NR expansion areas.
Qualcomm Research started design work on the new 5G wireless air interface well before 3GPP standard efforts kicked off. In a live demonstration to industry analysts, Qualcomm Research demonstrated a key 5G technology enabler to these extreme mobile broadband experiences — millimeter wave (mmWave).
Qualcomm is also working to design and standardize the new 5G NR unified air interface.
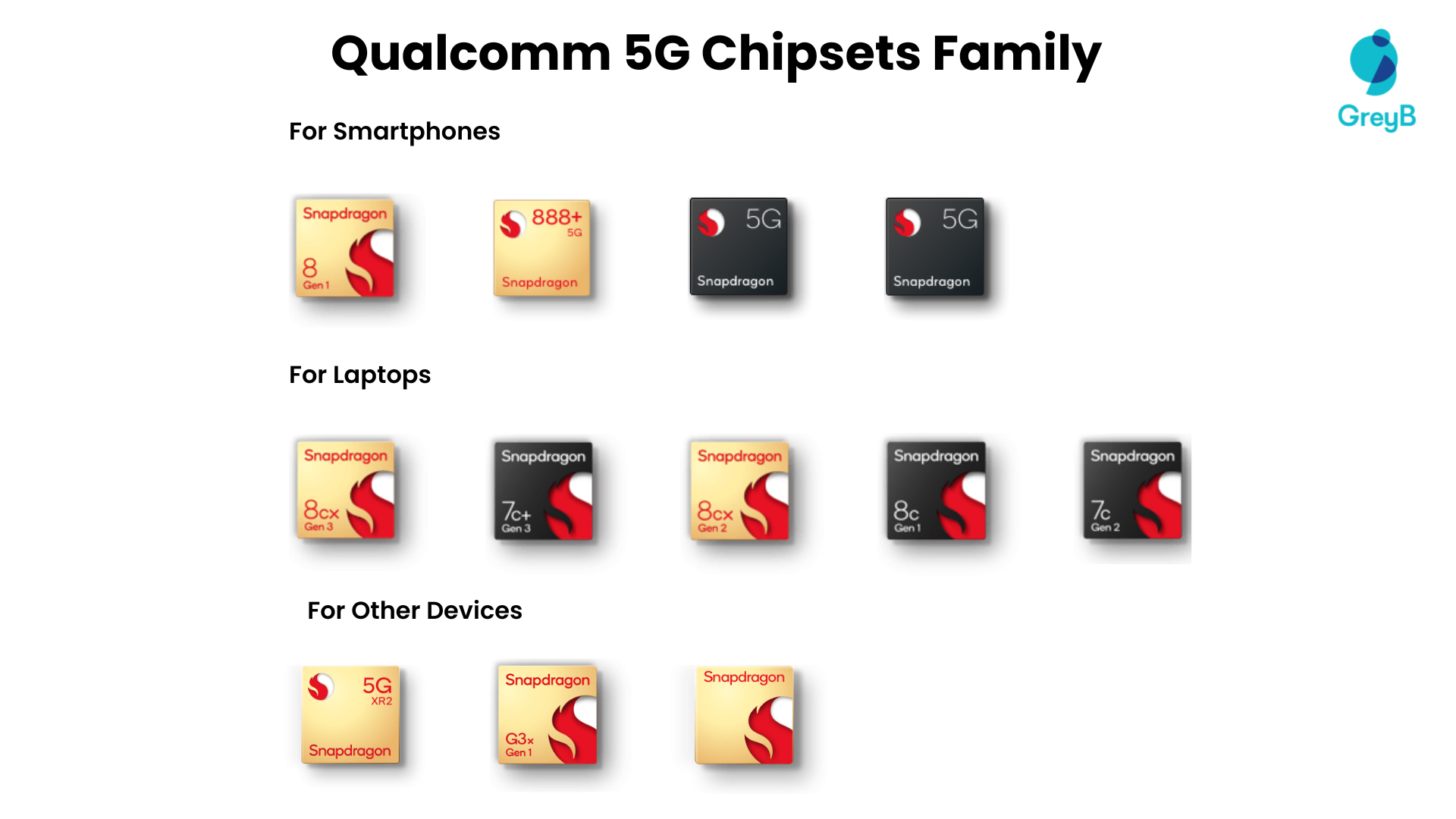
So, far Qualcomm is the most successful company in the 5G chipset market. Its 5G chipset family has more than 10 processors for devices like smartphones, laptops, wearables, etc.
 Mergers & Acquisitions
Mergers & Acquisitions
In 2015, Qualcomm acquired CSR for $2.4 billion. CSR was a leading fabless provider of end-to-end semiconductor and software solutions for the Internet of Everything (IoE) and automotive segments. With CSR, Qualcomm would be able to offer a compelling portfolio of new products for a large number of customers in the areas of Internet of Everything and automotive – both key growth priorities for Qualcomm.
Qualcomm announced its intent to acquire NXP Semiconductors for $47 billion in October 2016. The deal was approved by U.S. antitrust regulators in April 2017 with some standard-essential patents excluded to get the deal approved by antitrust regulators. As the NXP acquisition was ongoing, Broadcom made a $103 billion offer to acquire Qualcomm, and Qualcomm rejected the offer.
In 2021, Qualcomm acquired Nuvia, a world-class CPU and technology design company, for $1.4 billion. Nuvia’s expertise could enhance Qualcomm’s next-generation CPUs for use in smartphones, laptops, and other smart devices. The company understands the 5G potential and is ready to pay handsomely to acquire startups with excellent skills.
Investments
On October 24, 2019, Qualcomm announced it created a $200 million venture capital fund to invest in startup companies looking to use 5G technology in devices other than smartphones.
Samsung
Samsung is actively engaged in the key of global 5G research initiatives, such as membership of the Steering Board of European 5G PPP projects of Horizon 2020, as well as coordination and leadership of the very large industry-led 5G PPP mmMAGIC consortium, 5G Innovation Centre (5GIC) in the UK, NYU Wireless Center in the US, Giga KOREA project and Chinese 836 project.
The company is leading various collaborations with industrial partners and academics over the world. In particular, Samsung has played an important role as the full-time member of the 5G PPP Infrastructure Association, the executive board member of the 5G Forum in Korea, and the chair of the vision sub-working group for Future IMT (5G) in ITU-R WP5D.
In order to keep a consistent perspective on 5G with those of other academic institutes, we are vigorously developing 5G core technologies with several outstanding universities around the world.
Samsung has mainly built 5G chipsets for its smartphones.

Mergers & Acquisitions
Samsung made just one acquisition which is directly related to semiconductors. In 2012, Samsung acquired Nanoradio, a Swedish wireless chip manufacturer, in order to make their smartphone efficient for Wi-Fi. The acquisition makes sense as the smartphone market was growing at that time and WiFi availability and connectivity were a huge deal for smartphone manufacturers.
Nanoradio chips can be used in smartphones, tablets, mobile gaming terminals, portable multimedia players, digital cameras, and e-readers. Since Samsung had even at that time products in most of the categories, the acquisition made a good fit for the company.
Investments
In 2018 Samsung Group announced that it will invest about $22 billion over the next three years in growth areas such as artificial intelligence and 5G technology. That would be part of Samsung’s overall $161 billion investment plans that include capital expenditure and research and development. Samsung said a large portion of that total would be spent in South Korea.
South Korea’s largest conglomerate Samsung Group is planning to invest about 25 trillion Korean won ($22 billion) over the next three years into new growth areas, led primarily by Samsung Electronics.
Those investments would be made in four key areas: artificial intelligence (AI), fifth-generation mobile network technology, electronic components for future cars, and biopharmaceuticals.
To expand its AI capability, Samsung will be increasing the number of researchers to 1,000 across its global AI centers in the UK, Canada, Russia, the US, and South Korea.
Samsung Electronics is currently the world’s largest smartphone-maker but also boasts a very strong semiconductor business that supplies chips to companies such as Apple.
Overall, the conglomerate said it planned to invest a total of 180 trillion won ($161 billion) over the next three years, which will include capital expenditures as well as research and development in its semiconductors and displays businesses. Most of that investment — about 130 trillion won (US$114.4 billion) of the total — will be spent in South Korea, the company said without giving further breakdowns.
In April 2020, Samsung announced that there is a possibility it might delay or cut its investment in 5G technology in the wake of the COVID-19 crisis.
Huawei
Huawei has approximately 96,000 employees in R&D, representing 49% of its workforce. By 2019, Huawei had achieved 85,000 patents in its portfolio. It’s not surprising for a company that last year invested 15.3% of its revenue, i.e., about $17 billion USD, into R&D. As of early 2017, 10% of 1450 patents essential for 5G networks were in Chinese hands in which the majority belongs to Huawei and ZTE.
The company wants to involve AI in 5G which according to them is a much more integral element of Huawei’s 5G strategy. The company also plans to launch a full range of Huawei commercial equipment including wireless access networks, core networks, and devices.
The breadth of Huawei’s 2019 Annual Report is staggering and reveals a company undaunted by myriad obstacles. Through its leadership in enterprise 5G, cloud, and AI distinguishes Huawei in the technology space, one cannot help but recognize its continued success in smartphone design and market share.
Huawei uses its 5G chipsets in its smartphones.
 Mergers & Acquisitions
Mergers & Acquisitions
Huawei Technologies has acquired 9 companies as of now but none of the acquisitions is related to semiconductors.
Investments
Huawei has continuously invested over 10% of its revenue into R&D. Huawei’s chief executive and founder, Ren Zhengfei, announced that the company “plans to boost its research and development budget this year by $5.8 billion to more than $20 billion.”
Between 2009 and 2013, Huawei invested more than US$600 million into 5G technology research. Following this, in 2017 and 2018 Huawei invested almost US$1.4 billion into 5G product development.
MediaTek
MediaTek has been conducting research and development in 5G for about 8 years. In addition to the headquarters’ R&D center, they also have an R&D center in Finland (the homeland of Nokia). This research and development center participates in 5G and other latest wireless technologies.
It also develops communication technology and collaborates with European telecommunication customers to carry out testing. Its collaboration extends to the research and development institute of Finland, academic institutions, and Nokia. MediaTek has dedicated 6G R&D staff in Finland, MediaTek’s staff in Finland is anticipated to grow to be a key to consider its future terminal chip growth.
The company also continuously invests in R&D. Its annual R&D expense reached NT$63 billion in 2019, ranking it at the top among the listed companies in Taiwan. The company’s long-term hard work in technology has also received global recognition repeatedly. In 2008, a total of 11 papers were published in the ISSCC (International Solid-State Circuits Symposium) by them and the number of papers ranked among the top three in the world.
Mediatek 5G chipset family is huge compared to the other three top players:
 Patents are a specific indicator of a company’s efforts in innovation and R&D. MediaTek’s patent strategy for 2018 continues to consider both quantity and quality as Mediatek maintains over 9,000 patents. Mediatek was ranked the third-largest patent filer at the Taiwan Intellectual Property Office (TIPO) and the 25th largest global patent filer in the Digital Communication field of the European Patent Office (EPO).
Patents are a specific indicator of a company’s efforts in innovation and R&D. MediaTek’s patent strategy for 2018 continues to consider both quantity and quality as Mediatek maintains over 9,000 patents. Mediatek was ranked the third-largest patent filer at the Taiwan Intellectual Property Office (TIPO) and the 25th largest global patent filer in the Digital Communication field of the European Patent Office (EPO).
In 2018, Mediatek was granted 1,731 new patents, 574 of which were US patents. The number of US patents received for 2018 increased compared to the number of US patents received in 2017 (398; ranking among the top 100 of global patent filers).
Mergers & Acquisitions
In 2005, MediaTek acquired Inprocomm, a wireless semiconductor design company producing 802.11a, b, and a/g chips.
On September 10, 2007, MediaTek announced its intention to buy Analog Devices cellular radio and baseband chipset divisions for US$350 million. The acquisition was finalized by January 11, 2008.
On May 5, 2011, MediaTek acquired Ralink Technology Corporation, gaining products and expertise for Wi-Fi technology for mobile and non-mobile applications, as well as for wired DSL and Ethernet connectivity.
On April 11, 2012, MediaTek acquired Coresonic, a global producer of digital signal processing products based in Linköping, Sweden. Coresonic became a wholly-owned subsidiary of MediaTek in Europe.
In Aug 2021, MediaTek acquired MStar Semiconductor. MStar is a circuit designing company developing display IC products and technology solutions for mixed-mode ASIC services.
On Sep 18, 2015, MediaTek acquired Richtek Technology for $909 Million. Richtek Tech is principally engaged in the design, testing, manufacture, and distribution of analog integrated circuits (ICs).
Investments
In 2015, Mediatek opened up a US$300 million venture fund for investing in startups across the globe. MediaTek Ventures is a strategic investment arm of MediaTek that invests in startups in Greater China, Europe, Japan, and North America.
The firm seeks to invest in early-stage companies operating in the semiconductor, system and device, internet infrastructure, and information technology sectors.
Which other companies are working on 5G Chipsets?
Unisoc
Tsinghua Unigroup bought Spreadtrum and RDA, two of the top three-chip design companies in China, and became one of the most influential performers in the domestic market. In 2016, Tsinghua Unigroup integrated the acquired Spreadtrum and RDA into UNISOC, committed to the integration of mobile chip technology and the improvement of the firm’s independent R&D capacity.
Unisoc, then still known as Spreadtrum, was formerly a public company listed on NASDAQ but agreed to an acquisition by Tsinghua Unigroup in July 2013 for about $1.78 billion. In 2014, Intel invested $1.5 billion in Spreadtrum & RDA for a 20 percent stake, and at MWC 2018 Intel and Spreadtrum expanded their relationship to cover 5G modem development. But, in February 2019, Intel announced that it will no longer pursue this partnership in light of the US-China trade war and the market outlook.
Unisoc’s primary 3G customer Samsung shifted 4G sourcing to Qualcomm and in-house primarily. This affected Spreadtrum’s 4G market position. The company has had some success in 4G feature phones, but in 4G smartphones, the company’s performance hasn’t been impressive.
Unisoc’s partnership with Intel didn’t yield good results either. Unisoc used Intel’s x86 cores in a couple of chips and used Intel’s fabs to manufacture those chips. Intel’s dream of expanding x86 technology in smartphones with the help of Unisoc’s strong presence in emerging markets however didn’t realize. This can be attributed to Intel’s slow progress in advancing its x86-based smartphone CPU roadmap.
In 2016, Intel itself had to retrench from the smartphone apps processor market as the company abandoned its internal integrated chip effort. Intel originally thought Unisoc partnership would help it to proliferate its 5G modem technology in smartphones. But the latest development suggests Intel and Unisoc will compete on their own in 5G smartphones. Unisoc is hoping to get a piece of the 5G pie in China in 2020.
Unisoc has the financial backing of Tsinghua Unigroup. The company is prioritizing AI, 5G, and IoT as future growth areas. Tsinghua claims to have big ambitions in wireless.
The chipmaker has lately been active on a global scale, signing contracts with upstream and downstream partners, as well as various players in adjacent fields. In January 2019, it made a strategic deal with American test equipment giant Keysight. A few months later, it partnered with British Intellectual Property (IP) licensing firm Imagination on brand-new neural network accelerator IMG Series3NX.
As China is taking steps toward semiconductor self-reliance, investing lavishly in budding local chipmakers, the state regulators are striving to create new channels to public capital for high-tech-driven enterprises. One of the recent projects – the Shanghai bourse-based Star Market – helped a handful of companies in the space to boost their financial resources.
UNISOC raised CNY 2.25 billion (around USD 320 million) from the China National Integrated Circuit Industry Investment Fund, known as the ‘Big Fund,’ in its Series B on March 17, 2020.
UNISOC is reportedly preparing a public offering in the new marketplace too. It has started an equity optimization project in conjunction with an organizational structure upgrade. The new generation of wireless technology (5G) infrastructure will present new opportunities for the company, which, as mentioned above, has already jumped on the bandwagon.
The funding round follows the rollout of UNISOC T7520, the company’s debut mobile application System-on-a-Chip (SoC) processor with an integrated 5G modem. Remarkably, the chipmaker has been mainly involved in the production of low-end chipsets for affordable smartphones. For one, it inked a partnership with South African phone maker Mobicel in 2018. The two agreed to launch a new handset that will be manufactured and marketed locally.
Founded in 2001, the company has grown into a 4500+ people-large chipset developer, with over 90% of employees directly involved in the research and development process. It claims to have 15 R&D centers and seven customer support centers around the world.
Recent Developments
In February 2018, as a core subsidiary of Tsinghua Unigroup, Unigroup Spreadtrum & RDA and Intel Corporation officially announced a long-term strategic collaboration on 5G. The companies plan to develop a 5G smartphone platform for the China market that will feature an Intel 5G modem and will be targeted to coincide with 5G network deployments in 2019.
In February 2018, Keysight Technologies, Inc. announced the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Unigroup Spreadtrum & RDA, at Mobile World Congress in Barcelona. The MoU is an extension of the existing collaboration the two companies initiated more than ten years ago. It aims to accelerate the development of 5G technology by coordinating 5G chipset and device-related design, verification, test, and measurement.
In March 2018, in an MoU signed at Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, Rohde & Schwarz and Unigroup Spreadtrum & RDA agreed to collaborate on five important fields: 5G communications, network operator tests, automotive electronics products, broadcasting products, and IoT applications.
In November 2018, Unisoc (formerly Spreadtrum Communications) showcased its wide range of future-ready 5G and IoT offerings at the India Mobile Congress 2018. The three-day event was organized by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) along with the Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) on October 25-27, 2018 at Aerocity Grounds, New Delhi.
In November 2018, Unisoc released the Proposal for Building 5G Industrial Ecology along with over 10 domestic and overseas industrial chain partners at the 2018 China IC Summit. Initiated by domestic chip designer Unisoc, this proposal won extensive supports and responses across the industrial chain.
In February 2019, Unisoc launched the 5G technology platform MAKALU and its first 5G Modem IVY510, at MWC 2019 in Barcelona. The release of MAKALU and IVY510 is expected to accelerate the commercialization of 5G technology and provide consumers with a brand new mobile broadband experience.
In February 2019, UNISOC announced its IVY brand which supports IoT products to build a connected society. As a brand new 5G technology platform, MAKALU will help power a huge rise in the Internet of Things. Unisoc plans to launch a series of IVY products based on the MAKALU platform in the near future.
Unisoc IVY510 is the first 5G Modem of UNISOC based on the MAKALU technology platform, produced with TSMC’s 12nm process. As the first 2G/3G/4G/5G multimode platform of Unisoc, IVY510 complies with the latest 3GPP R15 standard, supports Sub-6GHz 5G spectrum with a channel bandwidth of 100MHz, which is a highly integrated, high performance, low power 5G platform, and supports both standalone (SA) and non-standalone (NSA) network configurations to meet communication and networking requirements during different stages of 5G deployment.
In February 2020, Unisoc announced that its 5G Modem V510 is powering China Unicom’s 5G CPE VN007 (Customer Premise Equipment). Selling for CNY 999, this 5G CPE provides a high-speed connection, allowing users to access a more intelligent and connected world.
In February 2020, Unisoc kicked off the 2020 Spring Press Conference themed at “Capture the future value of 5G” in the form of a live webcast, showcasing the latest technological breakthroughs and achievements of the company. Along with a number of blockbuster technologies and products, Hisense unveiled its first 5G smartphone F50 powered by Unisoc T7510 at the conference. This is a major landmark during their long-term partnership of the decade, and a milestone of great significance for promoting the commercialization of 5G mobile phones.
In March 2020, a press conference & developer summit was held by Unisoc at Shenzhen for new AIoT products, where the company officially announced IVY V5663 – a high-performance secure AIoT solution. With five outstanding features, including industry-leading technologies, powerful computing capability, security and reliability, rich sets of features, and ease of application development, IVY V5663 can be used extensively in diversified scenarios, such as smart home, healthcare, childhood education, aesthetic health care, warehousing, and logistics. In order to enable the AIoT value chain, Unisoc has built an open and innovative development platform AILIGO to help developers better align technologies with scenarios, as well as improving the time-to-market for smart endpoints.
In March 2020, Unisoc announced the completion of critical technology and service data testing for its 5G mmWave terminal prototype based on AiP (Antennas in Package), the core module of the 5G mmWave terminal. The success of the test marks a major step forward for Unisoc in driving the maturity of the mmWave industry. As an important part of 5G technology, mmWave can be applied to many scenarios including outdoor and indoor hotspots, FWA(Fixed Wireless Access), and backhaul, providing higher experienced data rates and lower latency.
In April 2020, Unisoc announced the official unveiling of Unisoc T7510-powered Hisense F50 5G.
In May 2020, Unisoc announced that it has upgraded its tablet portfolios to accelerate digital transformation. With them, Unisoc is delivering chipsets to premium, mainstream, and entry-level tablets. The portfolio is available at various price points allowing partners to design various tablets for a wide array of usage scenarios. Apart from a wealth of high-speed peripheral interfaces, the 7 series supports both 5G and 2.4G Wi-Fi connections, for faster transmission and higher security.
Nokia Networks
Nokia has also joined the race of 5G as the company is developing, researching, and partnering with other entities to render 5G communication as fast as possible.
The company uses an 8000-hectare site to carry out key 5G tests collaborating with Deutsche Telekom and Hamburg Port Authority for their project 5G MoNArch. The project’s main goal is to gain knowledge and experience from 5G networks in the real-world environment. Its industrial uses could be traffic light management, data processing from mobile sensors, and VR applications.
Nokia also implemented Future X network architecture for 5G to deliver robust network coverage and reduce costs. Future X includes high-capacity 5G New Radio, core, and SDN controlled ‘Anyhaul’ transport to provide a complete set of network capabilities for commercial 5G networks.
Nokia also unveiled its ReefShark chipsets for outlining the scope of its Future X architecture for 5G, the basis for its new reference silicon design, the foundation of its 5G technology, and services portfolio.
Their portfolio comprises a full, end-to-end network that delivers up to three times more data capacity per cell site and 30% lower total cost of operation through artificial intelligence-based automation.
Nokia also unveiled a bunch of services designed to help operators with the major undertaking of moving to 5G at 5G World 2018. The main offering was Nokia 5G Digital Design, which uses AI to simulate 5G use cases to help with real-world design and stress test the business cases for them.
Nokia also completed the 5G New Radio data call based on 4G/5G connectivity during a demonstration in China.
Recent Developments
In October 2019, Nokia hired 350 employees for research and development in Finland to fix a 5G chip problem that could be problematic to its mobile business. Nokia also said that it had been recruiting mainly for system-on-a-chip development but declined to provide staff numbers for its overall R&D function.
In March 2020, Nokia announced the declaration of 3000 5G patents to the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). The move launched into an emerging battle for 5G patent bragging rights among the world’s big-three vendors and also pumped approximately €4.4 billion into broader technology R&D in 2019 alone.
In March 2020, Nokia said that it sought the help of Marvell to resolve 5G product problems that have wiped billions off their market value and threatened its progress in the 5G market. Marvell has been hired to work on Nokia’s new range of system-on-a-chip and infrastructure processors under the ReefShark brand. It will specifically contribute customized chips based on processor designs by ARM, a UK-based company whose licensees compete against Intel in semiconductor markets.
In May 2020, Nokia revealed its WaveFabric Elements portfolio of photonic chips, devices, and subsystems, including Photonic Service Engine V (PSE-V). The surging demand in video and mobile bandwidth over the past 10 years has been met through the continual advancement of optical and silicon technology. But as the technology approaches its limit, network operators will need to find new ways to scale their networks to meet the surging demands of 5G and cloud networking, while containing cost. The key to this transition is 400 Gigabit Ethernet (400G) technology.
In June 2020, Nokia expanded the 5G ReefShark chipset portfolio with Broadcom collaboration. Nokia and Broadcom announced that they are collaborating on the development of advanced semiconductor technologies, including new custom system-on-chip (SoC) processors, which will be integrated into Nokia’s “5G Powered by ReefShark” portfolio.
Intel
As the promise of 5G takes hold, customers are demanding increased performance and flexibility they need to rapidly deliver services with lower latency where they are needed most.
In this light, Intel announced the following:
Launch of the Intel Atom P5900 platform, the first Intel architecture-based 10nm SoC for wireless base stations. With the launch of the Intel Atom P5900, the company is extending Intel architecture from the core to access and all the way to the farthest edge of the network. Intel expects to be the leading silicon provider in base stations by 2021.
As a highly integrated 10nm SoC, the Intel Atom P5900 is designed to meet critical 5G network needs, including high bandwidth and low latency to deliver what’s required for 5G base stations today and in the future. The product augments Intel’s rich silicon portfolio for network environments and introduces Intel silicon as the foundation for the wireless base stations market, with 6 million 5G base stations forecasted through 2024. Intel is working with leading providers to deliver this product as part of their future-differentiated solutions in the market.
New 2nd Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors: As the foundation for data platform infrastructure with over 30 million units sold, Intel Xeon Scalable processors have led the transformation of the network. This year, 50% of core network deployments are transforming to virtualized networks, with the expectation to grow beyond 80% by 2024, fueled by 5G.
Intel introduced “Diamond Mesa,” Intel’s first next-generation structured ASIC for 5G network acceleration. “Diamond Mesa” (code name) is designed to complement Intel’s unmatched portfolio of processors and FPGAs delivering the high performance and low latency required for 5G networks. Structured ASICs like Diamond Mesa provides a minimum-risk optimization path for workloads that do not require the full programmability of FPGAs, targeting double the performance efficiency versus the prior generation, and uniquely position Intel as the only provider delivering a full silicon platform foundation for network infrastructure. Diamond Mesa is open to early access customers.
Intel introduced the Intel® Ethernet 700 Series Network Adapter with hardware-enhanced Precision Time Protocol, the first 5G network-optimized Ethernet NIC. The Ethernet 700 series (code-named “Edgewater Channel”) is Intel’s first 5G-optimized network adapter, offering GPS-based cross-network service synchronization with hardware-enhanced Precision Time Protocol (PTP).
Latency requirements across 5G network implementations have challenged existing Ethernet technology, especially in edge servers. Maintaining accurate time synchronization across the network at a cost-effective price point, however, is one avenue to help address application latency. The Ethernet 700 series adapter increases the timing precision required for 5G networks through a combination of hardware and software enhancements. Edgewater Channel is sampling now and was expected to enter production in 2020’s second quarter.
New Software Investments: Intel expands its industry-leading edge computing software toolkits to accelerate time-to-market innovation for its customers and partners with new capabilities integrated into the Open Network Edge Services Software (OpenNESS) toolkit. OpenNESS now supports standalone 5GNR and Enhanced Platform Awareness (EPA) deployments, giving customers the flexibility to easily deploy their choice of cloud-native edge microservices. Intel is delivering customized OpenNESS experience kits to accelerate custom 5G deployments. OpenNESS complements Intel’s OpenVINO™ and Open Visual Cloud for edge computing development needs.
Unrivaled Ecosystem Collaborations: Technology innovation requires deep collaboration across industry innovators that build on each other’s contributions. Given its rich heritage in leading technology transitions, Intel is in a unique position to accelerate collaboration across its customers and partners. Intel has announced strategic collaborations with industry leaders, including Altiostar, Dell, Deutsche Telecom, HPE, Lenovo, QCT, Rakuten, VMware, and ZTE to advance network infrastructure capability and speed edge solutions in the market.
Intel has been at the forefront of technology innovation for 51 years. By delivering the broadest silicon portfolio for 5G network infrastructure, the company continues to open a world of opportunity for its customers and partners.
Recent Developments
In February 2016, Intel Corporation announced new industry partnerships and products that lay the groundwork for faster, smarter, and more efficient 5G wireless networks designed to deliver amazing new experiences throughout daily life.
In February 2017, Intel and Ericsson launched 5G Innovators Initiative with Honeywell, GE, and the University of California Berkeley. Ericsson and Intel Corporation are launching the 5G Innovators Initiative (5GI2), an open industry initiative designed to create transformative experiences that change lives, businesses, and society.
In June 2017, IOC and Intel announced Worldwide TOP Partnership through 2024. Intel’s 5G platforms will be used at the Olympic Games to demonstrate how 5G will transform communications over the next decade.
In September 2017, Telia said that it is deploying the first public 5G live network use cases in Europe in collaboration with Ericsson and Intel. This includes a high-speed 5G connection to a commercial passenger cruise ship delivering internet connectivity to the ship and its passengers while in port, and an industrial use case featuring a construction excavator remotely controlled with a live 5G network.
In August 2018, Intel and Ericsson achieved a milestone with First 3GPP NR-Compliant End-to-End Data Call over 39 GHz SpectrumL Intel and Ericsson delivered a first 3GPP New Radio (NR) 5G-compliant live data call operating over the 39 GHz band using Intel’s RF mm-Wave chip with Ericsson Radio System commercial equipment including the 5G NR radio AIR 5331, baseband and Intel® 5G Mobile Trial Platform.
In September 2018, Intel announced details on the expansion of its portfolio of 100G silicon photonics transceivers beyond the data center and into the network edge. At the European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC) in Rome, Intel unveiled specifics on new silicon photonics products that are optimized to accelerate the movement of massive amounts of data being generated by new 5G use cases and Internet of Things (IoT) applications. The latest 100G silicon photonics transceivers are optimized to meet the bandwidth requirements of next-generation communications infrastructure while withstanding harsh environmental conditions.
In November 2018, Intel announced the Intel® XMM™ 8160 5G modem, a multimode modem optimized to provide 5G connectivity to devices like phones, PCs, and broadband access gateways. Intel has accelerated the timing of this modem by pulling in the launch by more than a half-year. The XMM 8160 5G will support peak speeds up to 6 gigabits per second, making it three to six times faster than the latest LTE modems available.
In January 2019, Intel, T-Mobile, and Ericsson completed World’s First 5G Call on 600 MHz (T-Mobile).
In February 2019, Intel announced it will provide technology to Rakuten for a new cloud-native network. It will be fully virtualized from the radio access network (RAN) to core and will adopt an innovative 5G systems architecture from its launch. The network is significant as it will offer end-to-end automation for both network and services. It is being built to serve millions of subscribers in Japan.
At Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2019, Intel announced the Intel® FPGA Programmable Acceleration Card N3000 (Intel® FPGA PAC N3000), designed for service providers to enable 5G next-generation core and virtualized radio access network solutions. The Intel FPGA PAC N3000 accelerates many virtualized workloads, ranging from 5G radio access networks to core network applications.
In April 2019, Intel announced the general availability of the 2nd-Generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable processor optimized for customers’ most demanding processing requirements from the intelligent edge to the cloud, and across artificial intelligence (AI) and 5G.
In July 2019, Apple acquired the majority of Intel’s smartphone modem business.
In November 2019, Intel and MediaTek became partners to Deliver 5G on the PC. Intel partnered with MediaTek on the development, certification, and support of 5G modem solutions for the next generation of PC experiences. As part of the partnership, Intel will define a 5G solution specification, including a 5G modem to be developed and delivered by MediaTek. Intel will also provide optimization and validation across the platform and lend system integration and co-engineering support to further enable its OEM partners.
In December 2019, Intel completed the sale of smartphone modem business to Apple.
Broadcom
Broadcom is a prominent designer, developer, manufacturer, and global supplier of a wide range of semiconductors and infrastructure software products.
Broadcom hasn’t been much in this news since it wished to acquire Qualcomm for $130 billion in 2017. Considering Qualcomm’s position, it is highly likely that the deal is never going to happen. Broadcom despite not being able to get its hands on Qualcomm is still doing research in chipsets and has released some products as well. They have also undergone a few partnerships and signed collaborations to get a place in the chipset market.
Besides, Broadcom made some acquisitions involving huge money such as the acquisition of CA Technologies, a software company, in Nov 2018 for $18.9 billion.
Recent Developments
In April 2017, Broadcom introduced the BCM53570 Ethernet switch family that is the industry’s first to offer full compliance with all available IEEE Time Sensitive Networks (TSN) standards. BCM53570 family supports industry-leading time synchronization accuracy that powers next generation (5G & beyond) Ethernet-based radio access networks with coordinated features and massive MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output).
In November 2017, Broadcom announced the industry’s first silicon-proven 7nm intellectual property (IP) for an ASIC platform targeting deep learning and networking applications. Broadcom’s broad 7nm IP portfolio enables SoC integration required to meet 5G needs for bandwidth, coverage, and equipment form factors.
In March 2018, Broadcom announced the immediate availability of Jericho2® and FE9600 – the next generation of the StrataDNX family of system-on-chip (SoC) Switch-Routers. Shipping within 24 months from its predecessor Jericho+, Jericho2 delivers 5X higher bandwidth at 70% lower power per gigabit.
In March 2018, Broadcom announced the availability of the Broadcom® Monterey Ethernet switch (BCM56670), the industry’s first, built specifically for cellular fronthaul networks. This high capacity device meets the stringent performance demands of new Ethernet-based 5G radios and supports existing CPRI-based radios, thus consolidating all radio traffic onto a standard, Ethernet-based infrastructure.
In November 2018, Broadcom announced the immediate availability of its 7nm 400G PAM-4 PHY device, the BCM87400, designed for data center and cloud infrastructure. Built on Broadcom’s state-of-art 7nm Centenario™ 112G PAM-4 DSP platform, the device provides best-in-class 400G 8:4 gearbox performance while delivering the lowest power, enabling broad market adoption of 400bE links in hyper-scale datacenter and cloud networks.
In February 2019, Broadcom announced the completion of its 5G switching portfolio, designed to enable the deployment of end-to-end networks that consolidate all radio and fixed-line traffic onto a standard, Ethernet-based infrastructure. The six devices that make up this portfolio – Monterey, Quartz, Qumran2a, Jericho2, Jericho2c, and Ramon – are designed for switches with capacities greater than 100 Tbps and offer the complete feature set needed to meet the stringent performance demands of new Ethernet-based 5G New Radios (NR) and base stations.
In February 2019, Broadcom announced the expansion of the Jericho2 Series to include the 5 Tbps Jericho2c, the 2.4Tbps Qumran2c, and the 800Gbps Qumran2a devices, delivering the industry’s only comprehensive merchant silicon portfolio of carrier-grade routing chipsets and enabling production network deployments in 2019. The new Jericho2c, Qumran2c, and Qumran2a products add 5G network slicing support, high-speed channelized interfaces up to 400GE, direct OTN framer support, and Flexible Ethernet (FlexE) ports.
In March 2019, Broadcom launched the BCM8956X, a family of automotive multilayer Ethernet switches, designed to address the growing need for bandwidth, flexibility, security, and time-sensitive networking (TSN) for autonomous and connected vehicles. In addition, Broadcom began shipping production quantities of its automotive 1000BASE-T1 PHY transceiver device, the BCM8988X, enabling automotive OEMs to immediately deploy Gigabit Ethernet on single-pair UTP cables for in-car networking applications.
In September 2019, Broadcom announced commercial availability of its BCM81343 device, a dual 400G MACSec PHY with AES-256, designed to address security requirements for high speed interconnects in modern network infrastructure including hyper-scale, cloud, service provider, and enterprise networks. Expanding upon the previous generation dual 100G MACSec PHY, the BCM81343 quadruples the switch bandwidth capability with dual 400G ports and supports the IEEE 1588 precision time protocol (PTP) providing accurate clock timing for time-sensitive transactions and mission-critical tasks.
In May 2020, Broadcom announced the availability of DX NetOps powered by Broadcom Silicon, the industry’s first AI-driven, high scale operations monitoring and analytics solution. Broadcom provides next-generation high-scale operations monitoring that simplifies 5G, IoT, Cloud, and SD-WAN deployments by applying AI and ML to the rich granular data captured at the chip level— enabling a unique automated AI-driven solution that remediates network congestion.
In June 2020, Nokia and Broadcom announced a collaboration for the development of advanced semiconductor technologies, including new custom system-on-chip (SoC) processors, which will be integrated into Nokia’s “5G Powered by ReefShark” portfolio. The collaboration further expands the range of Nokia ReefShark chipsets available for 5G solutions and will improve both the system performance and energy footprint of 5G networks. The two companies will work to develop new custom system-on-chip (SoC) solutions, which utilize Nokia’s wireless technology and Broadcom’s expertise in application-specific integrated circuit ASIC technologies.
Analog Devices
Analog is a prominent American chipset company and has been in business for more than half a century. The Massachusetts-based company designs and manufactures analog, mixed-signal, and digital signal processing integrated circuits.
Just like the company participated in 2G, 3G, and 4G communications, they intend to do the same with 5G.
The company first talked about its plan for 5G in mid-2018 when they published a whitepaper written by Dr. Thomas Cameron, Director of wireless technology at Analog Devices.
“ADI helps customers design complex radio architectures for 5G full-spectrum systems, integrating unprecedented high performance with low power, security, and smart algorithms.”, claims the company.
Analog since then participated in quite a number of research activities and partnerships to position itself as an innovator among 5G chip manufacturers.
Recent Developments
In March 2017, Analog Devices announced the completion of its acquisition of Linear Technology Corporation. The combination creates the premier analog technology company with the industry’s most comprehensive suite of high-performance analog offerings and integrated engineering, manufacturing, sales, and support operations that will accelerate innovation and revenue growth opportunities.
In April 2017, Analog Devices introduced the AD9208, engineered for gigahertz-bandwidth applications, an A/D converter that meets the increased spectral efficiency demands of 4G/5G multi-band wireless communications base stations. It also meets the reduced run-time targets of multi-standard production instrumentation and provides greater detection range and sensitivity for defense electronics. Based on 28-nanometer CMOS technology, the AD9208 delivers industry-leading bandwidth and dynamic range to cover the largest number of signal bands. It also features low-noise spectral density for diversity radio and I/Q demodulation systems, while consuming half of the power, when compared to alternative solutions.
In April 2017, Analog Devices introduced a 28-nanometer D/A converter as part of a new series of high-speed digital-to-analog converters (D/A converters). The AD9172 meets the demands of gigahertz bandwidth applications and delivers the increased spectral efficiency needed for 4G/5G multi-band wireless communications base stations and 2 GHz E-band microwave point-to-point backhaul platforms. Its design also benefits production instrumentation targeting multi-standard direct-to-RF signal synthesis.
In May 2017, Analog Devices announced the LTC5553, a double-balanced mixer providing best-in-class matched bandwidth capability from 3GHz to 20GHz. The mixer can be used either as an up- or downconverter.
In June 2017, Analog Devices announced the latest update to its award-winning RadioVerse™ technology and design ecosystem, which simplifies and accelerates radio development for wireless carriers and telecommunications equipment manufacturers as they transition their cellular base stations from 4G to 5G networks. ADI’s expanded RadioVerse portfolio features new radio transceiver hardware, software tools, and a robust design environment that enables the smaller, lower power radios necessary in next-generation networks. The new offering allows customers to quickly evaluate and develop radio designs for 4G small cell and Pre-5G massive MIMO systems, key building blocks in the transition to 5G, enabling faster data rates while improving connectivity and data throughput in densely populated, high-traffic areas such as office buildings, sports stadiums, and public transit systems.
In February 2018, Analog Devices announced LTC5594, a wideband, high linearity true zero-IF (ZIF) demodulator with 1GHz instantaneous I and Q 1dB bandwidth. The LTC5594 is ideally suited for 5G microwave wireless infrastructure platforms that require 1GHz or more bandwidth, and dynamic range performance to support the high order modulation and gigabit data rates required.
In April 2018, Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI) opened an R&D facility in Ottawa, Canada, to focus on the design, characterization, validation, and testing of highly integrated RF products across multiple industries including cellular infrastructure, instrumentation, and aerospace and defense. The LEED-certified facility is 50 percent larger than the previous facilities and houses engineering staff dedicated to advancing the company’s RF and wireless technology solutions.
In June 2018, Analog Devices announced the production release of its 44 GHz single-pole, double-throw (SPDT) switches, the ADRF5024, and ADRF5025 in advanced Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) technology. The two new switches are broadband, with the ADRF5024 yielding flat frequency response from 100 MHz to 44 GHz, while the ADRF5025 from 9 kHz to 44 GHz, with repeatable characteristics better than 1.7 dB insertion loss and 35 dB channel to channel isolation. Both parts support 27 dBm power handling for both through and hot-switching conditions.
In June 2018, Analog Devices expanded its award-winning RadioVerse™ technology and design ecosystem with the industry’s widest bandwidth RF transceiver, which provides designers with a single radio platform to accelerate the deployment of 5G, sustain 2G/3G/4G coverage, and simplify phased array radar design. The ADRV9009 RF transceiver delivers twice the bandwidth (200 MHz) of previous-generation devices and replaces as many as 20 components, cutting power in half and package size by 60 percent. With its industry-leading performance and reduced size, weight, and power, the ADRV9009 transceiver meets the rigorous antenna density and expanded network capacity requirements of emerging 5G wireless infrastructure equipment and aerospace and defense systems.
In November 2018, Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI) was recognized with four 2018 World Electronics Achievement Awards (WEAA) from ASPENCORE for its management capabilities and innovative product line.
In February 2019, Analog Devices announced it is expanding its Raleigh, NC office, and moved to The Dillon in downtown Raleigh’s growing Warehouse District. The Raleigh office is an ADI Center of Excellence focused on researching and developing the software-defined radio (SDR) systems that underpin modern wireless communication systems and infrastructures, including 5G networks. The Raleigh office has doubled in size over the past five years and this move facilitates the office’s continued growth by accommodating more than 120 employees.
In February 2019, Analog Devices announced the ADMV1013 and ADMV1014, a paired highly integrated microwave upconverter and downconverter, respectively. These ICs operate over a very wide frequency range with 50 Ω-match from 24 GHz up to 44 GHz, facilitating ease of design and reducing the costs of building a single platform that can cover all 5G mm-Wave frequency bands including 28 GHz and 39 GHz. Additionally, the chipset is capable of flat 1 GHz RF instantaneous bandwidth supporting all broadband services as well as other ultra-wide bandwidth transceiver applications.
In May 2019, Analog Devices introduced a new solution for millimeter-wave (mmWave) 5G with the highest available level of integration to reduce design requirements and complexity in the next generation of cellular network infrastructure. The solution combines ADI’s advanced beamformer IC, up/down frequency conversion (UDC), and additional mixed-signal circuitry. This optimized “Beams to Bits” signal chain represents a unique set of capabilities only available from ADI.
In June 2019, Analog Devices introduced a mixed-signal front-end (MxFE™) RF data converter platform that combines high-performance analog and digital signal processing for a range of wireless equipment such as 4G LTE and 5G millimeter-wave (mmWave) radios. ADI’s new AD9081/2 MxFE platform allows manufacturers to install multiband radios in the same footprint as single-band radios, which as much as triples call capacity available in today’s 4G LTE base stations. With a 1.2 GHz channel bandwidth, the new MxFE platform also enables wireless carriers that are adding more antennas to their cell towers to meet the higher radiodensity and data-rate requirements of emerging mmWave 5G.
In February 2020, Marvell and Analog Devices, Inc. announced a technology collaboration leveraging Marvell’s industry-leading 5G digital platform and ADI’s world-class wideband RF transceiver technology to deliver fully optimized solutions for 5G base stations. As part of the collaboration, the companies will offer fully integrated 5G digital front-end (DFE) ASIC solutions with tightly coupled RF transceivers and will collaborate to develop next-generation Radio Unit (RU) solutions including baseband and RF technology optimized for a diverse set of functional splits and architectures.
In July 2020, Analog Devices agreed to buy rival Maxim Integrated Products for about $21 billion, aiming to boost its market share in automotive and 5G chipmaking.
In August 2020, Analog Devices announced its collaboration with Intel Corporation to create a flexible radio platform that addresses 5G network design challenges and will enable customers to scale their 5G networks more quickly and economically. The new radio platform combines the advanced technology of ADI’s radio frequency (RF) transceivers with the high performance and low power of Intel Arria 10 Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) giving developers a new set of design tools for more easily creating optimized 5G solutions.
Marvell Technology
Marvell Technology, trying to further transform itself into one of the world’s largest vendors of network infrastructure chips, rolled out its latest line of Octeon networking chips to meet the throughput and latency demands of 5G telecom equipment. Marvell said it hammered out deals with telecom gear vendors, including Nokia and Samsung, to supply the Octeon chips for use in 5G base stations.
The company introduced the first chip in its latest generation of Octeon Fusion chips, the CNF95xx, which is targeted at the 5G infrastructure market. The chip incorporates a range of hardware accelerators for secure networking, baseband processors, and programmable DSP cores, ideal for 5G networks that offer far faster data transfers than 4G technology.
Marvell said it is currently the only merchant silicon on the market for 5G base stations. Marvell said the new Octeon Fusion chips pump out more performance per watt than its predecessors while also supporting the millimeter-wave bands used in 5G networks. The chip can be used in macro base stations with antennas and other hardware that beam out signals over long distances. The chip can also be used for massive MIMO, which is used to transfer data through targeted 5G beams, speeding up data rates, and lifting throughout.
The Santa Clara, California-based company is attempting to become a global powerhouse in chips used in 5G networking gear. Marvell is looking to gain ground with the world’s top players, including Nokia, which for about 22% of the market share in 2018, according to market researcher Omdia. Ericsson and Nokia have largely built chips in-house in recent years or partnered with Broadcom, Marvell, or other firms to build base station silicon.
Marvell is winning over other major customers for its Octeon Fusion processors. Nokia, one of the global leaders in the telecommunications gear market, said that it plans to roll out base stations with its Octeon Fusion family of chips, which can handle the global range of frequency bands used by 5G technology, including millimeter waves. In March, Marvell also agreed to help plot out future generations of Nokia’s 5G baseband ASICs.
Marvell also recently rolled out the latest generation of infrastructure processors, Octeon TX2, which can be used in 4G and 5G networking devices as well as switches, gateways, routers, and other gear drilled into data centers and cloud servers. The Octeon TX2 chips feature a range of programmable accelerators for moving massive amounts of data faster and more securely. The processors also use Marvell’s TX2 64-bit CPU microarchitecture.
The Octeon Fusion and Octeon TX2 chips are tailored for the latency and throughput demands of 5G networks. But they also deliver “a degree of programmability” so that they can be upgraded as 5G standards change. Marvell said its latest generation of Octeon processors slash the cost and the power consumption of other solutions based on FPGAs that telecom equipment vendors are using to build and test out 5G base stations.
The Silicon Valley company’s strategy is to start selling complete solutions for use in 5G networking infrastructure. The Octeon Fusion family of chips can be used as baseband processors, and the Octeon TX2 chips can handle transfer and control plane protocols. At the same time, Marvell’s Prestera Ethernet chips can be used for both fronthaul and backhaul, while its Thunder X2 CPUs can be added to data centers and core networks.
Marvell has also started to roll out ASICs for 5G networks through its $650 million deal for Avera Semiconductor in 2019. The company believes the networking chips it sells for 5G technology are worth four times more per 5G base station compared to 4G.
“Marvell has continued to innovate around the Octeon Fusion architecture,” said Caroline Gabriel, principal analyst at wireless market researcher Analysys Mason, in a statement. “The ability to address today’s 5G network rollout while offering future design flexibility makes lots of sense in an evolving market. There will be several different 5G networking configurations, and Marvell processors will be capable of addressing each one of them.”
Having covered in detail about its Octeon range of products, let’s now have a look at the recent developments by the company.
Recent Developments
In February 2019, Marvell announced a highly flexible end-to-end optimized 5G platform specifically tailored to exceed OEM design demands, accelerate the development of 5G New Radio (5G NR) systems and, ultimately, speed global carrier deployments.
In February 2019, Marvell announced with Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., the expansion of a long-term partnership for enabling leading wireless infrastructure networks. Samsung and Marvell are collaborating on the development and launch of multiple generations of radio and control plane processors for both LTE and 5G NR, enabling carriers to deploy multi-radio access technology in order to meet the ever-increasing data usage of today’s users and emerging applications.
In February 2019, Marvell announced a highly flexible end-to-end optimized 5G platform specifically tailored to exceed OEM design demands, accelerate the development of 5G New Radio (5G NR) systems and, ultimately, speed global carrier deployments.
In March 2019, Marvell announced a breakthrough Ethernet switch solution portfolio, ranging from 2 to 12.8 Terabits per second (Tbps), designed for edge and private data centers utilizing composable infrastructure. The Marvell® Prestera® CX 8500 family is architected with a robust feature set to meet the distinctive data center requirements needed to support the approaching tsunami of connected intelligence, edge computing, and 5G applications.
In May 2019, Marvell Technology Group and Aquantia, Corp. announced a definitive agreement, approved by the boards of directors of both companies, under which Marvell will acquire all outstanding shares of Aquantia common stock in exchange for consideration of $13.25 per share in cash. The acquisition of Aquantia complements Marvell’s portfolio of copper and optical physical layer product offerings and extends its position in the Multi-Gig 2.5G/5G/10G Ethernet segments.
In August 2019, Marvell released the industry’s lowest power PCIe® Gen4 NVMe™ solid-state drive (SSD) controller portfolio. Marvell’s newest SSD controllers are designed to meet the need for lower power and higher performance in next-generation data centers and edge devices as artificial intelligence (AI) and 5G gain momentum. This breakthrough technology delivers unparalleled performance in an ultra-compact footprint, leveraging the company’s complex system-on-chip (SoC) design expertise and groundbreaking storage IP to help data center, notebook, tablet, gaming, and edge computing platform architects advance their solutions for the highly distributed data era.
In September 2019, Marvell announced that it has completed its acquisition of Aquantia, Corp. Aquantia pioneered Multi-Gig technology – now the basis for high-speed networking in a broad range of applications from enterprise campuses to autonomous cars. Marvell’s combined portfolio of industry-leading PHYs, switches, and processors creates an unparalleled networking platform and enables customers to develop systems that span megabits to terabits per second.
In November 2019, Marvell announced that it has completed its acquisition of Avera Semiconductor, the Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) business of GlobalFoundries for ~$600 million. By combining Marvell’s advanced technology platform and scale with Avera’s custom design capabilities, Marvell is now able to offer the complete spectrum of semiconductor solutions spanning 5G, data center, enterprise, and automotive applications.
In February 2020, Marvell announced its dual 400GbE (Gigabit Ethernet) MACsec PHY transceiver with 256-bit encryption and Class C compliant precision time protocol (PTP) timestamping, bringing advanced performance, security, and transfer speeds for next-generation networking infrastructure. Hardware-based point-to-point encryption encompassing Ethernet speeds up to 400G is being deployed in the cloud, carrier, and enterprise networks to address the market demand for enhanced data security. In addition, the stringent timing requirements of 5G radios are driving the timing accuracy that needs to be delivered by networks supporting these services.
In March 2020, Marvell announced OCTEON® TX2, the latest family of infrastructure processors targeting a wide variety of wired and wireless networking equipment including switches, routers, secure gateways, firewall, network monitoring, 5G base stations, and smart network interface controllers (NICs).
In March 2020, Marvell introduced a new generation family of OCTEON Fusion® processors built on the OCTEON® TX2 platform and optimized for cellular base station designs including baseband unit and smart radio unit applications. 5G wireless networks promise a dramatic improvement in bandwidth and latency, delivering an unprecedented level of service and unlocking new use cases for mobile operators. To make this promise a reality, 5G wireless infrastructure requires more processing power, and OCTEON Fusion is optimized to meet this surging demand for computing. Built on Marvell’s OCTEON TX2 platform, which provides a complex of Arm® v8 cores and a series of hardware accelerators for networking and security, OCTEON Fusion adds programmable DSP cores and baseband accelerators making it the optimal solution for base stations.
In March 2020, Marvell and Samsung Electronics Co announced that the companies are extending their collaboration to encompass infrastructure innovations across additional segments of the Radio Access Network (RAN). Marvell and Samsung have worked closely to deliver multiple generations of market-leading baseband and transport processing solutions for base stations based on Marvell’s OCTEON® and OCTEON Fusion® processors. In addition, the companies are collaborating on innovative radio unit architectures designed to meet the dramatic increase in computing power required for the complex beamforming algorithms inherent to massive MIMO deployments. Building on the OCTEON Fusion platform and integrating Samsung’s unique intellectual property provides a differentiated offering while speeding time-to-market with an optimized solution.
In March 2020, Nokia and Marvell announced that they are working together to develop leading 5G multi-RAT (Radio Access Technology) silicon innovations, including multiple generations of custom silicon and infrastructure processors to further expand the range of Nokia ReefShark chipsets available for 5G solutions.
In July 2020, Marvell announced a unique custom ASIC offering that addresses the stringent requirements of next-generation 5G carriers, cloud data centers, enterprise, and automotive applications. Marvell’s comprehensive custom ASIC solution enables a multitude of customization options and a differentiated approach with best-in-class standard product IP including Arm®-based processors, embedded memories, high-speed SerDes, networking, security, and a wide range of storage controller and accelerators in 5nm and beyond.
In August 2020, Marvell announced an extension of its long-term partnership with TSMC, the world’s largest dedicated semiconductor foundry, to deliver a comprehensive silicon portfolio for the data infrastructure market leveraging the industry’s most advanced 5 nanometers (nm) process technology.
In September 2020, Marvell announced that it has joined the Open RAN Policy Coalition. The coalition, composed of leading policymakers, operators, and equipment providers, promotes policies that advance the adoption of open and interoperable solutions in the RAN market. Marvell, a member of the O-RAN Alliance and contributor to the Open Networking Foundation CORD project, brings wireless technology expertise and radio access network (RAN) industry perspectives along with a commitment to open standards.
In September 2020, Marvell announced the shipment of the 1 Millionth OCTEON-powered LiquidIO® SmartNIC. Marvell’s OCTEON® family is the most widely deployed data processing unit (DPU) for SmartNIC cloud applications. Following on the heels of multiple generations of proven OCTEON solutions, the latest release, LiquidIO III SmartNIC, is now being deployed at scale.
In October 2020, Marvell announced with Samsung Electronics, the expansion of a long-term partnership for enabling leading wireless infrastructure networks. Samsung and Marvell are collaborating on the development and launch of multiple generations of radio and control plane processors for both LTE and 5G NR, enabling carriers to deploy multi-radio access technology in order to meet the ever-increasing data usage of today’s users and emerging applications.
Xilinx Inc.
Xilinx is a Silicon-Valley technology company that also works on programmable chips. Founded in 1984, the company has grown and entered the leagues of big semiconductor companies. And now, the company is hugely researching in 5G chipsets.
Its position in the chipset industry can be judged from the fact that AMD wants to buy it for over $35 billion.
What is it up to?
Let’s find it out for ourselves by exploring Xilinx’s research activity and collaborations w.r.t 5G chipsets.
Recent Developments
In February 2018, Barefoot Networks and Xilinx Inc demonstrated an end-to-end network performance monitoring solution that gives network operators per-packet visibility at nanosecond granularity. Barefoot Tofino ASIC-based P4 switches with INT, combined with Xilinx® FPGA-based P4 SmartNICs with INT, give 5G network operators the per-packet visibility and the ability to define innovative features in the network to augment compute resources and accelerate VNF performance.
In March 2018, Xilinx, Inc. announced it will be showcasing its technology leadership in optical networking at OFC 2018. The company will be giving attendees a glimpse into the future of networking with the FPGA industry’s first demonstration of breakthrough 112G PAM4 electrical signaling technology for optical networks, as well as announcing the addition of 58G PAM4 transceivers to its 16nm Virtex® UltraScale+™ portfolio.
In March 2018, the University of Bristol, Smart Internet Lab, leveraged Xilinx® silicon technology to deploy and demonstrated the world’s first end-to-end 5G urban network. This flexible and programmable 5G network testbed consisting of 5G NR radio heads connected to the 5G virtualized baseband pool using multiple protocols with dynamic low latency aggregation and elastic bandwidth allocation into the fiber backhaul utilizing an end to end SDN controlled environment. Use cases are demonstrated in a hyper-connected Smart City environment, Augmented Reality, Autonomous Transport, and Smart Tourism are being showcased with this 5G network testbed. The project is funded by the UK Government’s Department of Digital Culture Media and Sports (DCMS).
In March 2018, Xilinx, Inc. announced a new breakthrough product category called adaptive compute acceleration platform (ACAP) that goes far beyond the capabilities of an FPGA. An ACAP is a highly integrated multi-core heterogeneous compute platform that can be changed at the hardware level to adapt to the needs of a wide range of applications and workloads. An ACAP’s adaptability, which can be done dynamically during operation, delivers levels of performance and performance-per-watt that is unmatched by CPUs or GPUs.
In February 2019, the company announced two new generations of its Zynq UltraScale+ RF system on chip (RFSoC) portfolio. The device covers the entire sub-6 GHz spectrum, which is necessary for 5G, and the updates included: an extended millimeter wave interface, up to 20% power reduction in the RF data converter subsystem compared to the base portfolio, and support of 5G New Radio.
In February 2019, Xilinx introduced an HDMI 2.1 IP subsystem core, which enabled the company’s devices to transmit, receive, and process up to 8K (7680 x 4320 pixels) UHD video in media players, cameras, monitors, LED walls, projectors, and kernel-based virtual machines.
In Feb 2019, Xilinx and Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., announced an expanded collaboration that has resulted in the world’s first 5G New Radio (NR) commercial deployment. This world-first deployment is in South Korea and would be followed by additional countries globally.
In April 2019, Xilinx announced it entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Solarflare Communications, Inc. Xilinx became a strategic investor in Solarflare in 2017. The companies have been collaborating since then on advanced networking technology, and in March 2019 demonstrated their first joint solution a single-chip FPGA-based 100G smart NICs. The acquisition enables Xilinx to combine its FPGA, MPSoC, and ACAP solutions with Solarflare’s NIC technology and Onload application acceleration software to enable new converged SmartNIC solutions.
In June 2019, Xilinx, Inc. announced that it has shipped Versal™ AI Core series and Versal Prime series devices to multiple tier-one customers through the company’s early access program. Versal is the industry’s first adaptive compute acceleration platform (ACAP), a revolutionary new category of heterogeneous computing devices with capabilities that far exceed those of conventional CPUs, GPUs, and FPGAs.
In June 2019, Xilinx announced that it was shipping its first Versal chips. Using ACAP, the chips’ hardware and software can be programmed to run almost any kind of AI software.
In August 2019, Xilinx announced that the company would be adding the world’s largest FPGA – the Virtex Ultrascale+ VU19P, to the 16 nm Virtex Ultrascale+ family. The VU19P contains 35 billion transistors.
On October 1, 2019, Xilinx announced the launch of Vitis, a unified software platform that helps developers take advantage of hardware adaptability.
In January 2020, Xilinx, Inc. announced that it has filed claims against Analog Devices, Inc., asserting infringement of eight United States patents in the United States District Court for the District of Delaware. The lawsuit details the unauthorized use by Analog Devices of certain Xilinx technologies involving serializers/deserializers (SerDes), high-speed analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), and digital-to-analog converters (DACs), as well as mixed-signal devices targeting 5G and other markets. In addition to seeking damages, Xilinx is requesting that Analog Devices be enjoined from selling, offering to sell, or importing into the United States, products that infringe Xilinx’s asserted patents.
In March 2020, Xilinx, Inc. announced Versal™ Premium, the third series in the Versal ACAP portfolio. The Versal Premium series features highly integrated, networked, and power-optimized cores and the industry’s highest bandwidth and compute density on an adaptable platform. Versal Premium is designed for the highest bandwidth networks operating in thermally and spatially constrained environments, as well as for cloud providers who need scalable, adaptable application acceleration.
In March 2020, Telefónica announced an agreement that it is driving a strategic ecosystem collaboration with Altiostar, Gigatera Communications, Intel, Supermicro, and Xilinx, Inc., to foster the development of Open RAN technologies in 4G and 5G. With this collaboration, Telefonica will launch 4G and 5G Open RAN trials in the UK, Germany, Spain, and Brazil this year.
In April 2020, Xilinx, Inc. announced that the Xilinx® Versal™ adaptive compute acceleration platform (ACAP) will be utilized by Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., for worldwide 5G commercial deployments. Xilinx Versal ACAPs provides a universal, flexible, and scalable platform that can address multiple operator requirements across multiple geographies.
In July 2020, Xilinx, Inc. announced it has joined the Open RAN Policy Coalition to support the development and deployment of Open RAN 5G technologies. The Open RAN Policy Coalition membership promotes Open RAN as the solution of choice for greater interoperability and security among a multi-vendor ecosystem. Xilinx has been an active member of the O-RAN Alliance and a contributor to the 3GPP specifications for 5G mobile networks. Under the Open RAN Policy Coalition, Xilinx will continue to collaborate with members and key stakeholders to ensure 5G and future networks will be openly developed, interoperable, and adaptable.
In August 2020, Subaru announced the use of one of Xilinx’s chips as processing power for camera images in its driver-assistance system. In September 2020, Xilinx announced its new chipset, the T1 Telco Accelerator card, that can be used for units running on an open RAN 5G network.
In September 2020, Xilinx, Inc. announced the T1 Telco Accelerator Card for O-RAN distributed units (O-DUs) and virtual baseband units (vBBUs) in 5G networks. Built using the same field-proven Xilinx silicon and IP already being deployed in 5G networks, the T1 card is the only multi-function PCIe form factor card that performs both O-RAN fronthaul protocols and layer 1 offload. With its advanced offload capabilities, the T1 card provides a dramatic reduction in the number of CPU cores required in a system. The T1 card also enables the O-DU to deliver greater 5G performance and services while reducing overall system power consumption and cost compared to competitive offerings.
In September 2020, Ribbon Communications Inc. announced that it developed a 5G hybrid slicing solution for next-generation networks in collaboration with Xilinx Inc.
U-Blox
U-Blox is a swiss company that works on chipset modules for consumer, automotive, and industrial markets. The company does not have a good market share as compared to other companies we mentioned but it has been providing 5G chipsets modules mostly for the IoT market.
Recent Developments
In November 2018, U-Blox announced the ZED-F9T high accuracy timing module. This module meets even the most stringent timing synchronization requirements in 5G mobile networks on a global scale. Although the previous generation of cellular networks has already been using GNSS time as the primary source of synchronization, better synchronization throughout the network will be a key enabler for 5G. The 5G cellular network will require tighter coordination to offer much greater bandwidth and a broader range of services to the user than 4G, supporting sophisticated features such as beam-forming, carrier aggregation, and massive MIMO.
In November 2018, U-Blox announced a globally configurable NB-IoT module ready for 3GPP Rel 14 and 5G. The SARA-N3 is a multi-band NB-IoT module that supports a preliminary set of 3GPP Release 14 features (LTE Cat NB2) and is available in two variants: one dedicated to China and another that can operate across multiple bands on any NB-IoT network globally.
In June 2019, U-Blox redefined IoT security with a 5G-ready cellular module and chipset for low power wide area IoT applications. The module offers unprecedented wireless technology integration with the end-to-end device and data security, making it ideal for mission-critical or long life cycle IoT applications.
In July 2019, U-Blox and Arvento Mobile Systems announced the imminent launch of the brand new imt.x1 vehicle tracking system. As for previous Arvento products, collaboration with U Blox was a key factor in the imt.x1 product development process, and the system’s high position sensitivity and accuracy are based on the integration of U-Blox’s 2G, 4G, and 5G-ready cellular modules as well as GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite Systems) modules.
In February 2020, U-Blox said that it will strengthen the security of IoT ecosystems built upon its dedicated LTE-M and NB-IoT chipset by implementing a key set of security features endorsed by the GSMA. Support for the IoT SAFE (IoT SIM applet for secure end-to-end communication) implementation guide will be included in a software maintenance release for u blox devices based on the UBX-R5 chipset, such as the new SARA-R5 series in 2020.
In March 2020, U-Blox announced certification by the Global Certification Forum (GCF) of the UBX-R5, U-Blox’s proprietary multi-band LTE-M/NB-IoT chipset featuring end-to-end device security, data security, and access control management. The U-Blox UBX-R5 is a 5G-ready cellular chipset for low power wide area (LPWA) mission-critical or long life-cycle IoT applications such as smart metering, telematics, tracking, security systems, building automation, as well as smart lighting solutions, and connected health.
In October 2020, U-Blox announced that its SARA-R5 LTE-M and NB-IoT cellular series is in production and LTE-M certified with several North American Tier 1 operators. The SARA-R5 series is the first product family based on the UBX-R5, U-Blox’s own low power wide area (LPWA) chipset, to achieve North American operator certification.
Concluding Notes
This gets us to the end of our list today, but that’s not it.
There is a lot happening in the 5G chipset domain, which is expected to reach USD 277 Billion by 2025. If you have any other questions on 5G chipsets or if you are looking to do M&As in the domain and want to know who would be the right choice to partner with or invest in. Let’s have a chat?